Yian Yin
Department of Information Science, Cornell University
Scientific production in the era of Large Language Models
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are rapidly reshaping scientific research. We analyze these changes in multiple, large-scale datasets with 2.1M preprints, 28K peer review reports, and 246M online accesses to scientific documents. We find: 1) scientists adopting LLMs to draft manuscripts demonstrate a large increase in paper production, ranging from 23.7-89.3% depending on scientific field and author background, 2) LLM use has reversed the relationship between writing complexity and paper quality, leading to an influx of manuscripts that are linguistically complex but substantively underwhelming, and 3) LLM adopters access and cite more diverse prior work, including books and younger, less-cited documents. These findings highlight a stunning shift in scientific production that will likely require a change in how journals, funding agencies, and tenure committees evaluate scientific works.
* This is the author's version of the work. The definitive version was published in Science on 18 Dec 2025, DOI: 10.1126/science.adw3000. Link to the Final Published Version: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adw3000
Benchmark Datasets for Lead-Lag Forecasting on Social Platforms
Nov 05, 2025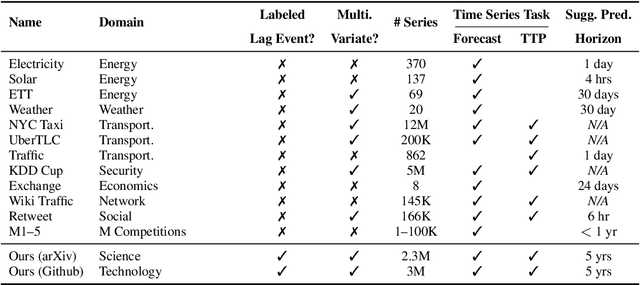
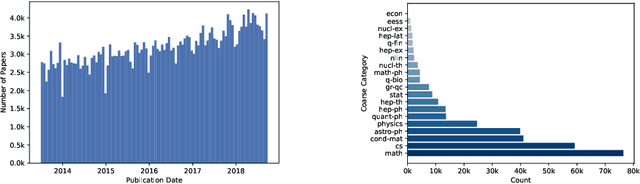
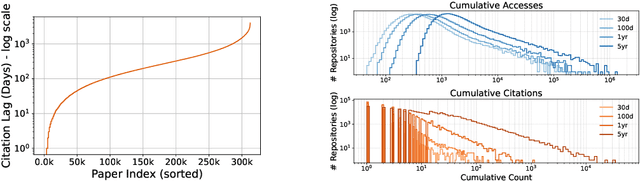
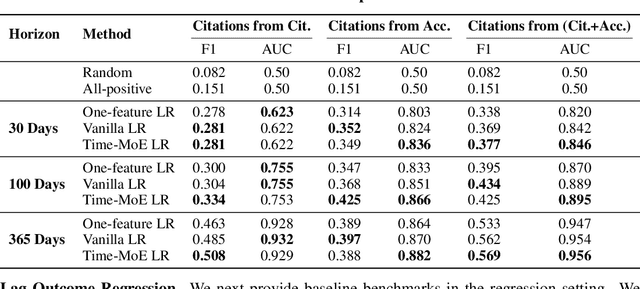
Abstract:Social and collaborative platforms emit multivariate time-series traces in which early interactions-such as views, likes, or downloads-are followed, sometimes months or years later, by higher impact like citations, sales, or reviews. We formalize this setting as Lead-Lag Forecasting (LLF): given an early usage channel (the lead), predict a correlated but temporally shifted outcome channel (the lag). Despite the ubiquity of such patterns, LLF has not been treated as a unified forecasting problem within the time-series community, largely due to the absence of standardized datasets. To anchor research in LLF, here we present two high-volume benchmark datasets-arXiv (accesses -> citations of 2.3M papers) and GitHub (pushes/stars -> forks of 3M repositories)-and outline additional domains with analogous lead-lag dynamics, including Wikipedia (page views -> edits), Spotify (streams -> concert attendance), e-commerce (click-throughs -> purchases), and LinkedIn profile (views -> messages). Our datasets provide ideal testbeds for lead-lag forecasting, by capturing long-horizon dynamics across years, spanning the full spectrum of outcomes, and avoiding survivorship bias in sampling. We documented all technical details of data curation and cleaning, verified the presence of lead-lag dynamics through statistical and classification tests, and benchmarked parametric and non-parametric baselines for regression. Our study establishes LLF as a novel forecasting paradigm and lays an empirical foundation for its systematic exploration in social and usage data. Our data portal with downloads and documentation is available at https://lead-lag-forecasting.github.io/.
Language Agents for Detecting Implicit Stereotypes in Text-to-image Models at Scale
Nov 02, 2023



Abstract:The recent surge in the research of diffusion models has accelerated the adoption of text-to-image models in various Artificial Intelligence Generated Content (AIGC) commercial products. While these exceptional AIGC products are gaining increasing recognition and sparking enthusiasm among consumers, the questions regarding whether, when, and how these models might unintentionally reinforce existing societal stereotypes remain largely unaddressed. Motivated by recent advancements in language agents, here we introduce a novel agent architecture tailored for stereotype detection in text-to-image models. This versatile agent architecture is capable of accommodating free-form detection tasks and can autonomously invoke various tools to facilitate the entire process, from generating corresponding instructions and images, to detecting stereotypes. We build the stereotype-relevant benchmark based on multiple open-text datasets, and apply this architecture to commercial products and popular open source text-to-image models. We find that these models often display serious stereotypes when it comes to certain prompts about personal characteristics, social cultural context and crime-related aspects. In summary, these empirical findings underscore the pervasive existence of stereotypes across social dimensions, including gender, race, and religion, which not only validate the effectiveness of our proposed approach, but also emphasize the critical necessity of addressing potential ethical risks in the burgeoning realm of AIGC. As AIGC continues its rapid expansion trajectory, with new models and plugins emerging daily in staggering numbers, the challenge lies in the timely detection and mitigation of potential biases within these models.
Can large language models provide useful feedback on research papers? A large-scale empirical analysis
Oct 03, 2023



Abstract:Expert feedback lays the foundation of rigorous research. However, the rapid growth of scholarly production and intricate knowledge specialization challenge the conventional scientific feedback mechanisms. High-quality peer reviews are increasingly difficult to obtain. Researchers who are more junior or from under-resourced settings have especially hard times getting timely feedback. With the breakthrough of large language models (LLM) such as GPT-4, there is growing interest in using LLMs to generate scientific feedback on research manuscripts. However, the utility of LLM-generated feedback has not been systematically studied. To address this gap, we created an automated pipeline using GPT-4 to provide comments on the full PDFs of scientific papers. We evaluated the quality of GPT-4's feedback through two large-scale studies. We first quantitatively compared GPT-4's generated feedback with human peer reviewer feedback in 15 Nature family journals (3,096 papers in total) and the ICLR machine learning conference (1,709 papers). The overlap in the points raised by GPT-4 and by human reviewers (average overlap 30.85% for Nature journals, 39.23% for ICLR) is comparable to the overlap between two human reviewers (average overlap 28.58% for Nature journals, 35.25% for ICLR). The overlap between GPT-4 and human reviewers is larger for the weaker papers. We then conducted a prospective user study with 308 researchers from 110 US institutions in the field of AI and computational biology to understand how researchers perceive feedback generated by our GPT-4 system on their own papers. Overall, more than half (57.4%) of the users found GPT-4 generated feedback helpful/very helpful and 82.4% found it more beneficial than feedback from at least some human reviewers. While our findings show that LLM-generated feedback can help researchers, we also identify several limitations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge