Yanan Xin
Counterfactual Explanations for Deep Learning-Based Traffic Forecasting
May 01, 2024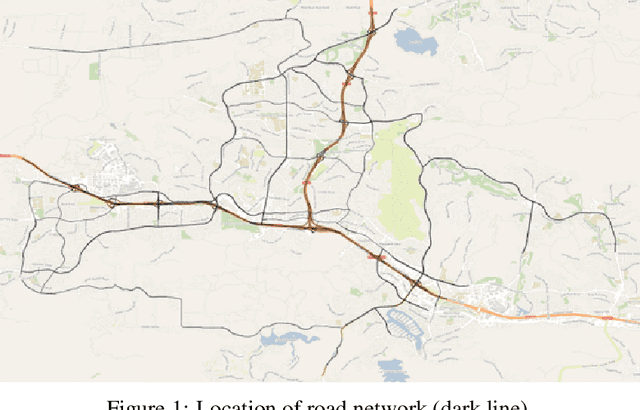
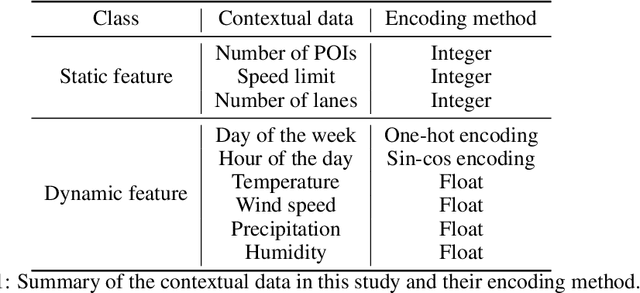
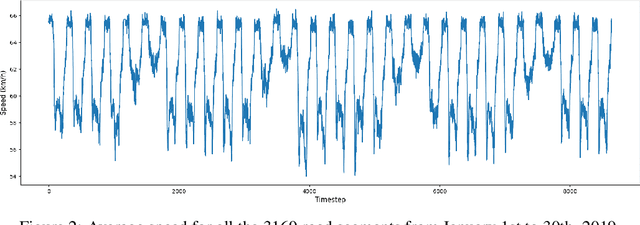
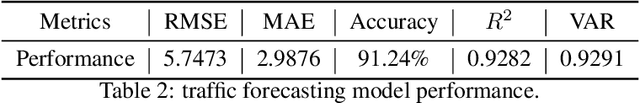
Abstract:Deep learning models are widely used in traffic forecasting and have achieved state-of-the-art prediction accuracy. However, the black-box nature of those models makes the results difficult to interpret by users. This study aims to leverage an Explainable AI approach, counterfactual explanations, to enhance the explainability and usability of deep learning-based traffic forecasting models. Specifically, the goal is to elucidate relationships between various input contextual features and their corresponding predictions. We present a comprehensive framework that generates counterfactual explanations for traffic forecasting and provides usable insights through the proposed scenario-driven counterfactual explanations. The study first implements a deep learning model to predict traffic speed based on historical traffic data and contextual variables. Counterfactual explanations are then used to illuminate how alterations in these input variables affect predicted outcomes, thereby enhancing the transparency of the deep learning model. We investigated the impact of contextual features on traffic speed prediction under varying spatial and temporal conditions. The scenario-driven counterfactual explanations integrate two types of user-defined constraints, directional and weighting constraints, to tailor the search for counterfactual explanations to specific use cases. These tailored explanations benefit machine learning practitioners who aim to understand the model's learning mechanisms and domain experts who seek insights for real-world applications. The results showcase the effectiveness of counterfactual explanations in revealing traffic patterns learned by deep learning models, showing its potential for interpreting black-box deep learning models used for spatiotemporal predictions in general.
Revealing behavioral impact on mobility prediction networks through causal interventions
Nov 20, 2023Abstract:Deep neural networks are increasingly utilized in mobility prediction tasks, yet their intricate internal workings pose challenges for interpretability, especially in comprehending how various aspects of mobility behavior affect predictions. In this study, we introduce a causal intervention framework to assess the impact of mobility-related factors on neural networks designed for next location prediction -- a task focusing on predicting the immediate next location of an individual. To achieve this, we employ individual mobility models to generate synthetic location visit sequences and control behavior dynamics by intervening in their data generation process. We evaluate the interventional location sequences using mobility metrics and input them into well-trained networks to analyze performance variations. The results demonstrate the effectiveness in producing location sequences with distinct mobility behaviors, thus facilitating the simulation of diverse spatial and temporal changes. These changes result in performance fluctuations in next location prediction networks, revealing impacts of critical mobility behavior factors, including sequential patterns in location transitions, proclivity for exploring new locations, and preferences in location choices at population and individual levels. The gained insights hold significant value for the real-world application of mobility prediction networks, and the framework is expected to promote the use of causal inference for enhancing the interpretability and robustness of neural networks in mobility applications.
Uncertainty quantification and out-of-distribution detection using surjective normalizing flows
Nov 01, 2023



Abstract:Reliable quantification of epistemic and aleatoric uncertainty is of crucial importance in applications where models are trained in one environment but applied to multiple different environments, often seen in real-world applications for example, in climate science or mobility analysis. We propose a simple approach using surjective normalizing flows to identify out-of-distribution data sets in deep neural network models that can be computed in a single forward pass. The method builds on recent developments in deep uncertainty quantification and generative modeling with normalizing flows. We apply our method to a synthetic data set that has been simulated using a mechanistic model from the mobility literature and several data sets simulated from interventional distributions induced by soft and atomic interventions on that model, and demonstrate that our method can reliably discern out-of-distribution data from in-distribution data. We compare the surjective flow model to a Dirichlet process mixture model and a bijective flow and find that the surjections are a crucial component to reliably distinguish in-distribution from out-of-distribution data.
Spatially-Aware Car-Sharing Demand Prediction
Mar 25, 2023Abstract:In recent years, car-sharing services have emerged as viable alternatives to private individual mobility, promising more sustainable and resource-efficient, but still comfortable transportation. Research on short-term prediction and optimization methods has improved operations and fleet control of car-sharing services; however, long-term projections and spatial analysis are sparse in the literature. We propose to analyze the average monthly demand in a station-based car-sharing service with spatially-aware learning algorithms that offer high predictive performance as well as interpretability. In particular, we compare the spatially-implicit Random Forest model with spatially-aware methods for predicting average monthly per-station demand. The study utilizes a rich set of socio-demographic, location-based (e.g., POIs), and car-sharing-specific features as input, extracted from a large proprietary car-sharing dataset and publicly available datasets. We show that the global Random Forest model with geo-coordinates as an input feature achieves the highest predictive performance with an R-squared score of 0.87, while local methods such as Geographically Weighted Regression perform almost on par and additionally yield exciting insights into the heterogeneous spatial distributions of factors influencing car-sharing behaviour. Additionally, our study offers effective as well as highly interpretable methods for diagnosing and planning the placement of car-sharing stations.
Metropolitan Segment Traffic Speeds from Massive Floating Car Data in 10 Cities
Feb 17, 2023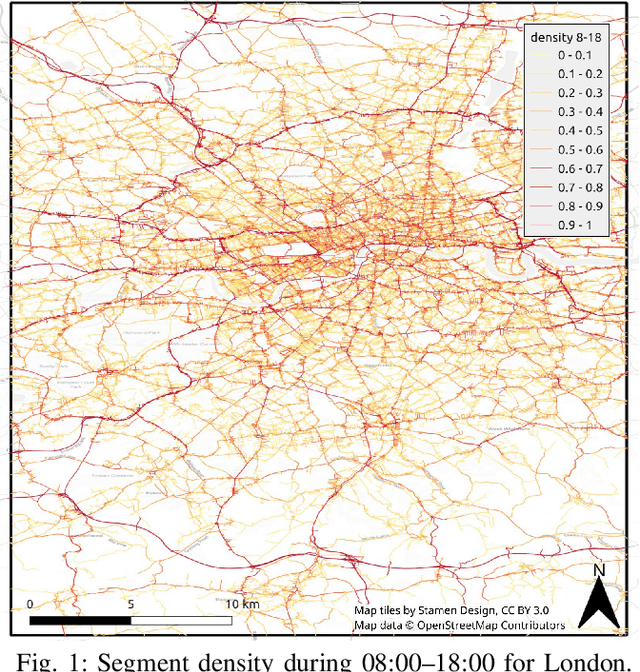
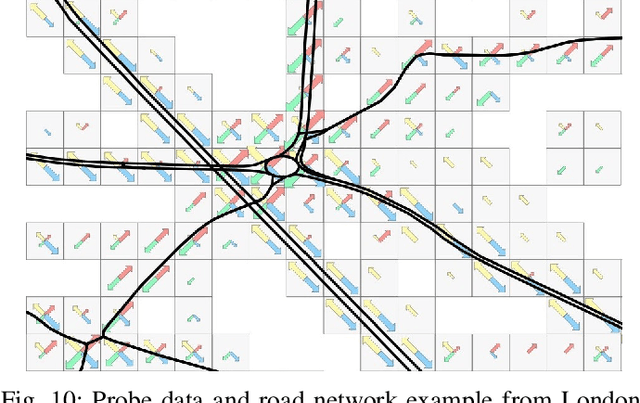
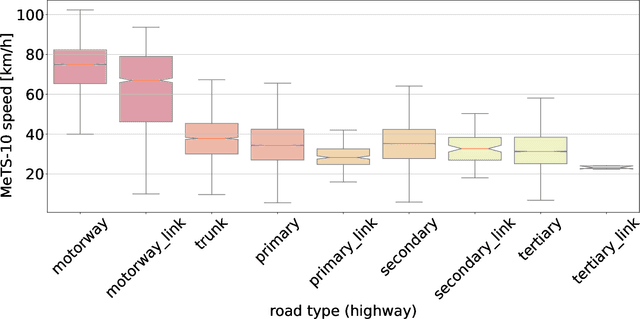
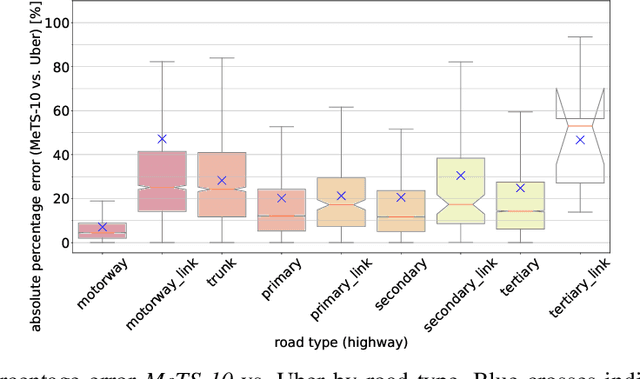
Abstract:Traffic analysis is crucial for urban operations and planning, while the availability of dense urban traffic data beyond loop detectors is still scarce. We present a large-scale floating vehicle dataset of per-street segment traffic information, Metropolitan Segment Traffic Speeds from Massive Floating Car Data in 10 Cities (MeTS-10), available for 10 global cities with a 15-minute resolution for collection periods ranging between 108 and 361 days in 2019-2021 and covering more than 1500 square kilometers per metropolitan area. MeTS-10 features traffic speed information at all street levels from main arterials to local streets for Antwerp, Bangkok, Barcelona, Berlin, Chicago, Istanbul, London, Madrid, Melbourne and Moscow. The dataset leverages the industrial-scale floating vehicle Traffic4cast data with speeds and vehicle counts provided in a privacy-preserving spatio-temporal aggregation. We detail the efficient matching approach mapping the data to the OpenStreetMap road graph. We evaluate the dataset by comparing it with publicly available stationary vehicle detector data (for Berlin, London, and Madrid) and the Uber traffic speed dataset (for Barcelona, Berlin, and London). The comparison highlights the differences across datasets in spatio-temporal coverage and variations in the reported traffic caused by the binning method. MeTS-10 enables novel, city-wide analysis of mobility and traffic patterns for ten major world cities, overcoming current limitations of spatially sparse vehicle detector data. The large spatial and temporal coverage offers an opportunity for joining the MeTS-10 with other datasets, such as traffic surveys in traffic planning studies or vehicle detector data in traffic control settings.
Vision Paper: Causal Inference for Interpretable and Robust Machine Learning in Mobility Analysis
Oct 18, 2022Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing many areas of our lives, leading a new era of technological advancement. Particularly, the transportation sector would benefit from the progress in AI and advance the development of intelligent transportation systems. Building intelligent transportation systems requires an intricate combination of artificial intelligence and mobility analysis. The past few years have seen rapid development in transportation applications using advanced deep neural networks. However, such deep neural networks are difficult to interpret and lack robustness, which slows the deployment of these AI-powered algorithms in practice. To improve their usability, increasing research efforts have been devoted to developing interpretable and robust machine learning methods, among which the causal inference approach recently gained traction as it provides interpretable and actionable information. Moreover, most of these methods are developed for image or sequential data which do not satisfy specific requirements of mobility data analysis. This vision paper emphasizes research challenges in deep learning-based mobility analysis that require interpretability and robustness, summarizes recent developments in using causal inference for improving the interpretability and robustness of machine learning methods, and highlights opportunities in developing causally-enabled machine learning models tailored for mobility analysis. This research direction will make AI in the transportation sector more interpretable and reliable, thus contributing to safer, more efficient, and more sustainable future transportation systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge