Yao Lai
Beyond GEMM-Centric NPUs: Enabling Efficient Diffusion LLM Sampling
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Large Language Models (dLLMs) introduce iterative denoising to enable parallel token generation, but their sampling phase displays fundamentally different characteristics compared to GEMM-centric transformer layers. Profiling on modern GPUs reveals that sampling can account for up to 70% of total model inference latency-primarily due to substantial memory loads and writes from vocabulary-wide logits, reduction-based token selection, and iterative masked updates. These processes demand large on-chip SRAM and involve irregular memory accesses that conventional NPUs struggle to handle efficiently. To address this, we identify a set of critical instructions that an NPU architecture must specifically optimize for dLLM sampling. Our design employs lightweight non-GEMM vector primitives, in-place memory reuse strategies, and a decoupled mixed-precision memory hierarchy. Together, these optimizations deliver up to a 2.53x speedup over the NVIDIA RTX A6000 GPU under an equivalent nm technology node. We also open-source our cycle-accurate simulation and post-synthesis RTL verification code, confirming functional equivalence with current dLLM PyTorch implementations.
Re$^{\text{2}}$MaP: Macro Placement by Recursively Prototyping and Packing Tree-based Relocating
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:This work introduces the Re$^{\text{2}}$MaP method, which generates expert-quality macro placements through recursively prototyping and packing tree-based relocating. We first perform multi-level macro grouping and PPA-aware cell clustering to produce a unified connection matrix that captures both wirelength and dataflow among macros and clusters. Next, we use DREAMPlace to build a mixed-size placement prototype and obtain reference positions for each macro and cluster. Based on this prototype, we introduce ABPlace, an angle-based analytical method that optimizes macro positions on an ellipse to distribute macros uniformly near chip periphery, while optimizing wirelength and dataflow. A packing tree-based relocating procedure is then designed to jointly adjust the locations of macro groups and the macros within each group, by optimizing an expertise-inspired cost function that captures various design constraints through evolutionary search. Re$^{\text{2}}$MaP repeats the above process: Only a subset of macro groups are positioned in each iteration, and the remaining macros are deferred to the next iteration to improve the prototype's accuracy. Using a well-established backend flow with sufficient timing optimizations, Re$^{\text{2}}$MaP achieves up to 22.22% (average 10.26%) improvement in worst negative slack (WNS) and up to 97.91% (average 33.97%) improvement in total negative slack (TNS) compared to the state-of-the-art academic placer Hier-RTLMP. It also ranks higher on WNS, TNS, power, design rule check (DRC) violations, and runtime than the conference version ReMaP, across seven tested cases. Our code is available at https://github.com/lamda-bbo/Re2MaP.
FUDOKI: Discrete Flow-based Unified Understanding and Generation via Kinetic-Optimal Velocities
May 26, 2025Abstract:The rapid progress of large language models (LLMs) has catalyzed the emergence of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) that unify visual understanding and image generation within a single framework. However, most existing MLLMs rely on autoregressive (AR) architectures, which impose inherent limitations on future development, such as the raster-scan order in image generation and restricted reasoning abilities in causal context modeling. In this work, we challenge the dominance of AR-based approaches by introducing FUDOKI, a unified multimodal model purely based on discrete flow matching, as an alternative to conventional AR paradigms. By leveraging metric-induced probability paths with kinetic optimal velocities, our framework goes beyond the previous masking-based corruption process, enabling iterative refinement with self-correction capability and richer bidirectional context integration during generation. To mitigate the high cost of training from scratch, we initialize FUDOKI from pre-trained AR-based MLLMs and adaptively transition to the discrete flow matching paradigm. Experimental results show that FUDOKI achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art AR-based MLLMs across both visual understanding and image generation tasks, highlighting its potential as a foundation for next-generation unified multimodal models. Furthermore, we show that applying test-time scaling techniques to FUDOKI yields significant performance gains, further underscoring its promise for future enhancement through reinforcement learning.
INSIGHT: Universal Neural Simulator for Analog Circuits Harnessing Autoregressive Transformers
Jul 10, 2024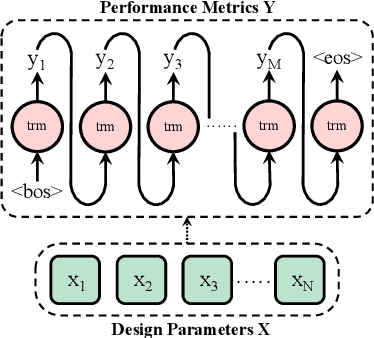



Abstract:Analog front-end design heavily relies on specialized human expertise and costly trial-and-error simulations, which motivated many prior works on analog design automation. However, efficient and effective exploration of the vast and complex design space remains constrained by the time-consuming nature of CPU-based SPICE simulations, making effective design automation a challenging endeavor. In this paper, we introduce INSIGHT, a GPU-powered, technology-independent, effective universal neural simulator in the analog front-end design automation loop. INSIGHT accurately predicts the performance metrics of analog circuits across various technology nodes, significantly reducing inference time. Notably, its autoregressive capabilities enable INSIGHT to accurately predict simulation-costly critical transient specifications leveraging less expensive performance metric information. The low cost and high fidelity feature make INSIGHT a good substitute for standard simulators in analog front-end optimization frameworks. INSIGHT is compatible with any optimization framework, facilitating enhanced design space exploration for sample efficiency through sophisticated offline learning and adaptation techniques. Our experiments demonstrate that INSIGHT-M, a model-based batch reinforcement learning framework that leverages INSIGHT for analog sizing, achieves at least 50X improvement in sample efficiency across circuits. To the best of our knowledge, this marks the first use of autoregressive transformers in analog front-end design.
LLM-Enhanced Bayesian Optimization for Efficient Analog Layout Constraint Generation
Jun 07, 2024



Abstract:Analog layout synthesis faces significant challenges due to its dependence on manual processes, considerable time requirements, and performance instability. Current Bayesian Optimization (BO)-based techniques for analog layout synthesis, despite their potential for automation, suffer from slow convergence and extensive data needs, limiting their practical application. This paper presents the \texttt{LLANA} framework, a novel approach that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance BO by exploiting the few-shot learning abilities of LLMs for more efficient generation of analog design-dependent parameter constraints. Experimental results demonstrate that \texttt{LLANA} not only achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art (SOTA) BO methods but also enables a more effective exploration of the analog circuit design space, thanks to LLM's superior contextual understanding and learning efficiency. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/dekura/LLANA}.
AnalogCoder: Analog Circuit Design via Training-Free Code Generation
May 23, 2024



Abstract:Analog circuit design is a significant task in modern chip technology, focusing on the selection of component types, connectivity, and parameters to ensure proper circuit functionality. Despite advances made by Large Language Models (LLMs) in digital circuit design, the complexity and scarcity of data in analog circuitry pose significant challenges. To mitigate these issues, we introduce AnalogCoder, the first training-free LLM agent for designing analog circuits through Python code generation. Firstly, AnalogCoder incorporates a feedback-enhanced flow with tailored domain-specific prompts, enabling the automated and self-correcting design of analog circuits with a high success rate. Secondly, it proposes a circuit tool library to archive successful designs as reusable modular sub-circuits, simplifying composite circuit creation. Thirdly, extensive experiments on a benchmark designed to cover a wide range of analog circuit tasks show that AnalogCoder outperforms other LLM-based methods. It has successfully designed 20 circuits, 5 more than standard GPT-4o. We believe AnalogCoder can significantly improve the labor-intensive chip design process, enabling non-experts to design analog circuits efficiently. Codes and the benchmark are provided at https://github.com/anonyanalog/AnalogCoder.
Scalable and Effective Arithmetic Tree Generation for Adder and Multiplier Designs
May 10, 2024



Abstract:Across a wide range of hardware scenarios, the computational efficiency and physical size of the arithmetic units significantly influence the speed and footprint of the overall hardware system. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of prior arithmetic design techniques proves inadequate, as it does not sufficiently optimize speed and area, resulting in a reduced processing rate and larger module size. To boost the arithmetic performance, in this work, we focus on the two most common and fundamental arithmetic modules: adders and multipliers. We cast the design tasks as single-player tree generation games, leveraging reinforcement learning techniques to optimize their arithmetic tree structures. Such a tree generation formulation allows us to efficiently navigate the vast search space and discover superior arithmetic designs that improve computational efficiency and hardware size within just a few hours. For adders, our approach discovers designs of 128-bit adders that achieve Pareto optimality in theoretical metrics. Compared with the state-of-the-art PrefixRL, our method decreases computational delay and hardware size by up to 26% and 30%, respectively. For multipliers, when compared to RL-MUL, our approach increases speed and reduces size by as much as 49% and 45%. Moreover, the inherent flexibility and scalability of our method enable us to deploy our designs into cutting-edge technologies, as we show that they can be seamlessly integrated into 7nm technology. We believe our work will offer valuable insights into hardware design, further accelerating speed and reducing size through the refined search space and our tree generation methodologies. See our introduction video at https://bit.ly/ArithmeticTree. Codes are released at https://github.com/laiyao1/ArithmeticTree.
ChiPFormer: Transferable Chip Placement via Offline Decision Transformer
Jun 26, 2023Abstract:Placement is a critical step in modern chip design, aiming to determine the positions of circuit modules on the chip canvas. Recent works have shown that reinforcement learning (RL) can improve human performance in chip placement. However, such an RL-based approach suffers from long training time and low transfer ability in unseen chip circuits. To resolve these challenges, we cast the chip placement as an offline RL formulation and present ChiPFormer that enables learning a transferable placement policy from fixed offline data. ChiPFormer has several advantages that prior arts do not have. First, ChiPFormer can exploit offline placement designs to learn transferable policies more efficiently in a multi-task setting. Second, ChiPFormer can promote effective finetuning for unseen chip circuits, reducing the placement runtime from hours to minutes. Third, extensive experiments on 32 chip circuits demonstrate that ChiPFormer achieves significantly better placement quality while reducing the runtime by 10x compared to recent state-of-the-art approaches in both public benchmarks and realistic industrial tasks. The deliverables are released at https://sites.google.com/view/chipformer/home.
MaskPlace: Fast Chip Placement via Reinforced Visual Representation Learning
Nov 24, 2022Abstract:Placement is an essential task in modern chip design, aiming at placing millions of circuit modules on a 2D chip canvas. Unlike the human-centric solution, which requires months of intense effort by hardware engineers to produce a layout to minimize delay and energy consumption, deep reinforcement learning has become an emerging autonomous tool. However, the learning-centric method is still in its early stage, impeded by a massive design space of size ten to the order of a few thousand. This work presents MaskPlace to automatically generate a valid chip layout design within a few hours, whose performance can be superior or comparable to recent advanced approaches. It has several appealing benefits that prior arts do not have. Firstly, MaskPlace recasts placement as a problem of learning pixel-level visual representation to comprehensively describe millions of modules on a chip, enabling placement in a high-resolution canvas and a large action space. It outperforms recent methods that represent a chip as a hypergraph. Secondly, it enables training the policy network by an intuitive reward function with dense reward, rather than a complicated reward function with sparse reward from previous methods. Thirdly, extensive experiments on many public benchmarks show that MaskPlace outperforms existing RL approaches in all key performance metrics, including wirelength, congestion, and density. For example, it achieves 60%-90% wirelength reduction and guarantees zero overlaps. We believe MaskPlace can improve AI-assisted chip layout design. The deliverables are released at https://laiyao1.github.io/maskplace.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge