Yiren Song
Loom: Diffusion-Transformer for Interleaved Generation
Dec 20, 2025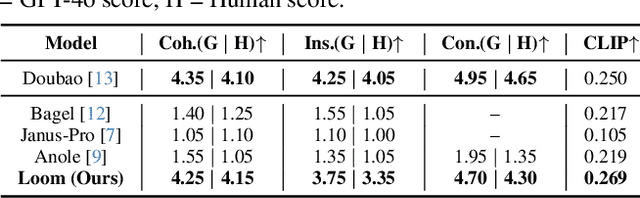
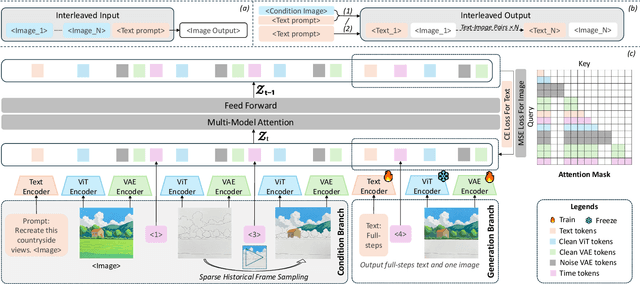
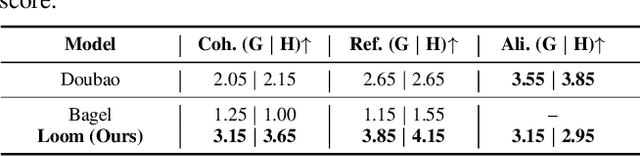
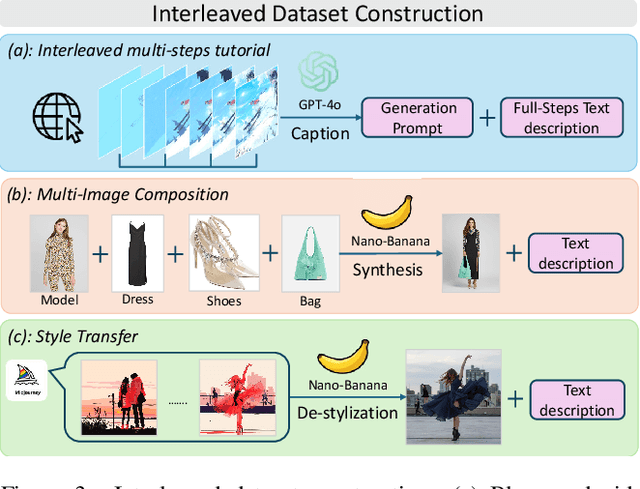
Abstract:Interleaved text-image generation aims to jointly produce coherent visual frames and aligned textual descriptions within a single sequence, enabling tasks such as style transfer, compositional synthesis, and procedural tutorials. We present Loom, a unified diffusion-transformer framework for interleaved text-image generation. Loom extends the Bagel unified model via full-parameter fine-tuning and an interleaved architecture that alternates textual and visual embeddings for multi-condition reasoning and sequential planning. A language planning strategy first decomposes a user instruction into stepwise prompts and frame embeddings, which guide temporally consistent synthesis. For each frame, Loom conditions on a small set of sampled prior frames together with the global textual context, rather than concatenating all history, yielding controllable and efficient long-horizon generation. Across style transfer, compositional generation, and tutorial-like procedures, Loom delivers superior compositionality, temporal coherence, and text-image alignment. Experiments demonstrate that Loom substantially outperforms the open-source baseline Anole, achieving an average gain of 2.6 points (on a 5-point scale) across temporal and semantic metrics in text-to-interleaved tasks. We also curate a 50K interleaved tutorial dataset and demonstrate strong improvements over unified and diffusion editing baselines.
Mitty: Diffusion-based Human-to-Robot Video Generation
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Learning directly from human demonstration videos is a key milestone toward scalable and generalizable robot learning. Yet existing methods rely on intermediate representations such as keypoints or trajectories, introducing information loss and cumulative errors that harm temporal and visual consistency. We present Mitty, a Diffusion Transformer that enables video In-Context Learning for end-to-end Human2Robot video generation. Built on a pretrained video diffusion model, Mitty leverages strong visual-temporal priors to translate human demonstrations into robot-execution videos without action labels or intermediate abstractions. Demonstration videos are compressed into condition tokens and fused with robot denoising tokens through bidirectional attention during diffusion. To mitigate paired-data scarcity, we also develop an automatic synthesis pipeline that produces high-quality human-robot pairs from large egocentric datasets. Experiments on Human2Robot and EPIC-Kitchens show that Mitty delivers state-of-the-art results, strong generalization to unseen environments, and new insights for scalable robot learning from human observations.
IC-Effect: Precise and Efficient Video Effects Editing via In-Context Learning
Dec 17, 2025



Abstract:We propose \textbf{IC-Effect}, an instruction-guided, DiT-based framework for few-shot video VFX editing that synthesizes complex effects (\eg flames, particles and cartoon characters) while strictly preserving spatial and temporal consistency. Video VFX editing is highly challenging because injected effects must blend seamlessly with the background, the background must remain entirely unchanged, and effect patterns must be learned efficiently from limited paired data. However, existing video editing models fail to satisfy these requirements. IC-Effect leverages the source video as clean contextual conditions, exploiting the contextual learning capability of DiT models to achieve precise background preservation and natural effect injection. A two-stage training strategy, consisting of general editing adaptation followed by effect-specific learning via Effect-LoRA, ensures strong instruction following and robust effect modeling. To further improve efficiency, we introduce spatiotemporal sparse tokenization, enabling high fidelity with substantially reduced computation. We also release a paired VFX editing dataset spanning $15$ high-quality visual styles. Extensive experiments show that IC-Effect delivers high-quality, controllable, and temporally consistent VFX editing, opening new possibilities for video creation.
H2R-Grounder: A Paired-Data-Free Paradigm for Translating Human Interaction Videos into Physically Grounded Robot Videos
Dec 10, 2025



Abstract:Robots that learn manipulation skills from everyday human videos could acquire broad capabilities without tedious robot data collection. We propose a video-to-video translation framework that converts ordinary human-object interaction videos into motion-consistent robot manipulation videos with realistic, physically grounded interactions. Our approach does not require any paired human-robot videos for training only a set of unpaired robot videos, making the system easy to scale. We introduce a transferable representation that bridges the embodiment gap: by inpainting the robot arm in training videos to obtain a clean background and overlaying a simple visual cue (a marker and arrow indicating the gripper's position and orientation), we can condition a generative model to insert the robot arm back into the scene. At test time, we apply the same process to human videos (inpainting the person and overlaying human pose cues) and generate high-quality robot videos that mimic the human's actions. We fine-tune a SOTA video diffusion model (Wan 2.2) in an in-context learning manner to ensure temporal coherence and leveraging of its rich prior knowledge. Empirical results demonstrate that our approach achieves significantly more realistic and grounded robot motions compared to baselines, pointing to a promising direction for scaling up robot learning from unlabeled human videos. Project page: https://showlab.github.io/H2R-Grounder/
OmniPSD: Layered PSD Generation with Diffusion Transformer
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion models have greatly improved image generation and editing, yet generating or reconstructing layered PSD files with transparent alpha channels remains highly challenging. We propose OmniPSD, a unified diffusion framework built upon the Flux ecosystem that enables both text-to-PSD generation and image-to-PSD decomposition through in-context learning. For text-to-PSD generation, OmniPSD arranges multiple target layers spatially into a single canvas and learns their compositional relationships through spatial attention, producing semantically coherent and hierarchically structured layers. For image-to-PSD decomposition, it performs iterative in-context editing, progressively extracting and erasing textual and foreground components to reconstruct editable PSD layers from a single flattened image. An RGBA-VAE is employed as an auxiliary representation module to preserve transparency without affecting structure learning. Extensive experiments on our new RGBA-layered dataset demonstrate that OmniPSD achieves high-fidelity generation, structural consistency, and transparency awareness, offering a new paradigm for layered design generation and decomposition with diffusion transformers.
MCA-Bench: A Multimodal Benchmark for Evaluating CAPTCHA Robustness Against VLM-based Attacks
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:As automated attack techniques rapidly advance, CAPTCHAs remain a critical defense mechanism against malicious bots. However, existing CAPTCHA schemes encompass a diverse range of modalities -- from static distorted text and obfuscated images to interactive clicks, sliding puzzles, and logic-based questions -- yet the community still lacks a unified, large-scale, multimodal benchmark to rigorously evaluate their security robustness. To address this gap, we introduce MCA-Bench, a comprehensive and reproducible benchmarking suite that integrates heterogeneous CAPTCHA types into a single evaluation protocol. Leveraging a shared vision-language model backbone, we fine-tune specialized cracking agents for each CAPTCHA category, enabling consistent, cross-modal assessments. Extensive experiments reveal that MCA-Bench effectively maps the vulnerability spectrum of modern CAPTCHA designs under varied attack settings, and crucially offers the first quantitative analysis of how challenge complexity, interaction depth, and model solvability interrelate. Based on these findings, we propose three actionable design principles and identify key open challenges, laying the groundwork for systematic CAPTCHA hardening, fair benchmarking, and broader community collaboration. Datasets and code are available online.
DiffDecompose: Layer-Wise Decomposition of Alpha-Composited Images via Diffusion Transformers
May 30, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have recently motivated great success in many generation tasks like object removal. Nevertheless, existing image decomposition methods struggle to disentangle semi-transparent or transparent layer occlusions due to mask prior dependencies, static object assumptions, and the lack of datasets. In this paper, we delve into a novel task: Layer-Wise Decomposition of Alpha-Composited Images, aiming to recover constituent layers from single overlapped images under the condition of semi-transparent/transparent alpha layer non-linear occlusion. To address challenges in layer ambiguity, generalization, and data scarcity, we first introduce AlphaBlend, the first large-scale and high-quality dataset for transparent and semi-transparent layer decomposition, supporting six real-world subtasks (e.g., translucent flare removal, semi-transparent cell decomposition, glassware decomposition). Building on this dataset, we present DiffDecompose, a diffusion Transformer-based framework that learns the posterior over possible layer decompositions conditioned on the input image, semantic prompts, and blending type. Rather than regressing alpha mattes directly, DiffDecompose performs In-Context Decomposition, enabling the model to predict one or multiple layers without per-layer supervision, and introduces Layer Position Encoding Cloning to maintain pixel-level correspondence across layers. Extensive experiments on the proposed AlphaBlend dataset and public LOGO dataset verify the effectiveness of DiffDecompose. The code and dataset will be available upon paper acceptance. Our code will be available at: https://github.com/Wangzt1121/DiffDecompose.
EasyText: Controllable Diffusion Transformer for Multilingual Text Rendering
May 30, 2025



Abstract:Generating accurate multilingual text with diffusion models has long been desired but remains challenging. Recent methods have made progress in rendering text in a single language, but rendering arbitrary languages is still an unexplored area. This paper introduces EasyText, a text rendering framework based on DiT (Diffusion Transformer), which connects denoising latents with multilingual character tokens encoded as character tokens. We propose character positioning encoding and position encoding interpolation techniques to achieve controllable and precise text rendering. Additionally, we construct a large-scale synthetic text image dataset with 1 million multilingual image-text annotations as well as a high-quality dataset of 20K annotated images, which are used for pretraining and fine-tuning respectively. Extensive experiments and evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness and advancement of our approach in multilingual text rendering, visual quality, and layout-aware text integration.
GRE Suite: Geo-localization Inference via Fine-Tuned Vision-Language Models and Enhanced Reasoning Chains
May 24, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in Visual Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated exceptional performance in visual reasoning tasks. However, geo-localization presents unique challenges, requiring the extraction of multigranular visual cues from images and their integration with external world knowledge for systematic reasoning. Current approaches to geo-localization tasks often lack robust reasoning mechanisms and explainability, limiting their effectiveness. To address these limitations, we propose the Geo Reason Enhancement (GRE) Suite, a novel framework that augments VLMs with structured reasoning chains for accurate and interpretable location inference. The GRE Suite is systematically developed across three key dimensions: dataset, model, and benchmark. First, we introduce GRE30K, a high-quality geo-localization reasoning dataset designed to facilitate fine-grained visual and contextual analysis. Next, we present the GRE model, which employs a multi-stage reasoning strategy to progressively infer scene attributes, local details, and semantic features, thereby narrowing down potential geographic regions with enhanced precision. Finally, we construct the Geo Reason Evaluation Benchmark (GREval-Bench), a comprehensive evaluation framework that assesses VLMs across diverse urban, natural, and landmark scenes to measure both coarse-grained (e.g., country, continent) and fine-grained (e.g., city, street) localization performance. Experimental results demonstrate that GRE significantly outperforms existing methods across all granularities of geo-localization tasks, underscoring the efficacy of reasoning-augmented VLMs in complex geographic inference. Code and data will be released at https://github.com/Thorin215/GRE.
OmniConsistency: Learning Style-Agnostic Consistency from Paired Stylization Data
May 24, 2025



Abstract:Diffusion models have advanced image stylization significantly, yet two core challenges persist: (1) maintaining consistent stylization in complex scenes, particularly identity, composition, and fine details, and (2) preventing style degradation in image-to-image pipelines with style LoRAs. GPT-4o's exceptional stylization consistency highlights the performance gap between open-source methods and proprietary models. To bridge this gap, we propose \textbf{OmniConsistency}, a universal consistency plugin leveraging large-scale Diffusion Transformers (DiTs). OmniConsistency contributes: (1) an in-context consistency learning framework trained on aligned image pairs for robust generalization; (2) a two-stage progressive learning strategy decoupling style learning from consistency preservation to mitigate style degradation; and (3) a fully plug-and-play design compatible with arbitrary style LoRAs under the Flux framework. Extensive experiments show that OmniConsistency significantly enhances visual coherence and aesthetic quality, achieving performance comparable to commercial state-of-the-art model GPT-4o.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge