Yang Tao
Enhanced Structured State Space Models via Grouped FIR Filtering and Attention Sink Mechanisms
Aug 01, 2024Abstract:Structured State Space Models (SSMs) have emerged as compelling alternatives to Transformer architectures, offering linear-time complexity and superior performance in various sequence modeling tasks. Despite their advantages, SSMs like the original Mamba-2 face training difficulties due to the sensitivities introduced by the extended series of recurrent matrix multiplications. In this paper, we propose an advanced architecture that mitigates these challenges by decomposing A-multiplications into multiple groups and optimizing positional encoding through Grouped Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filtering. This new structure, denoted as Grouped FIR-enhanced SSM (GFSSM), employs semiseparable matrices for efficient computation. Furthermore, inspired by the "attention sink" phenomenon identified in streaming language models, we incorporate a similar mechanism to enhance the stability and performance of our model over extended sequences. Our approach further bridges the gap between SSMs and Transformer architectures, offering a viable path forward for scalable and high-performing sequence modeling.
Few-Shot Image Classification and Segmentation as Visual Question Answering Using Vision-Language Models
Mar 15, 2024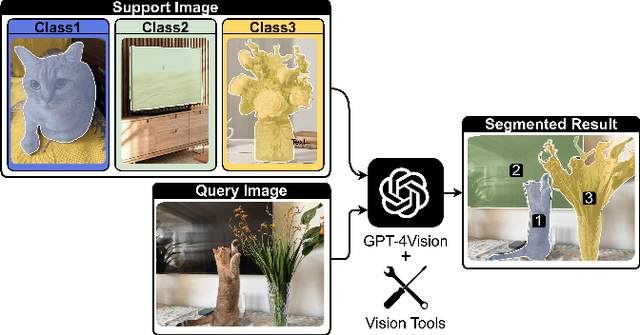
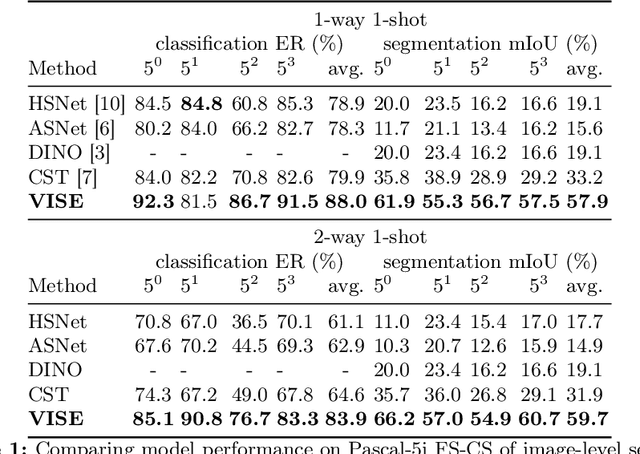
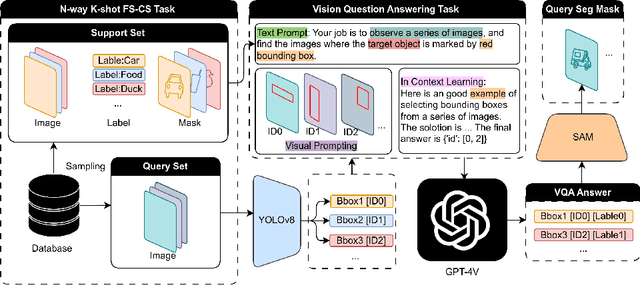
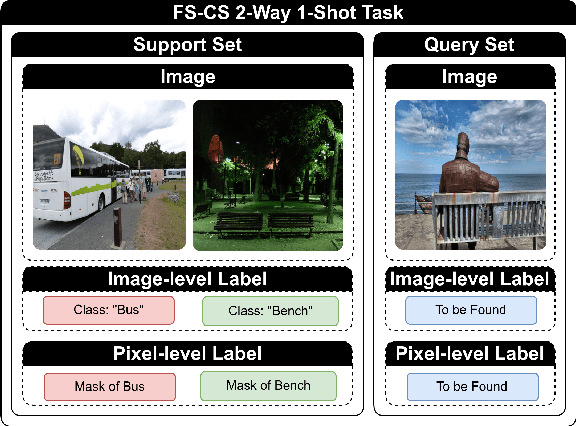
Abstract:The task of few-shot image classification and segmentation (FS-CS) involves classifying and segmenting target objects in a query image, given only a few examples of the target classes. We introduce the Vision-Instructed Segmentation and Evaluation (VISE) method that transforms the FS-CS problem into the Visual Question Answering (VQA) problem, utilising Vision-Language Models (VLMs), and addresses it in a training-free manner. By enabling a VLM to interact with off-the-shelf vision models as tools, the proposed method is capable of classifying and segmenting target objects using only image-level labels. Specifically, chain-of-thought prompting and in-context learning guide the VLM to answer multiple-choice questions like a human; vision models such as YOLO and Segment Anything Model (SAM) assist the VLM in completing the task. The modular framework of the proposed method makes it easily extendable. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Pascal-5i and COCO-20i datasets.
Few-Shot Classification & Segmentation Using Large Language Models Agent
Nov 19, 2023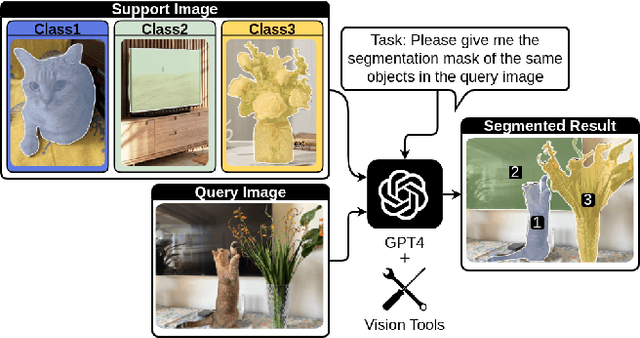
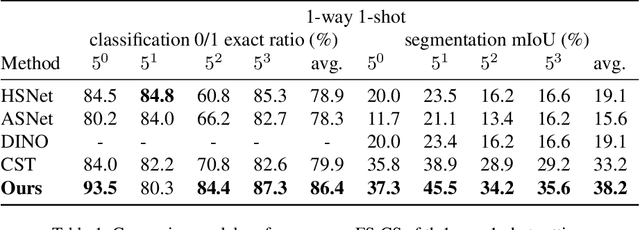
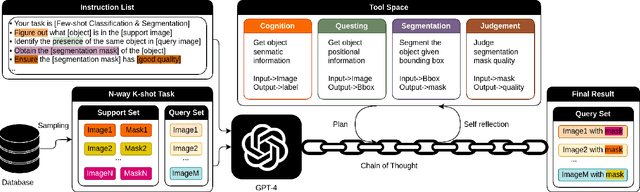
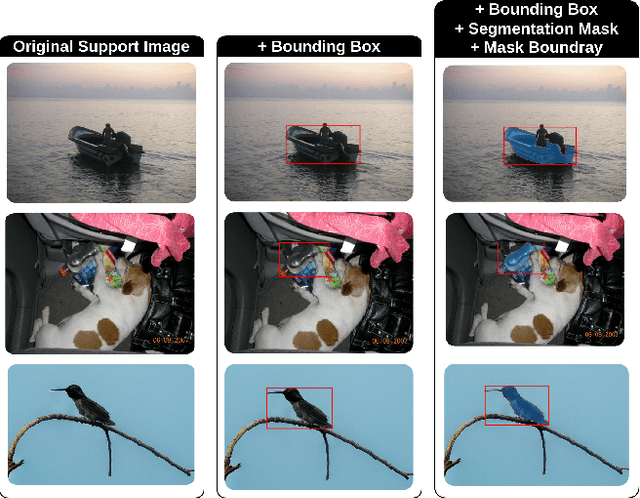
Abstract:The task of few-shot image classification and segmentation (FS-CS) requires the classification and segmentation of target objects in a query image, given only a few examples of the target classes. We introduce a method that utilises large language models (LLM) as an agent to address the FS-CS problem in a training-free manner. By making the LLM the task planner and off-the-shelf vision models the tools, the proposed method is capable of classifying and segmenting target objects using only image-level labels. Specifically, chain-of-thought prompting and in-context learning guide the LLM to observe support images like human; vision models such as Segment Anything Model (SAM) and GPT-4Vision assist LLM understand spatial and semantic information at the same time. Ultimately, the LLM uses its summarizing and reasoning capabilities to classify and segment the query image. The proposed method's modular framework makes it easily extendable. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Pascal-5i dataset.
MEMO: Dataset and Methods for Robust Multimodal Retinal Image Registration with Large or Small Vessel Density Differences
Sep 25, 2023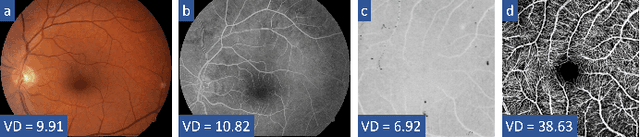
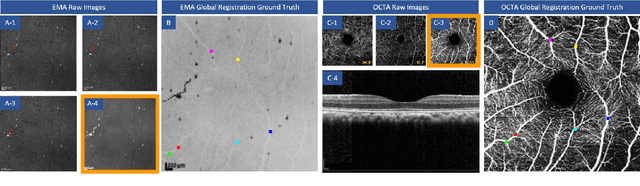
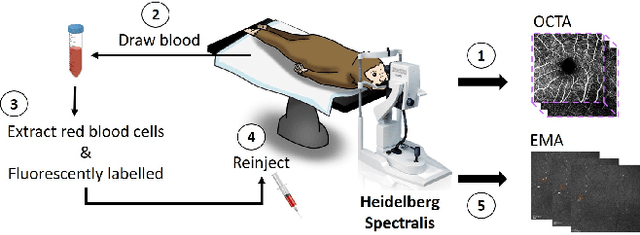
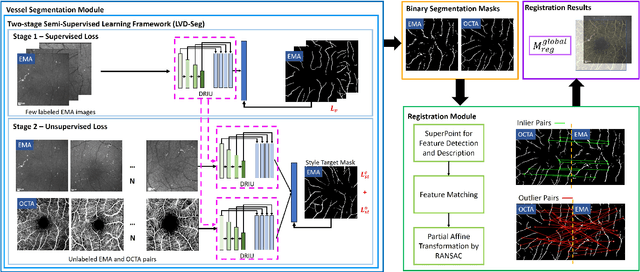
Abstract:The measurement of retinal blood flow (RBF) in capillaries can provide a powerful biomarker for the early diagnosis and treatment of ocular diseases. However, no single modality can determine capillary flowrates with high precision. Combining erythrocyte-mediated angiography (EMA) with optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) has the potential to achieve this goal, as EMA can measure the absolute 2D RBF of retinal microvasculature and OCTA can provide the 3D structural images of capillaries. However, multimodal retinal image registration between these two modalities remains largely unexplored. To fill this gap, we establish MEMO, the first public multimodal EMA and OCTA retinal image dataset. A unique challenge in multimodal retinal image registration between these modalities is the relatively large difference in vessel density (VD). To address this challenge, we propose a segmentation-based deep-learning framework (VDD-Reg) and a new evaluation metric (MSD), which provide robust results despite differences in vessel density. VDD-Reg consists of a vessel segmentation module and a registration module. To train the vessel segmentation module, we further designed a two-stage semi-supervised learning framework (LVD-Seg) combining supervised and unsupervised losses. We demonstrate that VDD-Reg outperforms baseline methods quantitatively and qualitatively for cases of both small VD differences (using the CF-FA dataset) and large VD differences (using our MEMO dataset). Moreover, VDD-Reg requires as few as three annotated vessel segmentation masks to maintain its accuracy, demonstrating its feasibility.
Detecting and Counting Oysters
May 20, 2021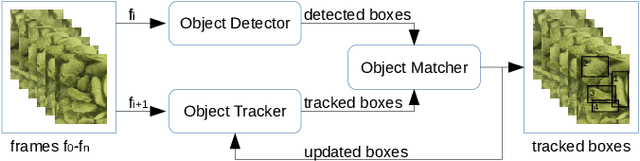
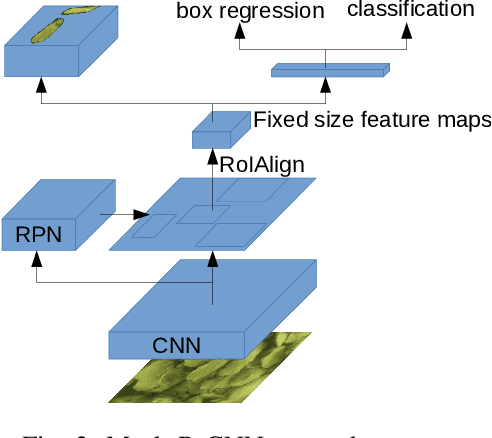
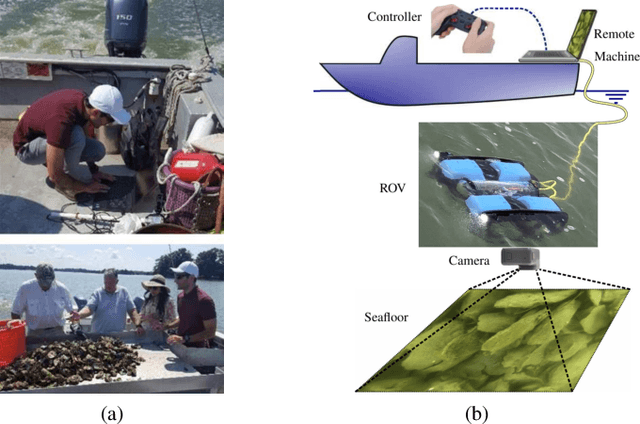
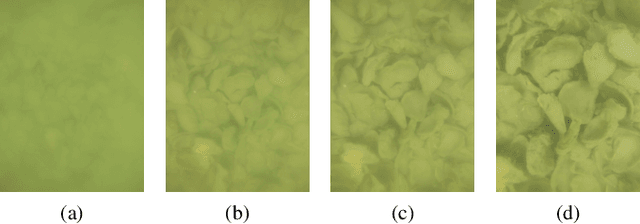
Abstract:Oysters are an essential species in the Chesapeake Bay living ecosystem. Oysters are filter feeders and considered the vacuum cleaners of the Chesapeake Bay that can considerably improve the Bay's water quality. Many oyster restoration programs have been initiated in the past decades and continued to date. Advancements in robotics and artificial intelligence have opened new opportunities for aquaculture. Drone-like ROVs with high maneuverability are getting more affordable and, if equipped with proper sensory devices, can monitor the oysters. This work presents our efforts for videography of the Chesapeake bay bottom using an ROV, constructing a database of oysters, implementing Mask R-CNN for detecting oysters, and counting their number in a video by tracking them.
Robust Reinforcement Learning for General Video Game Playing
Nov 11, 2020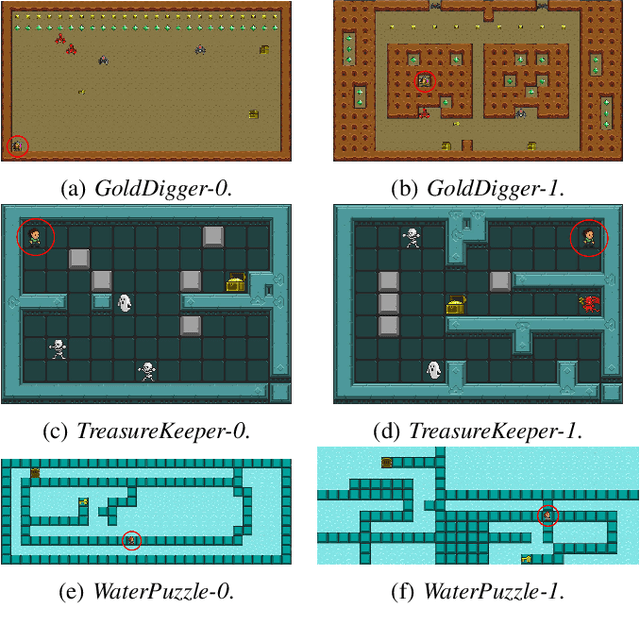
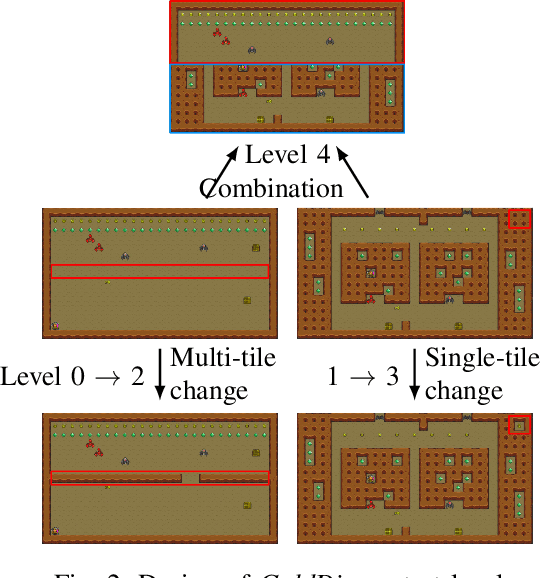
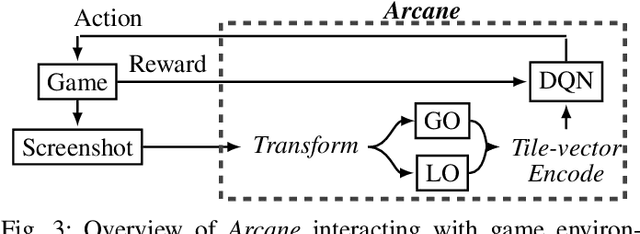
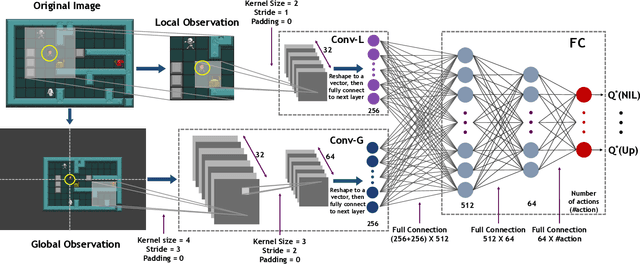
Abstract:Reinforcement learning has successfully learned to play challenging board and video games. However, its generalization ability remains under-explored. The General Video Game AI Learning Competition aims at designing agents that are capable of learning to play different games levels that were unseen during training. This paper presents the games, entries and results of the 2020 General Video Game AI Learning Competition, held at the Sixteenth International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving from Nature and the 2020 IEEE Conference on Games. Three new games with sparse, periodic and dense rewards, respectively, were designed for this competition and the test levels were generated by adding minor perturbations to training levels or combining training levels. In this paper, we also design a reinforcement learning agent, called Arcane, for general video game playing. We assume that it is more likely to observe similar local information in different levels rather than global information. Therefore, instead of directly inputting a single, raw pixel-based screenshot of current game screen, Arcane takes the encoded, transformed global and local observations of the game screen as two simultaneous inputs, aiming at learning local information for playing new levels. Two versions of Arcane, using a stochastic or deterministic policy for decision-making during test, both show robust performance on the game set of the 2020 General Video Game AI Learning Competition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge