Yingya Li
WorldMedQA-V: a multilingual, multimodal medical examination dataset for multimodal language models evaluation
Oct 16, 2024Abstract:Multimodal/vision language models (VLMs) are increasingly being deployed in healthcare settings worldwide, necessitating robust benchmarks to ensure their safety, efficacy, and fairness. Multiple-choice question and answer (QA) datasets derived from national medical examinations have long served as valuable evaluation tools, but existing datasets are largely text-only and available in a limited subset of languages and countries. To address these challenges, we present WorldMedQA-V, an updated multilingual, multimodal benchmarking dataset designed to evaluate VLMs in healthcare. WorldMedQA-V includes 568 labeled multiple-choice QAs paired with 568 medical images from four countries (Brazil, Israel, Japan, and Spain), covering original languages and validated English translations by native clinicians, respectively. Baseline performance for common open- and closed-source models are provided in the local language and English translations, and with and without images provided to the model. The WorldMedQA-V benchmark aims to better match AI systems to the diverse healthcare environments in which they are deployed, fostering more equitable, effective, and representative applications.
Identifying Task Groupings for Multi-Task Learning Using Pointwise V-Usable Information
Oct 16, 2024Abstract:The success of multi-task learning can depend heavily on which tasks are grouped together. Naively grouping all tasks or a random set of tasks can result in negative transfer, with the multi-task models performing worse than single-task models. Though many efforts have been made to identify task groupings and to measure the relatedness among different tasks, it remains a challenging research topic to define a metric to identify the best task grouping out of a pool of many potential task combinations. We propose a metric of task relatedness based on task difficulty measured by pointwise V-usable information (PVI). PVI is a recently proposed metric to estimate how much usable information a dataset contains given a model. We hypothesize that tasks with not statistically different PVI estimates are similar enough to benefit from the joint learning process. We conduct comprehensive experiments to evaluate the feasibility of this metric for task grouping on 15 NLP datasets in the general, biomedical, and clinical domains. We compare the results of the joint learners against single learners, existing baseline methods, and recent large language models, including Llama 2 and GPT-4. The results show that by grouping tasks with similar PVI estimates, the joint learners yielded competitive results with fewer total parameters, with consistent performance across domains.
From explainable to interpretable deep learning for natural language processing in healthcare: how far from reality?
Mar 18, 2024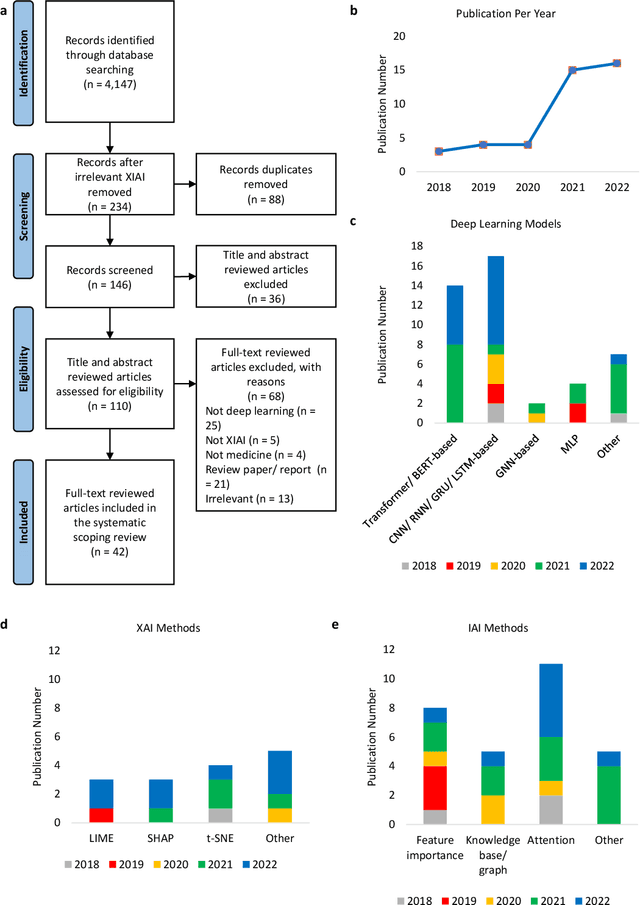
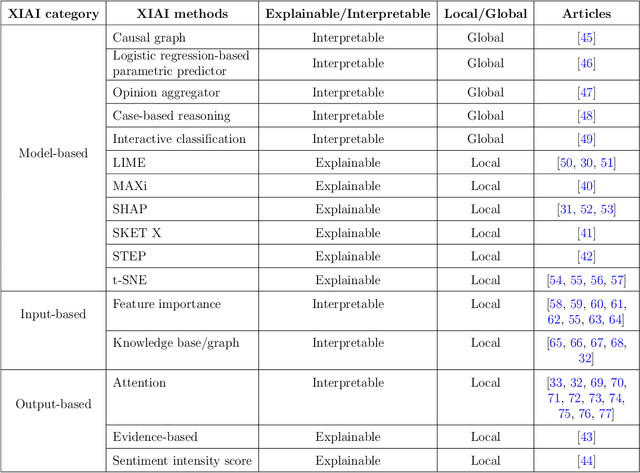
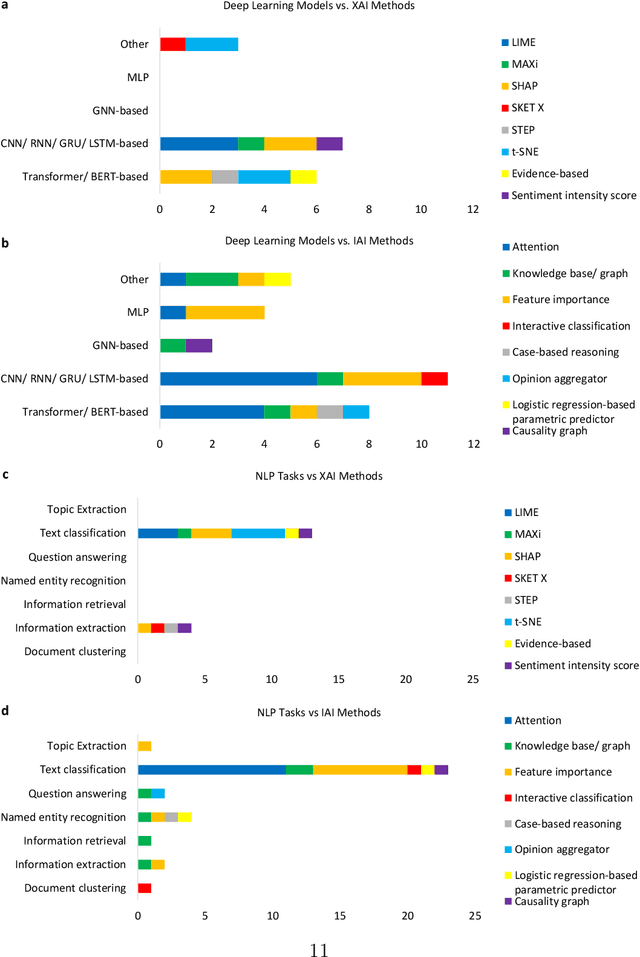
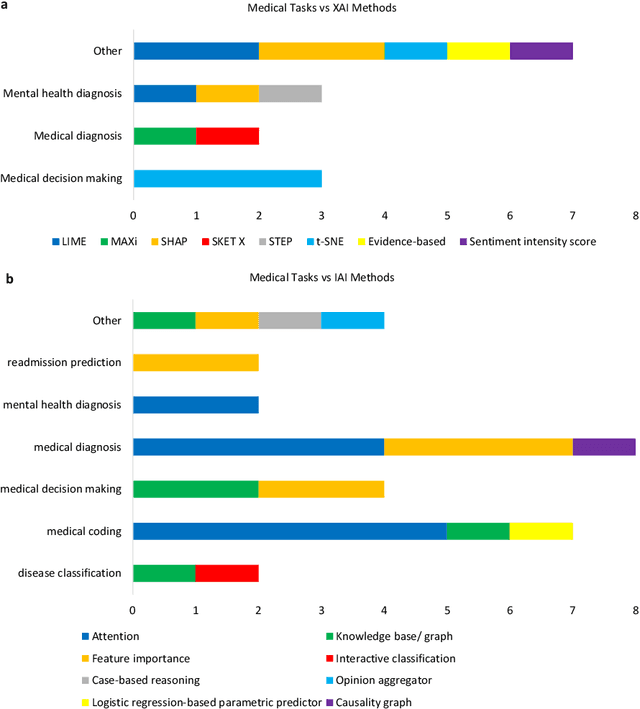
Abstract:Deep learning (DL) has substantially enhanced healthcare research by addressing various natural language processing (NLP) tasks. Yet, the increasing complexity of DL-based NLP methods necessitates transparent model interpretability, or at least explainability, for reliable decision-making. This work presents a thorough scoping review on explainable and interpretable DL in healthcare NLP. The term "XIAI" (eXplainable and Interpretable Artificial Intelligence) was introduced to distinguish XAI from IAI. Methods were further categorized based on their functionality (model-, input-, output-based) and scope (local, global). Our analysis shows that attention mechanisms were the most dominant emerging IAI. Moreover, IAI is increasingly used against XAI. The major challenges identified are that most XIAI do not explore "global" modeling processes, the lack of best practices, and the unmet need for systematic evaluation and benchmarks. Important opportunities were raised such as using "attention" to enhance multi-modal XIAI for personalized medicine and combine DL with causal reasoning. Our discussion encourages the integration of XIAI in LLMs and domain-specific smaller models. Our review can stimulate further research and benchmarks toward improving inherent IAI and engaging complex NLP in healthcare.
Measuring Pointwise $\mathcal{V}$-Usable Information In-Context-ly
Oct 18, 2023



Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) is a new learning paradigm that has gained popularity along with the development of large language models. In this work, we adapt a recently proposed hardness metric, pointwise $\mathcal{V}$-usable information (PVI), to an in-context version (in-context PVI). Compared to the original PVI, in-context PVI is more efficient in that it requires only a few exemplars and does not require fine-tuning. We conducted a comprehensive empirical analysis to evaluate the reliability of in-context PVI. Our findings indicate that in-context PVI estimates exhibit similar characteristics to the original PVI. Specific to the in-context setting, we show that in-context PVI estimates remain consistent across different exemplar selections and numbers of shots. The variance of in-context PVI estimates across different exemplar selections is insignificant, which suggests that in-context PVI are stable. Furthermore, we demonstrate how in-context PVI can be employed to identify challenging instances. Our work highlights the potential of in-context PVI and provides new insights into the capabilities of ICL.
Evaluation of ChatGPT Family of Models for Biomedical Reasoning and Classification
Apr 05, 2023



Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have shown impressive ability in biomedical question-answering, but have not been adequately investigated for more specific biomedical applications. This study investigates the performance of LLMs such as the ChatGPT family of models (GPT-3.5s, GPT-4) in biomedical tasks beyond question-answering. Because no patient data can be passed to the OpenAI API public interface, we evaluated model performance with over 10000 samples as proxies for two fundamental tasks in the clinical domain - classification and reasoning. The first task is classifying whether statements of clinical and policy recommendations in scientific literature constitute health advice. The second task is causal relation detection from the biomedical literature. We compared LLMs with simpler models, such as bag-of-words (BoW) with logistic regression, and fine-tuned BioBERT models. Despite the excitement around viral ChatGPT, we found that fine-tuning for two fundamental NLP tasks remained the best strategy. The simple BoW model performed on par with the most complex LLM prompting. Prompt engineering required significant investment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge