Yubin Zhang
Non-Invasive Diagnosis for Clubroot Using Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy and Physics-Constrained Neural Networks
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Clubroot, a major soilborne disease affecting canola and other cruciferous crops, is characterized by the development of large galls on the roots of susceptible hosts. In this study, we present the first application of terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) as a non-invasive diagnosis tool in plant pathology. Compared with conventional molecular, spectroscopic, and immunoassay-based methods, THz-TDS offers distinct advantages, including non-contact, non-destructive, and preparation-free measurement, enabling rapid in situ screening of plant and soil samples. Our results demonstrate that THz-TDS can differentiate between healthy and clubroot-infected tissues by detecting both structural and biochemical alterations. Specifically, infected roots exhibit a blue shift in the refractive index in the low-frequency THz range, along with distinct peaks-indicative of disruptions in water transport and altered metabolic activity in both roots and leaves. Interestingly, the characteristic root swelling observed in infected plants reflects internal tissue disorganization rather than an actual increase in water content. Furthermore, a physics-constrained neural network is proposed to extract the main feature in THz-TDS. A comprehensive evaluation, including time-domain signals, amplitude and phase images, refractive index and absorption coefficient maps, and principal component analysis, provides enhanced contrast and spatial resolution compared to raw time-domain or frequency signals. These findings suggest that THz-TDS holds significant potential for early, non-destructive detection of plant diseases and may serve as a valuable tool to limit their spread in agricultural systems.
A Metric for MLLM Alignment in Large-scale Recommendation
Aug 07, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal recommendation has emerged as a critical technique in modern recommender systems, leveraging content representations from advanced multimodal large language models (MLLMs). To ensure these representations are well-adapted, alignment with the recommender system is essential. However, evaluating the alignment of MLLMs for recommendation presents significant challenges due to three key issues: (1) static benchmarks are inaccurate because of the dynamism in real-world applications, (2) evaluations with online system, while accurate, are prohibitively expensive at scale, and (3) conventional metrics fail to provide actionable insights when learned representations underperform. To address these challenges, we propose the Leakage Impact Score (LIS), a novel metric for multimodal recommendation. Rather than directly assessing MLLMs, LIS efficiently measures the upper bound of preference data. We also share practical insights on deploying MLLMs with LIS in real-world scenarios. Online A/B tests on both Content Feed and Display Ads of Xiaohongshu's Explore Feed production demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method, showing significant improvements in user spent time and advertiser value.
Deep Speech Synthesis from MRI-Based Articulatory Representations
Jul 05, 2023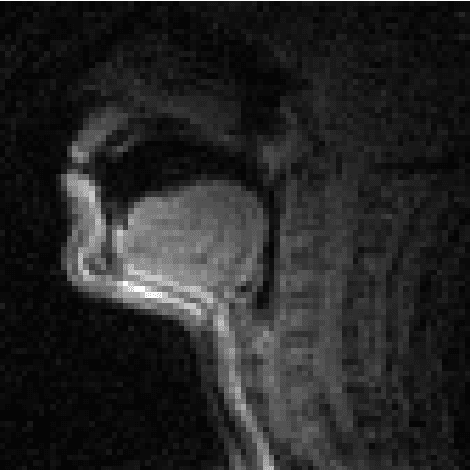
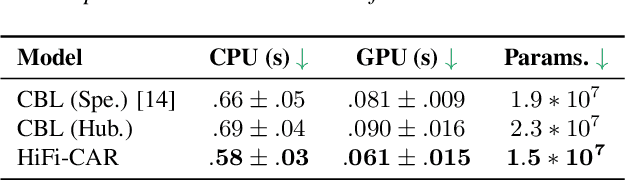
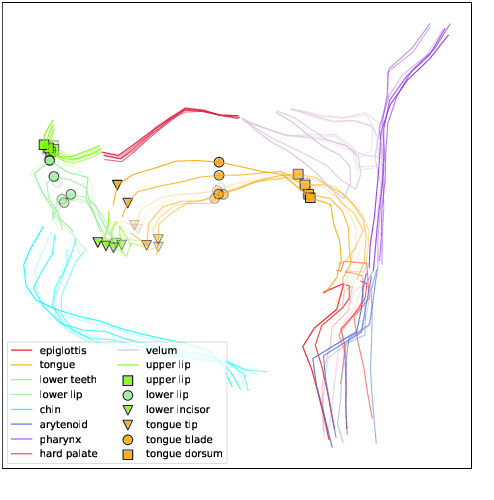
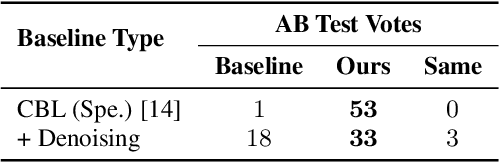
Abstract:In this paper, we study articulatory synthesis, a speech synthesis method using human vocal tract information that offers a way to develop efficient, generalizable and interpretable synthesizers. While recent advances have enabled intelligible articulatory synthesis using electromagnetic articulography (EMA), these methods lack critical articulatory information like excitation and nasality, limiting generalization capabilities. To bridge this gap, we propose an alternative MRI-based feature set that covers a much more extensive articulatory space than EMA. We also introduce normalization and denoising procedures to enhance the generalizability of deep learning methods trained on MRI data. Moreover, we propose an MRI-to-speech model that improves both computational efficiency and speech fidelity. Finally, through a series of ablations, we show that the proposed MRI representation is more comprehensive than EMA and identify the most suitable MRI feature subset for articulatory synthesis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge