Yuli Sun
Graph Signal Processing for Heterogeneous Change Detection Part II: Spectral Domain Analysis
Aug 08, 2022



Abstract:This is the second part of the paper that provides a new strategy for the heterogeneous change detection (HCD) problem, that is, solving HCD from the perspective of graph signal processing (GSP). We construct a graph to represent the structure of each image, and treat each image as a graph signal defined on the graph. In this way, we can convert the HCD problem into a comparison of responses of signals on systems defined on the graphs. In the part I, the changes are measured by comparing the structure difference between the graphs from the vertex domain. In this part II, we analyze the GSP for HCD from the spectral domain. We first analyze the spectral properties of the different images on the same graph, and show that their spectra exhibit commonalities and dissimilarities. Specially, it is the change that leads to the dissimilarities of their spectra. Then, we propose a regression model for the HCD, which decomposes the source signal into the regressed signal and changed signal, and requires the regressed signal have the same spectral property as the target signal on the same graph. With the help of graph spectral analysis, the proposed regression model is flexible and scalable. Experiments conducted on seven real data sets show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Graph Signal Processing for Heterogeneous Change Detection Part I: Vertex Domain Filtering
Aug 08, 2022



Abstract:This paper provides a new strategy for the Heterogeneous Change Detection (HCD) problem: solving HCD from the perspective of Graph Signal Processing (GSP). We construct a graph for each image to capture the structure information, and treat each image as the graph signal. In this way, we convert the HCD into a GSP problem: a comparison of the responses of the two signals on different systems defined on the two graphs, which attempts to find structural differences (Part I) and signal differences (Part II) due to the changes between heterogeneous images. In this first part, we analyze the HCD with GSP from the vertex domain. We first show that for the unchanged images, their structures are consistent, and then the outputs of the same signal on systems defined on the two graphs are similar. However, once a region has changed, the local structure of the image changes, i.e., the connectivity of the vertex containing this region changes. Then, we can compare the output signals of the same input graph signal passing through filters defined on the two graphs to detect changes. We design different filters from the vertex domain, which can flexibly explore the high-order neighborhood information hidden in original graphs. We also analyze the detrimental effects of changing regions on the change detection results from the viewpoint of signal propagation. Experiments conducted on seven real data sets show the effectiveness of the vertex domain filtering based HCD method.
A Dual Neighborhood Hypergraph Neural Network for Change Detection in VHR Remote Sensing Images
Feb 27, 2022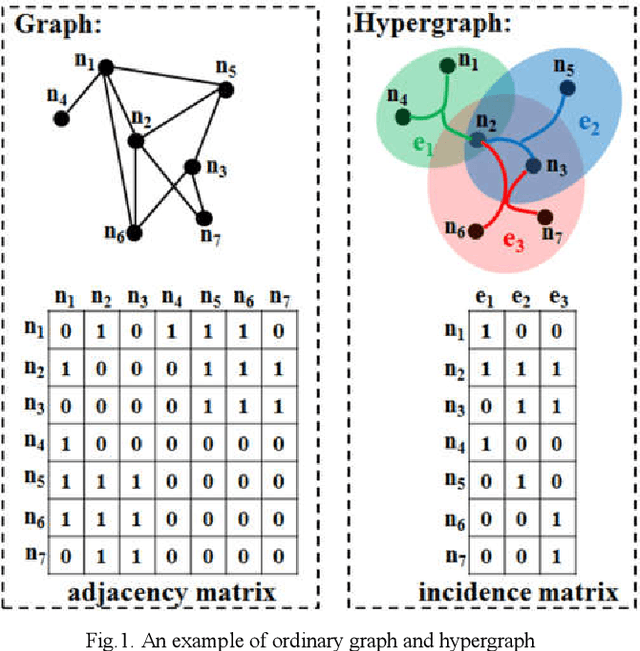
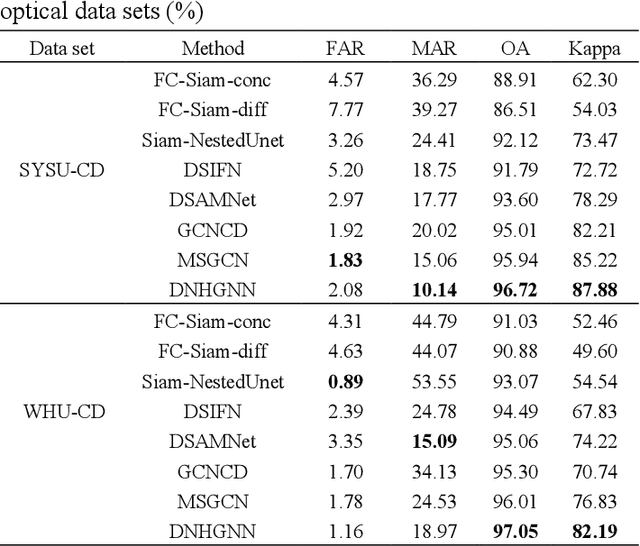
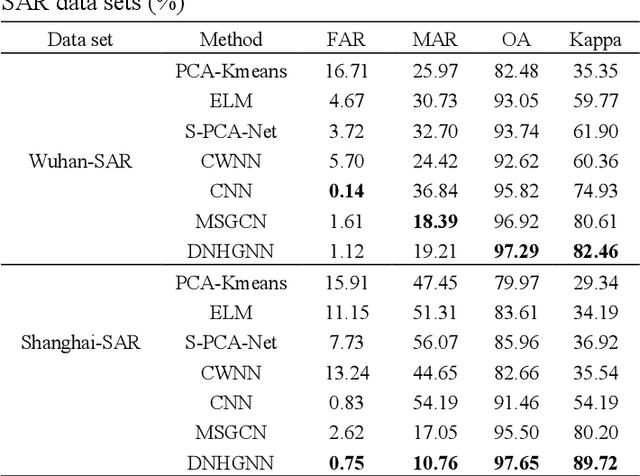
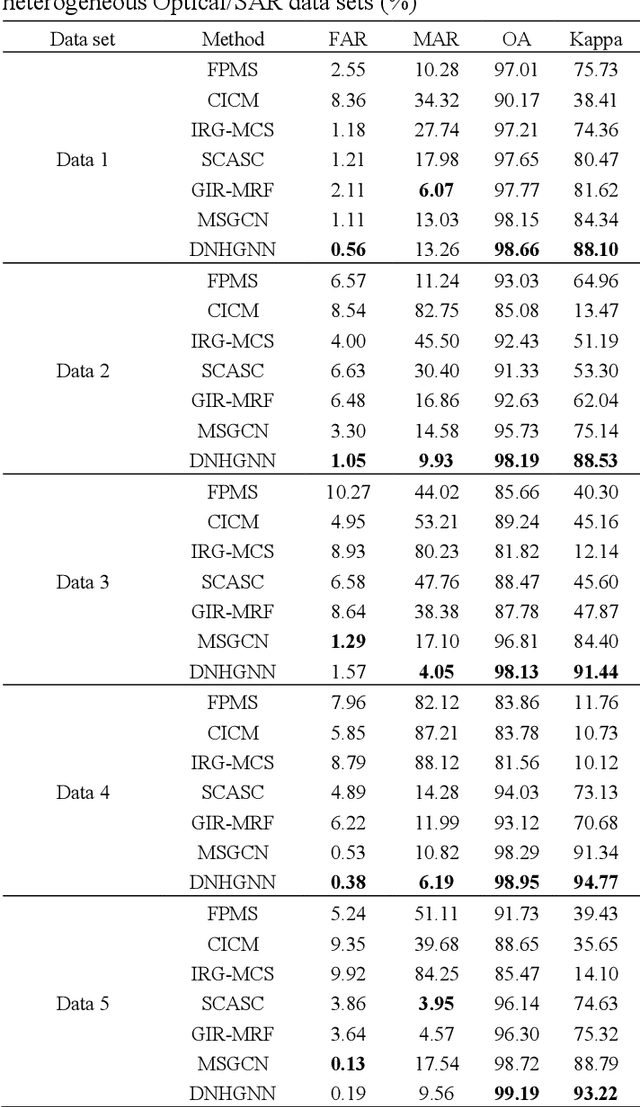
Abstract:The very high spatial resolution (VHR) remote sensing images have been an extremely valuable source for monitoring changes occurred on the earth surface. However, precisely detecting relevant changes in VHR images still remains a challenge, due to the complexity of the relationships among ground objects. To address this limitation, a dual neighborhood hypergraph neural network is proposed in this article, which combines the multiscale superpixel segmentation and hypergraph convolution to model and exploit the complex relationships. First, the bi-temporal image pairs are segmented under two scales and fed to a pre-trained U-net to obtain node features by treating each object under the fine scale as a node. The dual neighborhood is then defined using the father-child and adjacent relationships of the segmented objects to construct the hypergraph, which permits models to represent the higher-order structured information far more complex than just pairwise relationships. The hypergraph convolutions are conducted on the constructed hypergraph to propagate the label information from a small amount of labeled nodes to the other unlabeled ones by the node-edge-node transform. Moreover, to alleviate the problem of imbalanced sample, the focal loss function is adopted to train the hypergraph neural network. The experimental results on optical, SAR and heterogeneous optical/SAR data sets demonstrate that the proposed method comprises better effectiveness and robustness compared to many state-of-the-art methods.
Cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Based Distributed Dynamic Spectrum Access in Cognitive Radio Networks
Jun 17, 2021
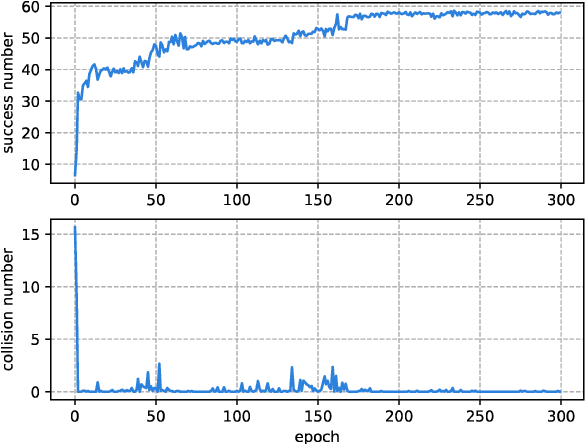
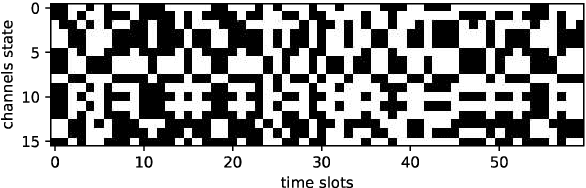
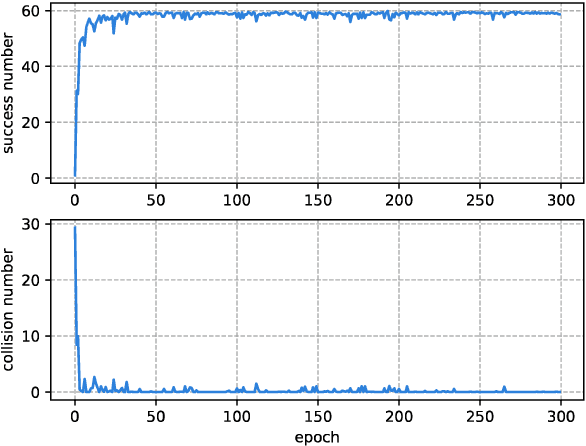
Abstract:With the development of the 5G and Internet of Things, amounts of wireless devices need to share the limited spectrum resources. Dynamic spectrum access (DSA) is a promising paradigm to remedy the problem of inefficient spectrum utilization brought upon by the historical command-and-control approach to spectrum allocation. In this paper, we investigate the distributed DSA problem for multi-user in a typical multi-channel cognitive radio network. The problem is formulated as a decentralized partially observable Markov decision process (Dec-POMDP), and we proposed a centralized off-line training and distributed on-line execution framework based on cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL). We employ the deep recurrent Q-network (DRQN) to address the partial observability of the state for each cognitive user. The ultimate goal is to learn a cooperative strategy which maximizes the sum throughput of cognitive radio network in distributed fashion without coordination information exchange between cognitive users. Finally, we validate the proposed algorithm in various settings through extensive experiments. From the simulation results, we can observe that the proposed algorithm can converge fast and achieve almost the optimal performance.
A Multiscale Graph Convolutional Network for Change Detection in Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Remote Sensing Images
Feb 16, 2021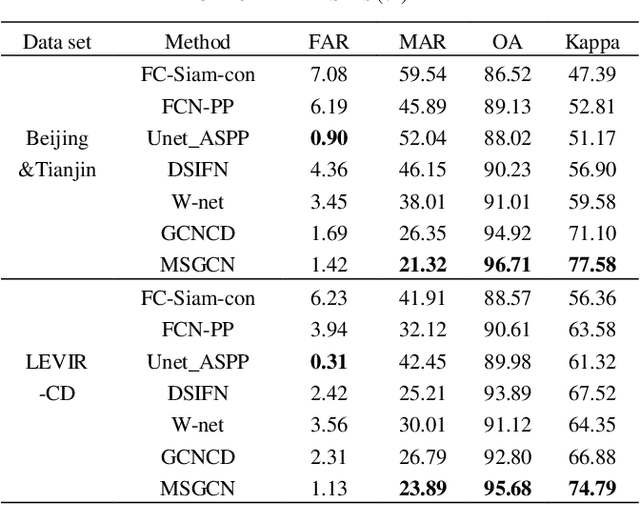
Abstract:Change detection (CD) in remote sensing images has been an ever-expanding area of research. To date, although many methods have been proposed using various techniques, accurately identifying changes is still a great challenge, especially in the high resolution or heterogeneous situations, due to the difficulties in effectively modeling the features from ground objects with different patterns. In this paper, a novel CD method based on the graph convolutional network (GCN) and multiscale object-based technique is proposed for both homogeneous and heterogeneous images. First, the object-wise high level features are obtained through a pre-trained U-net and the multiscale segmentations. Treating each parcel as a node, the graph representations can be formed and then, fed into the proposed multiscale graph convolutional network with each channel corresponding to one scale. The multiscale GCN propagates the label information from a small number of labeled nodes to the other ones which are unlabeled. Further, to comprehensively incorporate the information from the output channels of multiscale GCN, a fusion strategy is designed using the father-child relationships between scales. Extensive Experiments on optical, SAR and heterogeneous optical/SAR data sets demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms some state-of the-art methods in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations. Besides, the Influences of some factors are also discussed.
Adaptive Local Structure Consistency based Heterogeneous Remote Sensing Change Detection
Aug 29, 2020



Abstract:Change detection of heterogeneous remote sensing images is an important and challenging topic in remote sensing for emergency situation resulting from nature disaster. Due to the different imaging mechanisms of heterogeneous sensors, it is difficult to directly compare the images. To address this challenge, we explore an unsupervised change detection method based on adaptive local structure consistency (ALSC) between heterogeneous images in this letter, which constructs an adaptive graph representing the local structure for each patch in one image domain and then projects this graph to the other image domain to measure the change level. This local structure consistency exploits the fact that the heterogeneous images share the same structure information for the same ground object, which is imaging modality-invariant. To avoid the leakage of heterogeneous data, the pixelwise change image is calculated in the same image domain by graph projection. Experiment results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed ALSC based change detection method by comparing with some state-of-the-art methods.
Image reconstruction from few views by L0-norm optimization
Jan 09, 2014



Abstract:The L1-norm of the gradient-magnitude images (GMI), which is the well-known total variation (TV) model, is widely used as regularization in the few views CT reconstruction. As the L1-norm TV regularization is tending to uniformly penalize the image gradient and the low-contrast structures are sometimes over smoothed, we proposed a new algorithm based on the L0-norm of the GMI to deal with the few views problem. To rise to the challenges introduced by the L0-norm DGT, the algorithm uses a pseudo-inverse transform of DGT and adapts an iterative hard thresholding (IHT) algorithm, whose convergence and effective efficiency have been theoretically proven. The simulation indicates that the algorithm proposed in this paper can obviously improve the reconstruction quality.
An iterative algorithm for computed tomography image reconstruction from limited-angle projections
Sep 16, 2013

Abstract:In application of tomography imaging, limited-angle problem is a quite practical and important issue. In this paper, an iterative reprojection-reconstruction (IRR) algorithm using a modified Papoulis-Gerchberg (PG) iterative scheme is developed for reconstruction from limited-angle projections which contain noise. The proposed algorithm has two iterative update processes, one is the extrapolation of unknown data, and the other is the modification of the known noisy observation data. And the algorithm introduces scaling factors to control the two processes, respectively. The convergence of the algorithm is guaranteed, and the method of choosing the scaling factors is given with energy constraints. The simulation result demonstrates our conclusions and indicates that the algorithm proposed in this paper can obviously improve the reconstruction quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge