Yufeng Zhao
ATLAS: A High-Difficulty, Multidisciplinary Benchmark for Frontier Scientific Reasoning
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has led to performance saturation on many established benchmarks, questioning their ability to distinguish frontier models. Concurrently, existing high-difficulty benchmarks often suffer from narrow disciplinary focus, oversimplified answer formats, and vulnerability to data contamination, creating a fidelity gap with real-world scientific inquiry. To address these challenges, we introduce ATLAS (AGI-Oriented Testbed for Logical Application in Science), a large-scale, high-difficulty, and cross-disciplinary evaluation suite composed of approximately 800 original problems. Developed by domain experts (PhD-level and above), ATLAS spans seven core scientific fields: mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology, computer science, earth science, and materials science. Its key features include: (1) High Originality and Contamination Resistance, with all questions newly created or substantially adapted to prevent test data leakage; (2) Cross-Disciplinary Focus, designed to assess models' ability to integrate knowledge and reason across scientific domains; (3) High-Fidelity Answers, prioritizing complex, open-ended answers involving multi-step reasoning and LaTeX-formatted expressions over simple multiple-choice questions; and (4) Rigorous Quality Control, employing a multi-stage process of expert peer review and adversarial testing to ensure question difficulty, scientific value, and correctness. We also propose a robust evaluation paradigm using a panel of LLM judges for automated, nuanced assessment of complex answers. Preliminary results on leading models demonstrate ATLAS's effectiveness in differentiating their advanced scientific reasoning capabilities. We plan to develop ATLAS into a long-term, open, community-driven platform to provide a reliable "ruler" for progress toward Artificial General Intelligence.
P1: Mastering Physics Olympiads with Reinforcement Learning
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Recent progress in large language models (LLMs) has moved the frontier from puzzle-solving to science-grade reasoning-the kind needed to tackle problems whose answers must stand against nature, not merely fit a rubric. Physics is the sharpest test of this shift, which binds symbols to reality in a fundamental way, serving as the cornerstone of most modern technologies. In this work, we manage to advance physics research by developing large language models with exceptional physics reasoning capabilities, especially excel at solving Olympiad-level physics problems. We introduce P1, a family of open-source physics reasoning models trained entirely through reinforcement learning (RL). Among them, P1-235B-A22B is the first open-source model with Gold-medal performance at the latest International Physics Olympiad (IPhO 2025), and wins 12 gold medals out of 13 international/regional physics competitions in 2024/2025. P1-30B-A3B also surpasses almost all other open-source models on IPhO 2025, getting a silver medal. Further equipped with an agentic framework PhysicsMinions, P1-235B-A22B+PhysicsMinions achieves overall No.1 on IPhO 2025, and obtains the highest average score over the 13 physics competitions. Besides physics, P1 models also present great performance on other reasoning tasks like math and coding, showing the great generalibility of P1 series.
NoisyICL: A Little Noise in Model Parameters Calibrates In-context Learning
Feb 15, 2024



Abstract:In-Context Learning (ICL) is suffering from unsatisfactory performance and under-calibration due to high prior bias and unfaithful confidence. Some previous works fine-tuned language models for better ICL performance with enormous datasets and computing costs. In this paper, we propose NoisyICL, simply perturbing the model parameters by random noises to strive for better performance and calibration. Our experiments on two models and 12 downstream datasets show that NoisyICL can help ICL produce more accurate predictions. Our further analysis indicates that NoisyICL enables the model to provide more fair predictions, and also with more faithful confidence. Therefore, we believe that NoisyICL is an effective calibration of ICL. Our experimental code is uploaded to Github.
SkIn: Skimming-Intensive Long-Text Classification Using BERT for Medical Corpus
Sep 24, 2022
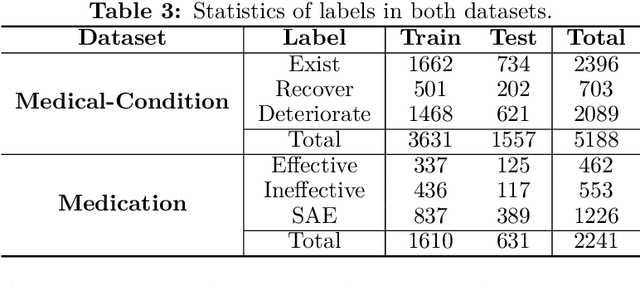
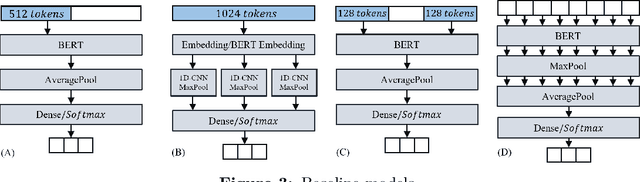
Abstract:BERT is a widely used pre-trained model in natural language processing. However, since BERT is quadratic to the text length, the BERT model is difficult to be used directly on the long-text corpus. In some fields, the collected text data may be quite long, such as in the health care field. Therefore, to apply the pre-trained language knowledge of BERT to long text, in this paper, imitating the skimming-intensive reading method used by humans when reading a long paragraph, the Skimming-Intensive Model (SkIn) is proposed. It can dynamically select the critical information in the text so that the sentence input into the BERT-Base model is significantly shortened, which can effectively save the cost of the classification algorithm. Experiments show that the SkIn method has achieved superior accuracy than the baselines on long-text classification datasets in the medical field, while its time and space requirements increase linearly with the text length, alleviating the time and space overflow problem of basic BERT on long-text data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge