Yuanbo Wang
Touch2Shape: Touch-Conditioned 3D Diffusion for Shape Exploration and Reconstruction
May 19, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have made breakthroughs in 3D generation tasks. Current 3D diffusion models focus on reconstructing target shape from images or a set of partial observations. While excelling in global context understanding, they struggle to capture the local details of complex shapes and limited to the occlusion and lighting conditions. To overcome these limitations, we utilize tactile images to capture the local 3D information and propose a Touch2Shape model, which leverages a touch-conditioned diffusion model to explore and reconstruct the target shape from touch. For shape reconstruction, we have developed a touch embedding module to condition the diffusion model in creating a compact representation and a touch shape fusion module to refine the reconstructed shape. For shape exploration, we combine the diffusion model with reinforcement learning to train a policy. This involves using the generated latent vector from the diffusion model to guide the touch exploration policy training through a novel reward design. Experiments validate the reconstruction quality thorough both qualitatively and quantitative analysis, and our touch exploration policy further boosts reconstruction performance.
A Comprehensive Review of Modern Object Segmentation Approaches
Jan 13, 2023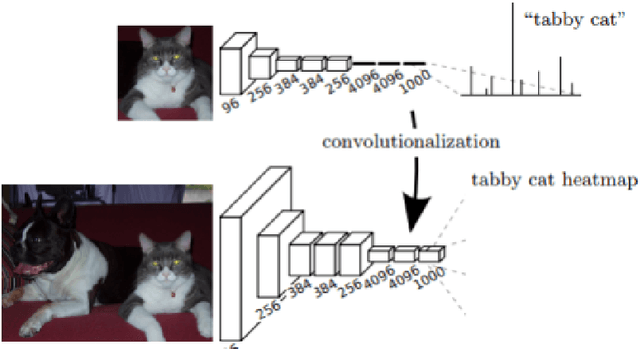



Abstract:Image segmentation is the task of associating pixels in an image with their respective object class labels. It has a wide range of applications in many industries including healthcare, transportation, robotics, fashion, home improvement, and tourism. Many deep learning-based approaches have been developed for image-level object recognition and pixel-level scene understanding-with the latter requiring a much denser annotation of scenes with a large set of objects. Extensions of image segmentation tasks include 3D and video segmentation, where units of voxels, point clouds, and video frames are classified into different objects. We use "Object Segmentation" to refer to the union of these segmentation tasks. In this monograph, we investigate both traditional and modern object segmentation approaches, comparing their strengths, weaknesses, and utilities. We examine in detail the wide range of deep learning-based segmentation techniques developed in recent years, provide a review of the widely used datasets and evaluation metrics, and discuss potential future research directions.
* 173 pages, 49 figures, published in Foundations and Trends in Computer Graphics and Vision on 10/4/22. Authors retain copyright
Adversarial recovery of agent rewards from latent spaces of the limit order book
Dec 09, 2019



Abstract:Inverse reinforcement learning has proved its ability to explain state-action trajectories of expert agents by recovering their underlying reward functions in increasingly challenging environments. Recent advances in adversarial learning have allowed extending inverse RL to applications with non-stationary environment dynamics unknown to the agents, arbitrary structures of reward functions and improved handling of the ambiguities inherent to the ill-posed nature of inverse RL. This is particularly relevant in real time applications on stochastic environments involving risk, like volatile financial markets. Moreover, recent work on simulation of complex environments enable learning algorithms to engage with real market data through simulations of its latent space representations, avoiding a costly exploration of the original environment. In this paper, we explore whether adversarial inverse RL algorithms can be adapted and trained within such latent space simulations from real market data, while maintaining their ability to recover agent rewards robust to variations in the underlying dynamics, and transfer them to new regimes of the original environment.
Model-based Reinforcement Learning for Predictions and Control for Limit Order Books
Oct 09, 2019



Abstract:We build a profitable electronic trading agent with Reinforcement Learning that places buy and sell orders in the stock market. An environment model is built only with historical observational data, and the RL agent learns the trading policy by interacting with the environment model instead of with the real-market to minimize the risk and potential monetary loss. Trained in unsupervised and self-supervised fashion, our environment model learned a temporal and causal representation of the market in latent space through deep neural networks. We demonstrate that the trading policy trained entirely within the environment model can be transferred back into the real market and maintain its profitability. We believe that this environment model can serve as a robust simulator that predicts market movement as well as trade impact for further studies.
Active Object Reconstruction Using a Guided View Planner
May 08, 2018



Abstract:Inspired by the recent advance of image-based object reconstruction using deep learning, we present an active reconstruction model using a guided view planner. We aim to reconstruct a 3D model using images observed from a planned sequence of informative and discriminative views. But where are such informative and discriminative views around an object? To address this we propose a unified model for view planning and object reconstruction, which is utilized to learn a guided information acquisition model and to aggregate information from a sequence of images for reconstruction. Experiments show that our model (1) increases our reconstruction accuracy with an increasing number of views (2) and generally predicts a more informative sequence of views for object reconstruction compared to other alternative methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge