Xugang Lu
Combining Deterministic Enhanced Conditions with Dual-Streaming Encoding for Diffusion-Based Speech Enhancement
May 20, 2025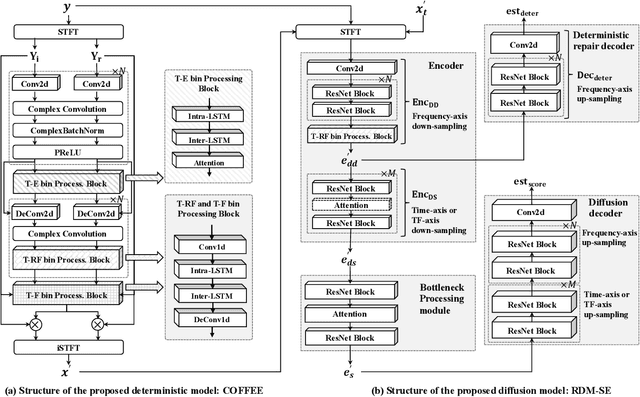
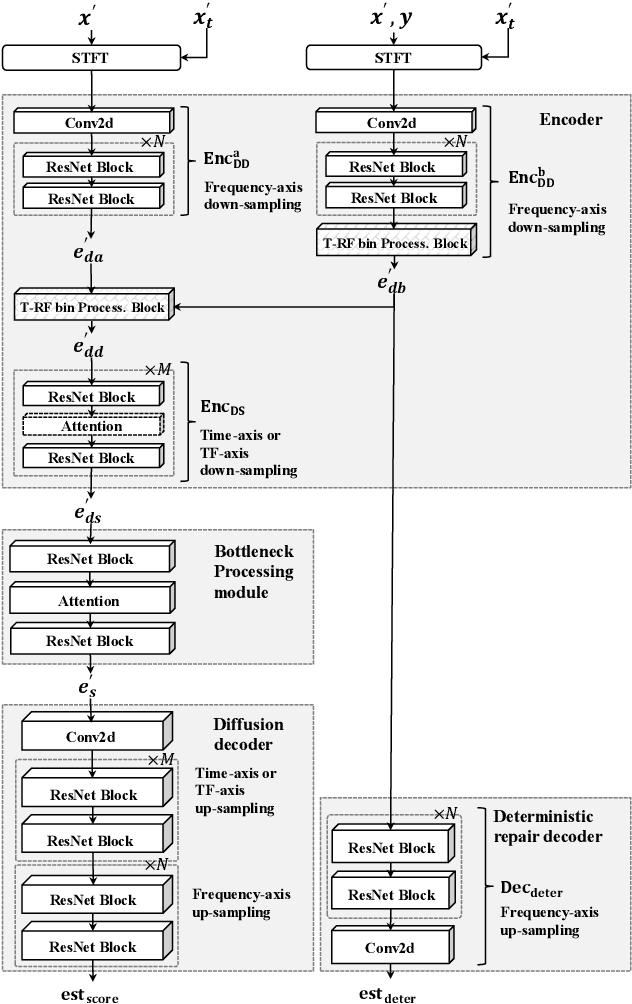
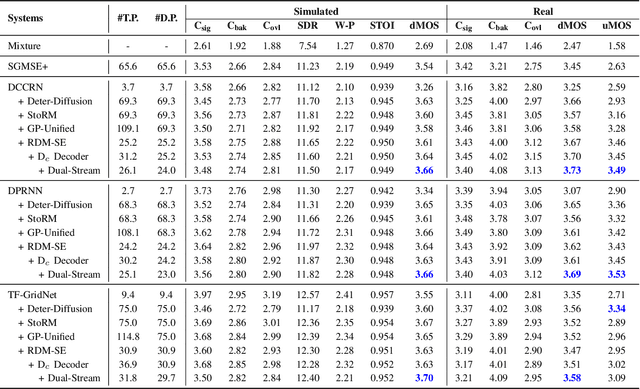
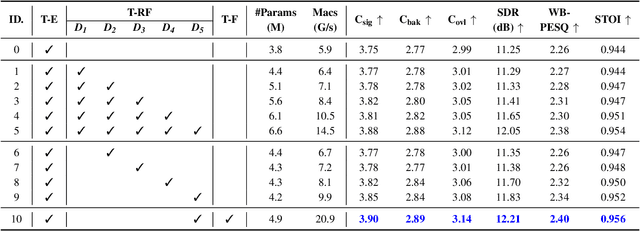
Abstract:Diffusion-based speech enhancement (SE) models need to incorporate correct prior knowledge as reliable conditions to generate accurate predictions. However, providing reliable conditions using noisy features is challenging. One solution is to use features enhanced by deterministic methods as conditions. However, the information distortion and loss caused by deterministic methods might affect the diffusion process. In this paper, we first investigate the effects of using different deterministic SE models as conditions for diffusion. We validate two conditions depending on whether the noisy feature was used as part of the condition: one using only the deterministic feature (deterministic-only), and the other using both deterministic and noisy features (deterministic-noisy). Preliminary investigation found that using deterministic enhanced conditions improves hearing experiences on real data, while the choice between using deterministic-only or deterministic-noisy conditions depends on the deterministic models. Based on these findings, we propose a dual-streaming encoding Repair-Diffusion Model for SE (DERDM-SE) to more effectively utilize both conditions. Moreover, we found that fine-grained deterministic models have greater potential in objective evaluation metrics, while UNet-based deterministic models provide more stable diffusion performance. Therefore, in the DERDM-SE, we propose a deterministic model that combines coarse- and fine-grained processing. Experimental results on CHiME4 show that the proposed models effectively leverage deterministic models to achieve better SE evaluation scores, along with more stable performance compared to other diffusion-based SE models.
Cross-modal Knowledge Transfer Learning as Graph Matching Based on Optimal Transport for ASR
May 19, 2025Abstract:Transferring linguistic knowledge from a pretrained language model (PLM) to acoustic feature learning has proven effective in enhancing end-to-end automatic speech recognition (E2E-ASR). However, aligning representations between linguistic and acoustic modalities remains a challenge due to inherent modality gaps. Optimal transport (OT) has shown promise in mitigating these gaps by minimizing the Wasserstein distance (WD) between linguistic and acoustic feature distributions. However, previous OT-based methods overlook structural relationships, treating feature vectors as unordered sets. To address this, we propose Graph Matching Optimal Transport (GM-OT), which models linguistic and acoustic sequences as structured graphs. Nodes represent feature embeddings, while edges capture temporal and sequential relationships. GM-OT minimizes both WD (between nodes) and Gromov-Wasserstein distance (GWD) (between edges), leading to a fused Gromov-Wasserstein distance (FGWD) formulation. This enables structured alignment and more efficient knowledge transfer compared to existing OT-based approaches. Theoretical analysis further shows that prior OT-based methods in linguistic knowledge transfer can be viewed as a special case within our GM-OT framework. We evaluate GM-OT on Mandarin ASR using a CTC-based E2E-ASR system with a PLM for knowledge transfer. Experimental results demonstrate significant performance gains over state-of-the-art models, validating the effectiveness of our approach.
Linguistic Knowledge Transfer Learning for Speech Enhancement
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Linguistic knowledge plays a crucial role in spoken language comprehension. It provides essential semantic and syntactic context for speech perception in noisy environments. However, most speech enhancement (SE) methods predominantly rely on acoustic features to learn the mapping relationship between noisy and clean speech, with limited exploration of linguistic integration. While text-informed SE approaches have been investigated, they often require explicit speech-text alignment or externally provided textual data, constraining their practicality in real-world scenarios. Additionally, using text as input poses challenges in aligning linguistic and acoustic representations due to their inherent differences. In this study, we propose the Cross-Modality Knowledge Transfer (CMKT) learning framework, which leverages pre-trained large language models (LLMs) to infuse linguistic knowledge into SE models without requiring text input or LLMs during inference. Furthermore, we introduce a misalignment strategy to improve knowledge transfer. This strategy applies controlled temporal shifts, encouraging the model to learn more robust representations. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that CMKT consistently outperforms baseline models across various SE architectures and LLM embeddings, highlighting its adaptability to different configurations. Additionally, results on Mandarin and English datasets confirm its effectiveness across diverse linguistic conditions, further validating its robustness. Moreover, CMKT remains effective even in scenarios without textual data, underscoring its practicality for real-world applications. By bridging the gap between linguistic and acoustic modalities, CMKT offers a scalable and innovative solution for integrating linguistic knowledge into SE models, leading to substantial improvements in both intelligibility and enhancement performance.
Retrieval-Augmented Speech Recognition Approach for Domain Challenges
Feb 21, 2025



Abstract:Speech recognition systems often face challenges due to domain mismatch, particularly in real-world applications where domain-specific data is unavailable because of data accessibility and confidentiality constraints. Inspired by Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) techniques for large language models (LLMs), this paper introduces a LLM-based retrieval-augmented speech recognition method that incorporates domain-specific textual data at the inference stage to enhance recognition performance. Rather than relying on domain-specific textual data during the training phase, our model is trained to learn how to utilize textual information provided in prompts for LLM decoder to improve speech recognition performance. Benefiting from the advantages of the RAG retrieval mechanism, our approach efficiently accesses locally available domain-specific documents, ensuring a convenient and effective process for solving domain mismatch problems. Experiments conducted on the CSJ database demonstrate that the proposed method significantly improves speech recognition accuracy and achieves state-of-the-art results on the CSJ dataset, even without relying on the full training data.
MECG-E: Mamba-based ECG Enhancer for Baseline Wander Removal
Sep 27, 2024Abstract:Electrocardiogram (ECG) is an important non-invasive method for diagnosing cardiovascular disease. However, ECG signals are susceptible to noise contamination, such as electrical interference or signal wandering, which reduces diagnostic accuracy. Various ECG denoising methods have been proposed, but most existing methods yield suboptimal performance under very noisy conditions or require several steps during inference, leading to latency during online processing. In this paper, we propose a novel ECG denoising model, namely Mamba-based ECG Enhancer (MECG-E), which leverages the Mamba architecture known for its fast inference and outstanding nonlinear mapping capabilities. Experimental results indicate that MECG-E surpasses several well-known existing models across multiple metrics under different noise conditions. Additionally, MECG-E requires less inference time than state-of-the-art diffusion-based ECG denoisers, demonstrating the model's functionality and efficiency.
Channel Adaptation for Speaker Verification Using Optimal Transport with Pseudo Label
Sep 14, 2024



Abstract:Domain gap often degrades the performance of speaker verification (SV) systems when the statistical distributions of training data and real-world test speech are mismatched. Channel variation, a primary factor causing this gap, is less addressed than other issues (e.g., noise). Although various domain adaptation algorithms could be applied to handle this domain gap problem, most algorithms could not take the complex distribution structure in domain alignment with discriminative learning. In this paper, we propose a novel unsupervised domain adaptation method, i.e., Joint Partial Optimal Transport with Pseudo Label (JPOT-PL), to alleviate the channel mismatch problem. Leveraging the geometric-aware distance metric of optimal transport in distribution alignment, we further design a pseudo label-based discriminative learning where the pseudo label can be regarded as a new type of soft speaker label derived from the optimal coupling. With the JPOT-PL, we carry out experiments on the SV channel adaptation task with VoxCeleb as the basis corpus. Experiments show our method reduces EER by over 10% compared with several state-of-the-art channel adaptation algorithms.
Integrated Multi-Level Knowledge Distillation for Enhanced Speaker Verification
Sep 14, 2024



Abstract:Knowledge distillation (KD) is widely used in audio tasks, such as speaker verification (SV), by transferring knowledge from a well-trained large model (the teacher) to a smaller, more compact model (the student) for efficiency and portability. Existing KD methods for SV often mirror those used in image processing, focusing on approximating predicted probabilities and hidden representations. However, these methods fail to account for the multi-level temporal properties of speech audio. In this paper, we propose a novel KD method, i.e., Integrated Multi-level Knowledge Distillation (IML-KD), to transfer knowledge of various temporal-scale features of speech from a teacher model to a student model. In the IML-KD, temporal context information from the teacher model is integrated into novel Integrated Gradient-based input-sensitive representations from speech segments with various durations, and the student model is trained to infer these representations with multi-level alignment for the output. We conduct SV experiments on the VoxCeleb1 dataset to evaluate the proposed method. Experimental results demonstrate that IML-KD significantly enhances KD performance, reducing the Equal Error Rate (EER) by 5%.
Temporal Order Preserved Optimal Transport-based Cross-modal Knowledge Transfer Learning for ASR
Sep 03, 2024


Abstract:Transferring linguistic knowledge from a pretrained language model (PLM) to an acoustic model has been shown to greatly improve the performance of automatic speech recognition (ASR). However, due to the heterogeneous feature distributions in cross-modalities, designing an effective model for feature alignment and knowledge transfer between linguistic and acoustic sequences remains a challenging task. Optimal transport (OT), which efficiently measures probability distribution discrepancies, holds great potential for aligning and transferring knowledge between acoustic and linguistic modalities. Nonetheless, the original OT treats acoustic and linguistic feature sequences as two unordered sets in alignment and neglects temporal order information during OT coupling estimation. Consequently, a time-consuming pretraining stage is required to learn a good alignment between the acoustic and linguistic representations. In this paper, we propose a Temporal Order Preserved OT (TOT)-based Cross-modal Alignment and Knowledge Transfer (CAKT) (TOT-CAKT) for ASR. In the TOT-CAKT, local neighboring frames of acoustic sequences are smoothly mapped to neighboring regions of linguistic sequences, preserving their temporal order relationship in feature alignment and matching. With the TOT-CAKT model framework, we conduct Mandarin ASR experiments with a pretrained Chinese PLM for linguistic knowledge transfer. Our results demonstrate that the proposed TOT-CAKT significantly improves ASR performance compared to several state-of-the-art models employing linguistic knowledge transfer, and addresses the weaknesses of the original OT-based method in sequential feature alignment for ASR.
Robust Channel Learning for Large-Scale Radio Speaker Verification
Jun 16, 2024Abstract:Recent research in speaker verification has increasingly focused on achieving robust and reliable recognition under challenging channel conditions and noisy environments. Identifying speakers in radio communications is particularly difficult due to inherent limitations such as constrained bandwidth and pervasive noise interference. To address this issue, we present a Channel Robust Speaker Learning (CRSL) framework that enhances the robustness of the current speaker verification pipeline, considering data source, data augmentation, and the efficiency of model transfer processes. Our framework introduces an augmentation module that mitigates bandwidth variations in radio speech datasets by manipulating the bandwidth of training inputs. It also addresses unknown noise by introducing noise within the manifold space. Additionally, we propose an efficient fine-tuning method that reduces the need for extensive additional training time and large amounts of data. Moreover, we develop a toolkit for assembling a large-scale radio speech corpus and establish a benchmark specifically tailored for radio scenario speaker verification studies. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed methodology effectively enhances performance and mitigates degradation caused by radio transmission in speaker verification tasks. The code will be available on Github.
A Non-Intrusive Neural Quality Assessment Model for Surface Electromyography Signals
Feb 08, 2024Abstract:In practical scenarios involving the measurement of surface electromyography (sEMG) in muscles, particularly those areas near the heart, one of the primary sources of contamination is the presence of electrocardiogram (ECG) signals. To assess the quality of real-world sEMG data more effectively, this study proposes QASE-net, a new non-intrusive model that predicts the SNR of sEMG signals. QASE-net combines CNN-BLSTM with attention mechanisms and follows an end-to-end training strategy. Our experimental framework utilizes real-world sEMG and ECG data from two open-access databases, the Non-Invasive Adaptive Prosthetics Database and the MIT-BIH Normal Sinus Rhythm Database, respectively. The experimental results demonstrate the superiority of QASE-net over the previous assessment model, exhibiting significantly reduced prediction errors and notably higher linear correlations with the ground truth. These findings show the potential of QASE-net to substantially enhance the reliability and precision of sEMG quality assessment in practical applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge