Zhiba Su
Out-of-Distribution Detection Based on Total Variation Estimation
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:This paper introduces a novel approach to securing machine learning model deployments against potential distribution shifts in practical applications, the Total Variation Out-of-Distribution (TV-OOD) detection method. Existing methods have produced satisfactory results, but TV-OOD improves upon these by leveraging the Total Variation Network Estimator to calculate each input's contribution to the overall total variation. By defining this as the total variation score, TV-OOD discriminates between in- and out-of-distribution data. The method's efficacy was tested across a range of models and datasets, consistently yielding results in image classification tasks that were either comparable or superior to those achieved by leading-edge out-of-distribution detection techniques across all evaluation metrics.
AccentBox: Towards High-Fidelity Zero-Shot Accent Generation
Sep 13, 2024

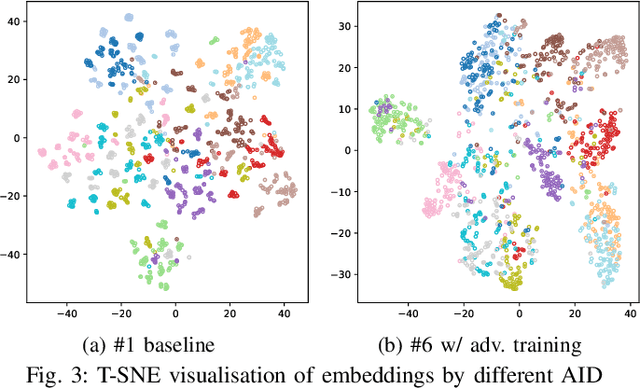

Abstract:While recent Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech (ZS-TTS) models have achieved high naturalness and speaker similarity, they fall short in accent fidelity and control. To address this issue, we propose zero-shot accent generation that unifies Foreign Accent Conversion (FAC), accented TTS, and ZS-TTS, with a novel two-stage pipeline. In the first stage, we achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) on Accent Identification (AID) with 0.56 f1 score on unseen speakers. In the second stage, we condition ZS-TTS system on the pretrained speaker-agnostic accent embeddings extracted by the AID model. The proposed system achieves higher accent fidelity on inherent/cross accent generation, and enables unseen accent generation.
Multi-Modal Automatic Prosody Annotation with Contrastive Pretraining of SSWP
Sep 11, 2023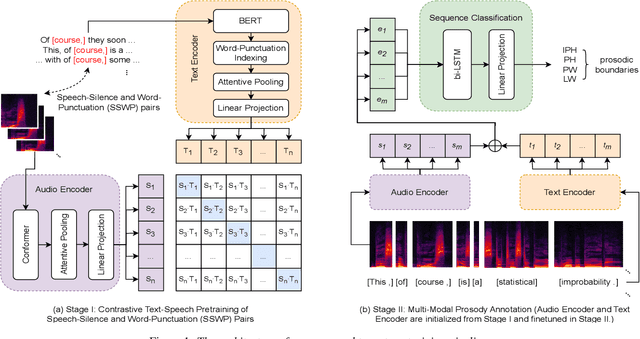

Abstract:In the realm of expressive Text-to-Speech (TTS), explicit prosodic boundaries significantly advance the naturalness and controllability of synthesized speech. While human prosody annotation contributes a lot to the performance, it is a labor-intensive and time-consuming process, often resulting in inconsistent outcomes. Despite the availability of extensive supervised data, the current benchmark model still faces performance setbacks. To address this issue, a two-stage automatic annotation pipeline is novelly proposed in this paper. Specifically, in the first stage, we propose contrastive text-speech pretraining of Speech-Silence and Word-Punctuation (SSWP) pairs. The pretraining procedure hammers at enhancing the prosodic space extracted from joint text-speech space. In the second stage, we build a multi-modal prosody annotator, which consists of pretrained encoders, a straightforward yet effective text-speech feature fusion scheme, and a sequence classifier. Extensive experiments conclusively demonstrate that our proposed method excels at automatically generating prosody annotation and achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance. Furthermore, our novel model has exhibited remarkable resilience when tested with varying amounts of data.
TranssionADD: A multi-frame reinforcement based sequence tagging model for audio deepfake detection
Jun 27, 2023Abstract:Thanks to recent advancements in end-to-end speech modeling technology, it has become increasingly feasible to imitate and clone a user`s voice. This leads to a significant challenge in differentiating between authentic and fabricated audio segments. To address the issue of user voice abuse and misuse, the second Audio Deepfake Detection Challenge (ADD 2023) aims to detect and analyze deepfake speech utterances. Specifically, Track 2, named the Manipulation Region Location (RL), aims to pinpoint the location of manipulated regions in audio, which can be present in both real and generated audio segments. We propose our novel TranssionADD system as a solution to the challenging problem of model robustness and audio segment outliers in the trace competition. Our system provides three unique contributions: 1) we adapt sequence tagging task for audio deepfake detection; 2) we improve model generalization by various data augmentation techniques; 3) we incorporate multi-frame detection (MFD) module to overcome limited representation provided by a single frame and use isolated-frame penalty (IFP) loss to handle outliers in segments. Our best submission achieved 2nd place in Track 2, demonstrating the effectiveness and robustness of our proposed system.
Improving Cross-lingual Speech Synthesis with Triplet Training Scheme
Feb 22, 2022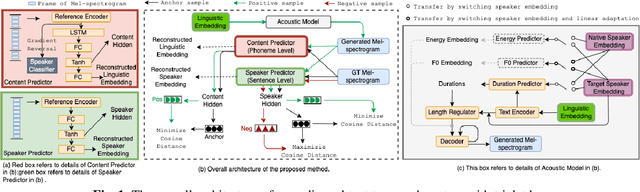
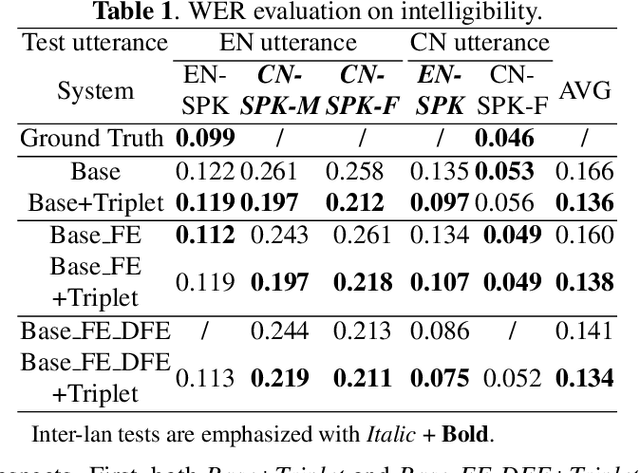
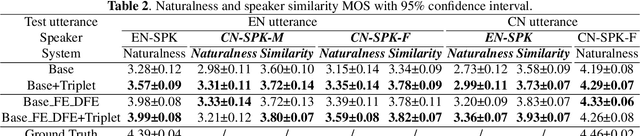
Abstract:Recent advances in cross-lingual text-to-speech (TTS) made it possible to synthesize speech in a language foreign to a monolingual speaker. However, there is still a large gap between the pronunciation of generated cross-lingual speech and that of native speakers in terms of naturalness and intelligibility. In this paper, a triplet training scheme is proposed to enhance the cross-lingual pronunciation by allowing previously unseen content and speaker combinations to be seen during training. Proposed method introduces an extra fine-tune stage with triplet loss during training, which efficiently draws the pronunciation of the synthesized foreign speech closer to those from the native anchor speaker, while preserving the non-native speaker's timbre. Experiments are conducted based on a state-of-the-art baseline cross-lingual TTS system and its enhanced variants. All the objective and subjective evaluations show the proposed method brings significant improvement in both intelligibility and naturalness of the synthesized cross-lingual speech.
FPUAS : Fully Parallel UFANS-based End-to-End Acoustic System with 10x Speed Up
Dec 18, 2018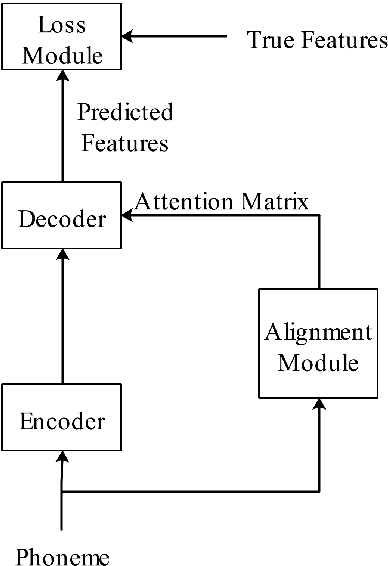
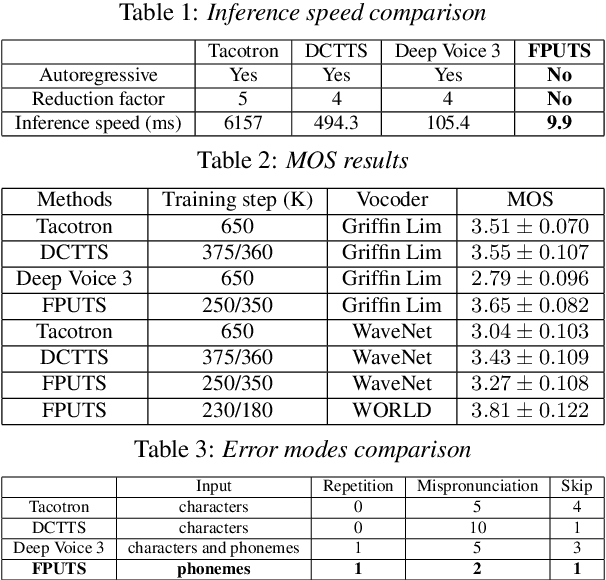

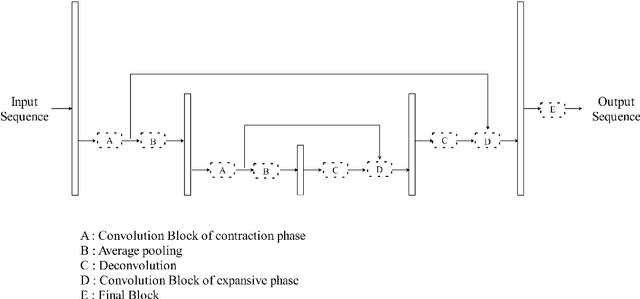
Abstract:A lightweight end-to-end acoustic system is crucial in the deployment of text-to-speech tasks. Finding one that produces good audios with small time latency and fewer errors remains a problem. In this paper, we propose a new non-autoregressive, fully parallel acoustic system that utilizes a new attention structure and a recently proposed convolutional structure. Compared with the most popular end-to-end text-to-speech systems, our acoustic system can produce equal or better quality audios with fewer errors and reach at least 10 times speed up of inference.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge