Yongqiang Li
Multi-Modality Driven LoRA for Adverse Condition Depth Estimation
Dec 28, 2024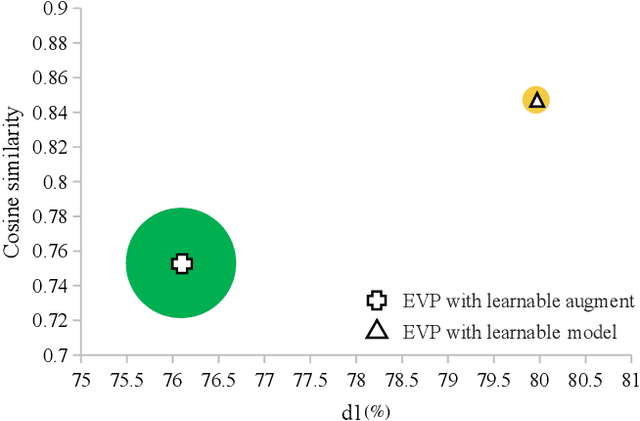
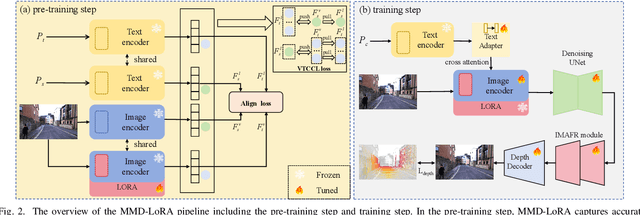
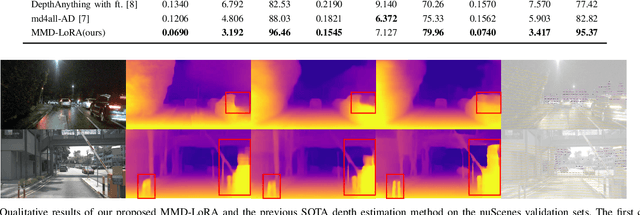
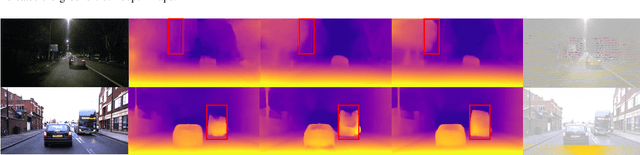
Abstract:The autonomous driving community is increasingly focused on addressing corner case problems, particularly those related to ensuring driving safety under adverse conditions (e.g., nighttime, fog, rain). To this end, the task of Adverse Condition Depth Estimation (ACDE) has gained significant attention. Previous approaches in ACDE have primarily relied on generative models, which necessitate additional target images to convert the sunny condition into adverse weather, or learnable parameters for feature augmentation to adapt domain gaps, resulting in increased model complexity and tuning efforts. Furthermore, unlike CLIP-based methods where textual and visual features have been pre-aligned, depth estimation models lack sufficient alignment between multimodal features, hindering coherent understanding under adverse conditions. To address these limitations, we propose Multi-Modality Driven LoRA (MMD-LoRA), which leverages low-rank adaptation matrices for efficient fine-tuning from source-domain to target-domain. It consists of two core components: Prompt Driven Domain Alignment (PDDA) and Visual-Text Consistent Contrastive Learning(VTCCL). During PDDA, the image encoder with MMD-LoRA generates target-domain visual representations, supervised by alignment loss that the source-target difference between language and image should be equal. Meanwhile, VTCCL bridges the gap between textual features from CLIP and visual features from diffusion model, pushing apart different weather representations (vision and text) and bringing together similar ones. Through extensive experiments, the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the nuScenes and Oxford RobotCar datasets, underscoring robustness and efficiency in adapting to varied adverse environments.
Enhanced channel estimation for near-field IRS-aided multi-user MIMO system via deep residual network
Oct 28, 2024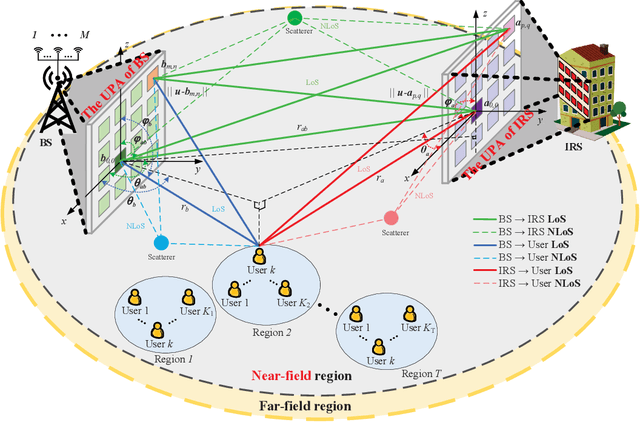
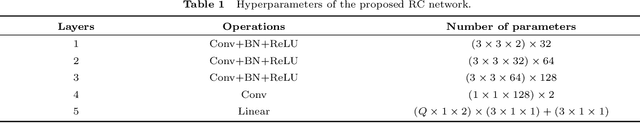
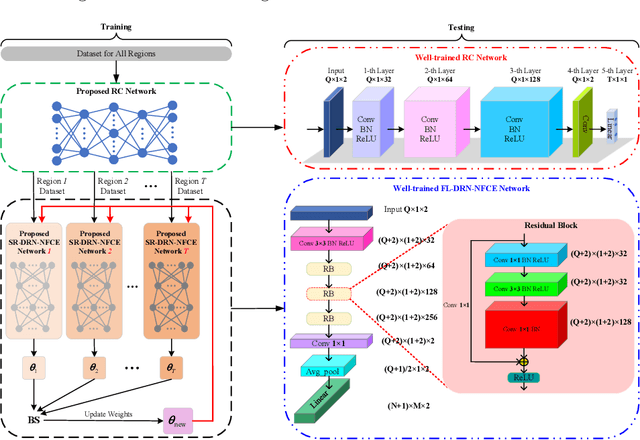

Abstract:In this paper, channel estimation (CE) of intelligent reflecting surface aided near-field (NF) multi-user communication is investigated. Initially, the least square (LS) estimator and minimum mean square error (MMSE) estimator for the estimated channel are designed, and their mean square errors (MSEs) are derived. Subsequently, to fully harness the potential of deep residual networks (DRNs) in denoising, the above CE problem is reconceptualized as a denoising task, and a DRN-driven NF CE (DRN-NFCE) framework is proposed, and the Cram$\acute{e}$r-Rao lower bound (CRLB) is derived to serve as a benchmark for performance evaluation. In addition, to effectively capture and leverage these diverse channel features, a federated learning (FL) based global DRN-NFCE network, namely FL-DRN-NFCE, is constructed through collaborative training and joint optimization of single region DRN-NFCE (SR-DRN-NFCE) networks in different user regions. Here, users are divided into multiple regions. Correspondingly, a user region classifier based on convolutional neural network is designed to achieve the goal of matching datasets from different user regions to the corresponding SR-DRN-NFCE network. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed FL-DRN-NFCE framework outperforms LS, MMSE, and no residual connections in terms of MSE, and the proposed FL-DRN-NFCE method has higher CE accuracy over the SR-DRN-NFCE method.
Orion-14B: Open-source Multilingual Large Language Models
Jan 20, 2024Abstract:In this study, we introduce Orion-14B, a collection of multilingual large language models with 14 billion parameters. We utilize a data scheduling approach to train a foundational model on a diverse corpus of 2.5 trillion tokens, sourced from texts in English, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and other languages. Additionally, we fine-tuned a series of models tailored for conversational applications and other specific use cases. Our evaluation results demonstrate that Orion-14B achieves state-of-the-art performance across a broad spectrum of tasks. We make the Orion-14B model family and its associated code publicly accessible https://github.com/OrionStarAI/Orion, aiming to inspire future research and practical applications in the field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge