Yudong Pan
COMET: Towards Partical W4A4KV4 LLMs Serving
Oct 16, 2024



Abstract:Quantization is a widely-used compression technology to reduce the overhead of serving large language models (LLMs) on terminal devices and in cloud data centers. However, prevalent quantization methods, such as 8-bit weight-activation or 4-bit weight-only quantization, achieve limited performance improvements due to poor support for low-precision (e.g., 4-bit) activation. This work, for the first time, realizes practical W4A4KV4 serving for LLMs, fully utilizing the INT4 tensor cores on modern GPUs and reducing the memory bottleneck caused by the KV cache. Specifically, we propose a novel fine-grained mixed-precision quantization algorithm (FMPQ) that compresses most activations into 4-bit with negligible accuracy loss. To support mixed-precision matrix multiplication for W4A4 and W4A8, we develop a highly optimized W4Ax kernel. Our approach introduces a novel mixed-precision data layout to facilitate access and fast dequantization for activation and weight tensors, utilizing the GPU's software pipeline to hide the overhead of data loading and conversion. Additionally, we propose fine-grained streaming multiprocessor (SM) scheduling to achieve load balance across different SMs. We integrate the optimized W4Ax kernel into our inference framework, COMET, and provide efficient management to support popular LLMs such as LLaMA-3-70B. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that, when running LLaMA family models on a single A100-80G-SMX4, COMET achieves a kernel-level speedup of \textbf{$2.88\times$} over cuBLAS and a \textbf{$2.02 \times$} throughput improvement compared to TensorRT-LLM from an end-to-end framework perspective.
Data is all you need: Finetuning LLMs for Chip Design via an Automated design-data augmentation framework
Mar 17, 2024
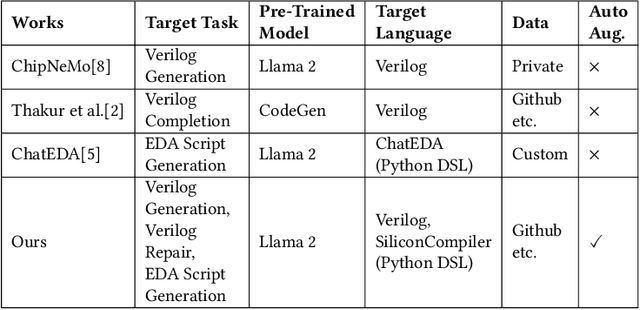


Abstract:Recent advances in large language models have demonstrated their potential for automated generation of hardware description language (HDL) code from high-level prompts. Researchers have utilized fine-tuning to enhance the ability of these large language models (LLMs) in the field of Chip Design. However, the lack of Verilog data hinders further improvement in the quality of Verilog generation by LLMs. Additionally, the absence of a Verilog and Electronic Design Automation (EDA) script data augmentation framework significantly increases the time required to prepare the training dataset for LLM trainers. This paper proposes an automated design-data augmentation framework, which generates high-volume and high-quality natural language aligned with Verilog and EDA scripts. For Verilog generation, it translates Verilog files to an abstract syntax tree and then maps nodes to natural language with a predefined template. For Verilog repair, it uses predefined rules to generate the wrong verilog file and then pairs EDA Tool feedback with the right and wrong verilog file. For EDA Script generation, it uses existing LLM(GPT-3.5) to obtain the description of the Script. To evaluate the effectiveness of our data augmentation method, we finetune Llama2-13B and Llama2-7B models using the dataset generated by our augmentation framework. The results demonstrate a significant improvement in the Verilog generation tasks with LLMs. Moreover, the accuracy of Verilog generation surpasses that of the current state-of-the-art open-source Verilog generation model, increasing from 58.8% to 70.6% with the same benchmark. Our 13B model (ChipGPT-FT) has a pass rate improvement compared with GPT-3.5 in Verilog generation and outperforms in EDA script (i.e., SiliconCompiler) generation with only 200 EDA script data.
Short-time SSVEP data extension by a novel generative adversarial networks based framework
Jan 18, 2023Abstract:Steady-state visual evoked potentials (SSVEPs) based brain-computer interface (BCI) has received considerable attention due to its high transfer rate and available quantity of targets. However, the performance of frequency identification methods heavily hinges on the amount of user calibration data and data length, which hinders the deployment in real-world applications. Recently, generative adversarial networks (GANs)-based data generation methods have been widely adopted to create supplementary synthetic electroencephalography (EEG) data, holds promise to address these issues. In this paper, we proposed a GAN-based end-to-end signal transformation network for data length window extension, termed as TEGAN. TEGAN transforms short-time SSVEP signals into long-time artificial SSVEP signals. By incorporating a novel U-Net generator architecture and auxiliary classifier into the network design, the TEGAN could produce conditioned features in the synthetic data. Additionally, to regularize the training process of GAN, we introduced a two-stage training strategy and the LeCam-divergence regularization term during the network implementation. The proposed TEGAN was evaluated on two public SSVEP datasets. With the assistance of TEGAN, the performance of traditional frequency recognition methods and deep learning-based methods have been significantly improved under limited calibration data. This study substantiates the feasibility of the proposed method to extend the data length for short-time SSVEP signals to develop a high-performance BCI system. The proposed GAN-based methods have the great potential of shortening the calibration time for various real-world BCI-based applications, while the novelty of our augmentation strategies shed some value light on understanding the subject-invariant properties of SSVEPs.
A Transformer-based deep neural network model for SSVEP classification
Oct 09, 2022



Abstract:Steady-state visual evoked potential (SSVEP) is one of the most commonly used control signal in the brain-computer interface (BCI) systems. However, the conventional spatial filtering methods for SSVEP classification highly depend on the subject-specific calibration data. The need for the methods that can alleviate the demand for the calibration data become urgent. In recent years, developing the methods that can work in inter-subject classification scenario has become a promising new direction. As the popular deep learning model nowadays, Transformer has excellent performance and has been used in EEG signal classification tasks. Therefore, in this study, we propose a deep learning model for SSVEP classification based on Transformer structure in inter-subject classification scenario, termed as SSVEPformer, which is the first application of the transformer to the classification of SSVEP. Inspired by previous studies, the model adopts the frequency spectrum of SSVEP data as input, and explores the spectral and spatial domain information for classification. Furthermore, to fully utilize the harmonic information, an extended SSVEPformer based on the filter bank technology (FB-SSVEPformer) is proposed to further improve the classification performance. Experiments were conducted using two open datasets (Dataset 1: 10 subjects, 12-class task; Dataset 2: 35 subjects, 40-class task) in the inter-subject classification scenario. The experimental results show that the proposed models could achieve better results in terms of classification accuracy and information transfer rate, compared with other baseline methods. The proposed model validates the feasibility of deep learning models based on Transformer structure for SSVEP classification task, and could serve as a potential model to alleviate the calibration procedure in the practical application of SSVEP-based BCI systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge