Yulan Gao
Trajectory-adaptive Beam Shaping: Towards Beam-Management-Free Near-field Communications
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:The quest for higher wireless carrier frequencies spanning the millimeter-wave (mmWave) and Terahertz (THz) bands heralds substantial enhancements in data throughput and spectral efficiency for next-generation wireless networks. However, these gains come at the cost of severe path loss and a heightened risk of beam misalignment due to user mobility, especially pronounced in near-field communication. Traditional solutions rely on extremely directional beamforming and frequent beam updates via beam management, but such techniques impose formidable computational and signaling overhead. In response, we propose a novel approach termed trajectory-adaptive beam shaping (TABS) that eliminates the need for real-time beam management by shaping the electromagnetic wavefront to follow the user's predefined trajectory. Drawing inspiration from self-accelerating beams in optics, TABS concentrates energy along pre-defined curved paths corresponding to the user's motion without requiring real-time beam reconfiguration. We further introduce a dedicated quantitative metric to characterize performance under the TABS framework. Comprehensive simulations substantiate the superiority of TABS in terms of link performance, overhead reduction, and implementation complexity.
MIMO Pinching-Antenna-Aided SWIPT
Jun 07, 2025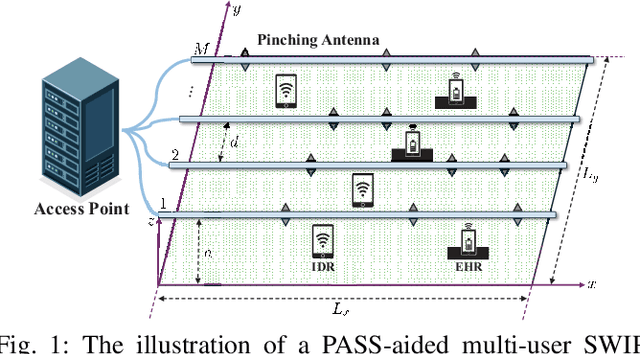
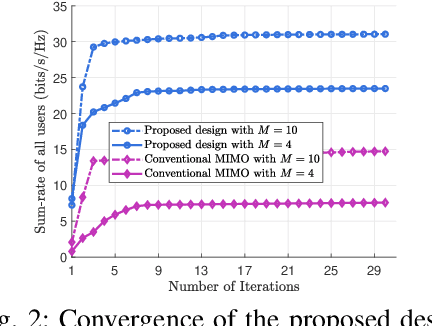
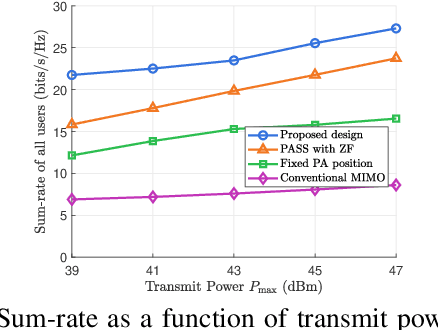
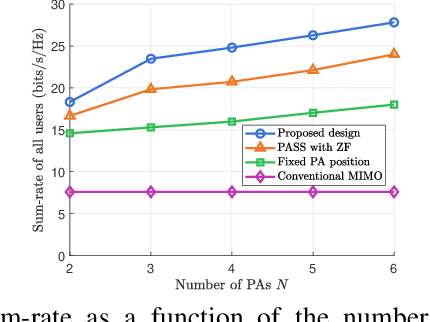
Abstract:Pinching-antenna systems (PASS) have recently emerged as a promising technology for improving wireless communications by establishing or strengthening reliable line-of-sight (LoS) links by adjusting the positions of pinching antennas (PAs). Motivated by these benefits, we propose a novel PASS-aided multi-input multi-output (MIMO) system for simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT), where the PASS are equipped with multiple waveguides to provide information transmission and wireless power transfer (WPT) for several multiple antenna information decoding receivers (IDRs), and energy harvesting receivers (EHRs), respectively. Based on the system, we consider maximizing the sum-rate of all IDRs while guaranteeing the minimum harvested energy of each EHR by jointly optimizing the pinching beamforming and the PA positions. To solve this highly non-convex problem, we iteratively optimize the pinching beamforming based on a weighted minimum mean-squared-error (WMMSE) method and update the PA positions with a Gauss-Seidel-based approach in an alternating optimization (AO) framework. Numerical results verify the significant superiority of the PASS compared with conventional designs.
Empowering Intelligent Low-altitude Economy with Large AI Model Deployment
May 28, 2025Abstract:Low-altitude economy (LAE) represents an emerging economic paradigm that redefines commercial and social aerial activities. Large artificial intelligence models (LAIMs) offer transformative potential to further enhance the intelligence of LAE services. However, deploying LAIMs in LAE poses several challenges, including the significant gap between their computational/storage demands and the limited onboard resources of LAE entities, the mismatch between lab-trained LAIMs and dynamic physical environments, and the inefficiencies of traditional decoupled designs for sensing, communication, and computation. To address these issues, we first propose a hierarchical system architecture tailored for LAIM deployment and present representative LAE application scenarios. Next, we explore key enabling techniques that facilitate the mutual co-evolution of LAIMs and low-altitude systems, and introduce a task-oriented execution pipeline for scalable and adaptive service delivery. Then, the proposed framework is validated through real-world case studies. Finally, we outline open challenges to inspire future research.
Pinching-Antenna Systems (PASS) Aided Over-the-air Computation
May 12, 2025Abstract:Over-the-air computation (AirComp) enables fast data aggregation for edge intelligence applications. However the performance of AirComp can be severely degraded by channel misalignments. Pinching antenna systems (PASS) have recently emerged as a promising solution for physically reshaping favorable wireless channels to reduce misalignments and thus AirComp errors, via low-cost, fully passive, and highly reconfigurable antenna deployment. Motivated by these benefits, we propose a novel PASS-aided AirComp system that introduces new design degrees of freedom through flexible pinching antenna (PA) placement. To improve performance, we consider a mean squared error (MSE) minimization problem by jointly optimizing the PA position, transmit power, and decoding vector. To solve this highly non-convex problem, we propose an alternating optimization based framework with Gauss-Seidel based PA position updates. Simulation results show that our proposed joint PA position and communication design significantly outperforms various benchmark schemes in AirComp accuracy.
ACSNet: A Deep Neural Network for Compound GNSS Jamming Signal Classification
Apr 15, 2025



Abstract:In the global navigation satellite system (GNSS), identifying not only single but also compound jamming signals is crucial for ensuring reliable navigation and positioning, particularly in future wireless communication scenarios such as the space-air-ground integrated network (SAGIN). However, conventional techniques often struggle with low recognition accuracy and high computational complexity, especially under low jamming-to-noise ratio (JNR) conditions. To overcome the challenge of accurately identifying compound jamming signals embedded within GNSS signals, we propose ACSNet, a novel convolutional neural network designed specifically for this purpose. Unlike traditional methods that tend to exhibit lower accuracy and higher computational demands, particularly in low JNR environments, ACSNet addresses these issues by integrating asymmetric convolution blocks, which enhance its sensitivity to subtle signal variations. Simulations demonstrate that ACSNet significantly improves accuracy in low JNR regions and shows robust resilience to power ratio (PR) variations, confirming its effectiveness and efficiency for practical GNSS interference management applications.
Optimizing Radio Access Technology Selection and Precoding in CV-Aided ISAC Systems
Oct 14, 2024Abstract:Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) systems promise to revolutionize wireless networks by concurrently supporting high-resolution sensing and high-performance communication. This paper presents a novel radio access technology (RAT) selection framework that capitalizes on vision sensing from base station (BS) cameras to optimize both communication and perception capabilities within the ISAC system. Our framework strategically employs two distinct RATs, LTE and millimeter wave (mmWave), to enhance system performance. We propose a vision-based user localization method that employs a 3D detection technique to capture the spatial distribution of users within the surrounding environment. This is followed by geometric calculations to accurately determine the state of mmWave communication links between the BS and individual users. Additionally, we integrate the SlowFast model to recognize user activities, facilitating adaptive transmission rate allocation based on observed behaviors. We develop a Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG)-based algorithm, utilizing the joint distribution of users and their activities, designed to maximize the total transmission rate for all users through joint RAT selection and precoding optimization, while adhering to constraints on sensing mutual information and minimum transmission rates. Numerical simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework in dynamically adjusting resource allocation, ensuring high-quality communication under challenging conditions.
GNSS Interference Classification Using Federated Reservoir Computing
Aug 23, 2024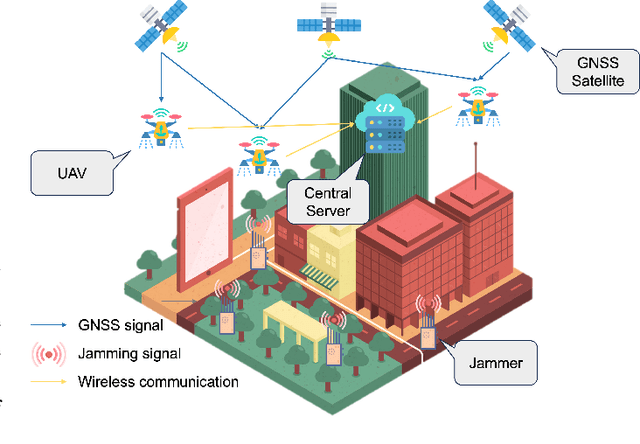
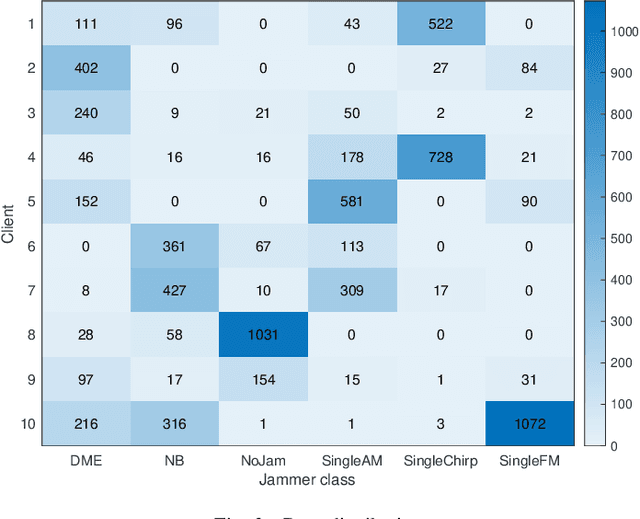


Abstract:The expanding use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) in vital areas like traffic management, surveillance, and environmental monitoring highlights the need for robust communication and navigation systems. Particularly vulnerable are Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), which face a spectrum of interference and jamming threats that can significantly undermine their performance. While traditional deep learning approaches are adept at mitigating these issues, they often fall short for UAV applications due to significant computational demands and the complexities of managing large, centralized datasets. In response, this paper introduces Federated Reservoir Computing (FedRC) as a potent and efficient solution tailored to enhance interference classification in GNSS systems used by UAVs. Our experimental results demonstrate that FedRC not only achieves faster convergence but also sustains lower loss levels than traditional models, highlighting its exceptional adaptability and operational efficiency.
CA-FedRC: Codebook Adaptation via Federated Reservoir Computing in 5G NR
Jul 08, 2024Abstract:With the burgeon deployment of the fifth-generation new radio (5G NR) networks, the codebook plays a crucial role in enabling the base station (BS) to acquire the channel state information (CSI). Different 5G NR codebooks incur varying overheads and exhibit performance disparities under diverse channel conditions, necessitating codebook adaptation based on channel conditions to reduce feedback overhead while enhancing performance. However, existing methods of 5G NR codebooks adaptation require significant overhead for model training and feedback or fall short in performance. To address these limitations, this letter introduces a federated reservoir computing framework designed for efficient codebook adaptation in computationally and feedback resource-constrained mobile devices. This framework utilizes a novel series of indicators as input training data, striking an effective balance between performance and feedback overhead. Compared to conventional models, the proposed codebook adaptation via federated reservoir computing (CA-FedRC), achieves rapid convergence and significant loss reduction in both speed and accuracy. Extensive simulations under various channel conditions demonstrate that our algorithm not only reduces resource consumption of users but also accurately identifies channel types, thereby optimizing the trade-off between spectrum efficiency, computational complexity, and feedback overhead.
Cost-Efficient Computation Offloading in SAGIN: A Deep Reinforcement Learning and Perception-Aided Approach
Jul 08, 2024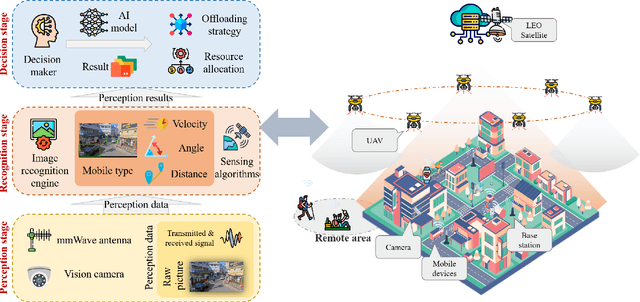

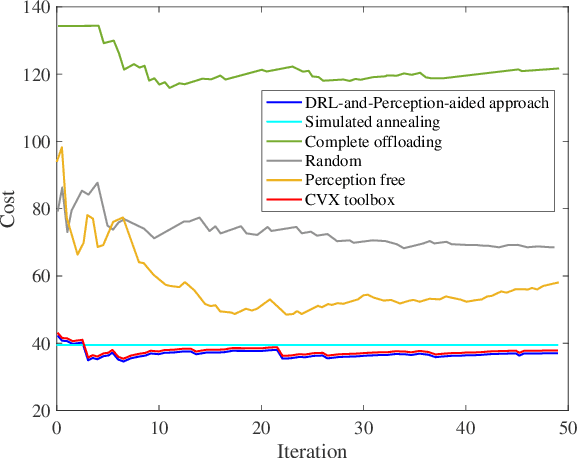

Abstract:The Space-Air-Ground Integrated Network (SAGIN), crucial to the advancement of sixth-generation (6G) technology, plays a key role in ensuring universal connectivity, particularly by addressing the communication needs of remote areas lacking cellular network infrastructure. This paper delves into the role of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) within SAGIN, where they act as a control layer owing to their adaptable deployment capabilities and their intermediary role. Equipped with millimeter-wave (mmWave) radar and vision sensors, these UAVs are capable of acquiring multi-source data, which helps to diminish uncertainty and enhance the accuracy of decision-making. Concurrently, UAVs collect tasks requiring computing resources from their coverage areas, originating from a variety of mobile devices moving at different speeds. These tasks are then allocated to ground base stations (BSs), low-earth-orbit (LEO) satellite, and local processing units to improve processing efficiency. Amidst this framework, our study concentrates on devising dynamic strategies for facilitating task hosting between mobile devices and UAVs, offloading computations, managing associations between UAVs and BSs, and allocating computing resources. The objective is to minimize the time-averaged network cost, considering the uncertainty of device locations, speeds, and even types. To tackle these complexities, we propose a deep reinforcement learning and perception-aided online approach (DRL-and-Perception-aided Approach) for this joint optimization in SAGIN, tailored for an environment filled with uncertainties. The effectiveness of our proposed approach is validated through extensive numerical simulations, which quantify its performance relative to various network parameters.
Advances and Open Challenges in Federated Learning with Foundation Models
Apr 29, 2024



Abstract:The integration of Foundation Models (FMs) with Federated Learning (FL) presents a transformative paradigm in Artificial Intelligence (AI), offering enhanced capabilities while addressing concerns of privacy, data decentralization, and computational efficiency. This paper provides a comprehensive survey of the emerging field of Federated Foundation Models (FedFM), elucidating their synergistic relationship and exploring novel methodologies, challenges, and future directions that the FL research field needs to focus on in order to thrive in the age of foundation models. A systematic multi-tiered taxonomy is proposed, categorizing existing FedFM approaches for model training, aggregation, trustworthiness, and incentivization. Key challenges, including how to enable FL to deal with high complexity of computational demands, privacy considerations, contribution evaluation, and communication efficiency, are thoroughly discussed. Moreover, the paper explores the intricate challenges of communication, scalability and security inherent in training/fine-tuning FMs via FL, highlighting the potential of quantum computing to revolutionize the training, inference, optimization and data encryption processes. This survey underscores the importance of further research to propel innovation in FedFM, emphasizing the need for developing trustworthy solutions. It serves as a foundational guide for researchers and practitioners interested in contributing to this interdisciplinary and rapidly advancing field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge