Xue Song
WEAVE: Unleashing and Benchmarking the In-context Interleaved Comprehension and Generation
Nov 14, 2025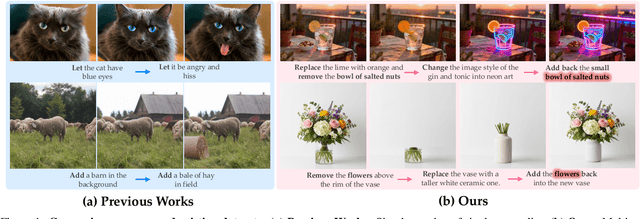
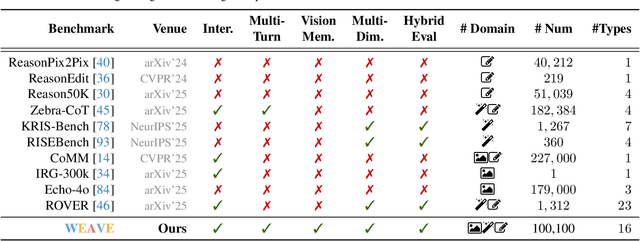
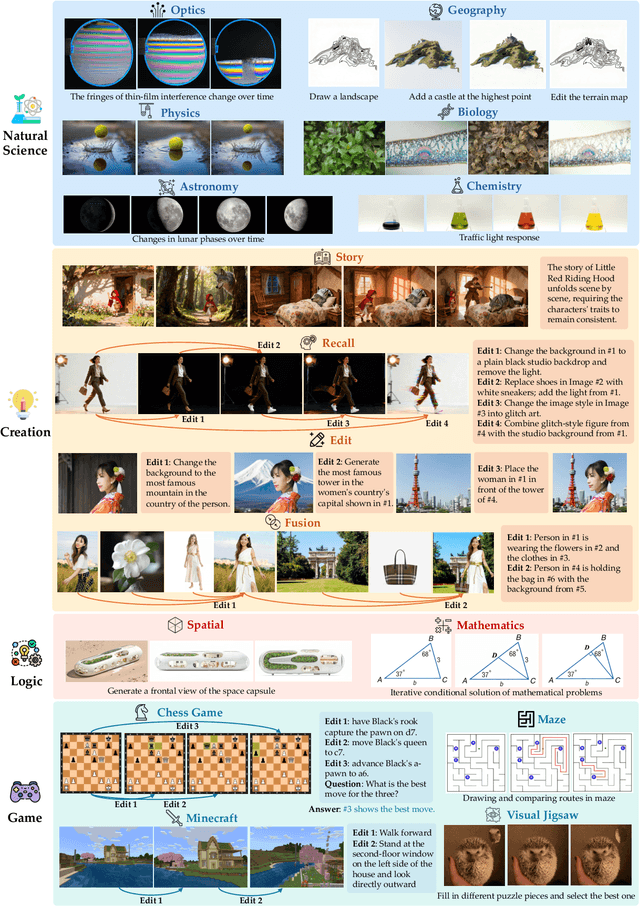

Abstract:Recent advances in unified multimodal models (UMMs) have enabled impressive progress in visual comprehension and generation. However, existing datasets and benchmarks focus primarily on single-turn interactions, failing to capture the multi-turn, context-dependent nature of real-world image creation and editing. To address this gap, we present WEAVE, the first suite for in-context interleaved cross-modality comprehension and generation. Our suite consists of two complementary parts. WEAVE-100k is a large-scale dataset of 100K interleaved samples spanning over 370K dialogue turns and 500K images, covering comprehension, editing, and generation tasks that require reasoning over historical context. WEAVEBench is a human-annotated benchmark with 100 tasks based on 480 images, featuring a hybrid VLM judger evaluation framework based on both the reference image and the combination of the original image with editing instructions that assesses models' abilities in multi-turn generation, visual memory, and world-knowledge reasoning across diverse domains. Experiments demonstrate that training on WEAVE-100k enables vision comprehension, image editing, and comprehension-generation collaboration capabilities. Furthermore, it facilitates UMMs to develop emergent visual-memory capabilities, while extensive evaluations on WEAVEBench expose the persistent limitations and challenges of current approaches in multi-turn, context-aware image generation and editing. We believe WEAVE provides a view and foundation for studying in-context interleaved comprehension and generation for multi-modal community.
Selftok: Discrete Visual Tokens of Autoregression, by Diffusion, and for Reasoning
May 18, 2025Abstract:We completely discard the conventional spatial prior in image representation and introduce a novel discrete visual tokenizer: Self-consistency Tokenizer (Selftok). At its design core, we compose an autoregressive (AR) prior -- mirroring the causal structure of language -- into visual tokens by using the reverse diffusion process of image generation. The AR property makes Selftok fundamentally distinct from traditional spatial tokens in the following two key ways: - Selftok offers an elegant and minimalist approach to unify diffusion and AR for vision-language models (VLMs): By representing images with Selftok tokens, we can train a VLM using a purely discrete autoregressive architecture -- like that in LLMs -- without requiring additional modules or training objectives. - We theoretically show that the AR prior satisfies the Bellman equation, whereas the spatial prior does not. Therefore, Selftok supports reinforcement learning (RL) for visual generation with effectiveness comparable to that achieved in LLMs. Besides the AR property, Selftok is also a SoTA tokenizer that achieves a favorable trade-off between high-quality reconstruction and compression rate. We use Selftok to build a pure AR VLM for both visual comprehension and generation tasks. Impressively, without using any text-image training pairs, a simple policy gradient RL working in the visual tokens can significantly boost the visual generation benchmark, surpassing all the existing models by a large margin. Therefore, we believe that Selftok effectively addresses the long-standing challenge that visual tokens cannot support effective RL. When combined with the well-established strengths of RL in LLMs, this brings us one step closer to realizing a truly multimodal LLM. Project Page: https://selftok-team.github.io/report/.
Discrete Visual Tokens of Autoregression, by Diffusion, and for Reasoning
May 12, 2025Abstract:We completely discard the conventional spatial prior in image representation and introduce a novel discrete visual tokenizer: Self-consistency Tokenizer (Selftok). At its design core, we compose an autoregressive (AR) prior -- mirroring the causal structure of language -- into visual tokens by using the reverse diffusion process of image generation. The AR property makes Selftok fundamentally distinct from traditional spatial tokens in the following two key ways: - Selftok offers an elegant and minimalist approach to unify diffusion and AR for vision-language models (VLMs): By representing images with Selftok tokens, we can train a VLM using a purely discrete autoregressive architecture -- like that in LLMs -- without requiring additional modules or training objectives. - We theoretically show that the AR prior satisfies the Bellman equation, whereas the spatial prior does not. Therefore, Selftok supports reinforcement learning (RL) for visual generation with effectiveness comparable to that achieved in LLMs. Besides the AR property, Selftok is also a SoTA tokenizer that achieves a favorable trade-off between high-quality reconstruction and compression rate. We use Selftok to build a pure AR VLM for both visual comprehension and generation tasks. Impressively, without using any text-image training pairs, a simple policy gradient RL working in the visual tokens can significantly boost the visual generation benchmark, surpassing all the existing models by a large margin. Therefore, we believe that Selftok effectively addresses the long-standing challenge that visual tokens cannot support effective RL. When combined with the well-established strengths of RL in LLMs, this brings us one step closer to realizing a truly multimodal LLM. Project Page: https://selftok-team.github.io/report/.
Revealing the Implicit Noise-based Imprint of Generative Models
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:With the rapid advancement of vision generation models, the potential security risks stemming from synthetic visual content have garnered increasing attention, posing significant challenges for AI-generated image detection. Existing methods suffer from inadequate generalization capabilities, resulting in unsatisfactory performance on emerging generative models. To address this issue, this paper presents a novel framework that leverages noise-based model-specific imprint for the detection task. Specifically, we propose a novel noise-based imprint simulator to capture intrinsic patterns imprinted in images generated by different models. By aggregating imprints from various generative models, imprints of future models can be extrapolated to expand training data, thereby enhancing generalization and robustness. Furthermore, we design a new pipeline that pioneers the use of noise patterns, derived from a noise-based imprint extractor, alongside other visual features for AI-generated image detection, resulting in a significant improvement in performance. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance across three public benchmarks including GenImage, Synthbuster and Chameleon.
StyleStudio: Text-Driven Style Transfer with Selective Control of Style Elements
Dec 11, 2024Abstract:Text-driven style transfer aims to merge the style of a reference image with content described by a text prompt. Recent advancements in text-to-image models have improved the nuance of style transformations, yet significant challenges remain, particularly with overfitting to reference styles, limiting stylistic control, and misaligning with textual content. In this paper, we propose three complementary strategies to address these issues. First, we introduce a cross-modal Adaptive Instance Normalization (AdaIN) mechanism for better integration of style and text features, enhancing alignment. Second, we develop a Style-based Classifier-Free Guidance (SCFG) approach that enables selective control over stylistic elements, reducing irrelevant influences. Finally, we incorporate a teacher model during early generation stages to stabilize spatial layouts and mitigate artifacts. Our extensive evaluations demonstrate significant improvements in style transfer quality and alignment with textual prompts. Furthermore, our approach can be integrated into existing style transfer frameworks without fine-tuning.
LoRA of Change: Learning to Generate LoRA for the Editing Instruction from A Single Before-After Image Pair
Nov 28, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we propose the LoRA of Change (LoC) framework for image editing with visual instructions, i.e., before-after image pairs. Compared to the ambiguities, insufficient specificity, and diverse interpretations of natural language, visual instructions can accurately reflect users' intent. Building on the success of LoRA in text-based image editing and generation, we dynamically learn an instruction-specific LoRA to encode the "change" in a before-after image pair, enhancing the interpretability and reusability of our model. Furthermore, generalizable models for image editing with visual instructions typically require quad data, i.e., a before-after image pair, along with query and target images. Due to the scarcity of such quad data, existing models are limited to a narrow range of visual instructions. To overcome this limitation, we introduce the LoRA Reverse optimization technique, enabling large-scale training with paired data alone. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate that our model produces high-quality images that align with user intent and support a broad spectrum of real-world visual instructions.
Doubly Abductive Counterfactual Inference for Text-based Image Editing
Mar 05, 2024
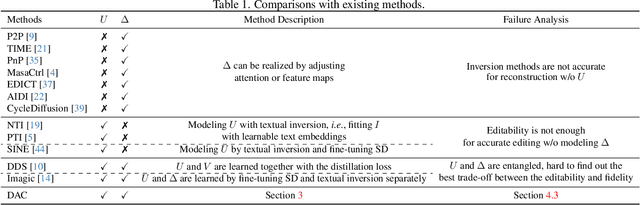
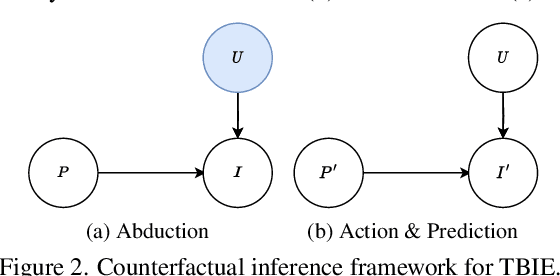

Abstract:We study text-based image editing (TBIE) of a single image by counterfactual inference because it is an elegant formulation to precisely address the requirement: the edited image should retain the fidelity of the original one. Through the lens of the formulation, we find that the crux of TBIE is that existing techniques hardly achieve a good trade-off between editability and fidelity, mainly due to the overfitting of the single-image fine-tuning. To this end, we propose a Doubly Abductive Counterfactual inference framework (DAC). We first parameterize an exogenous variable as a UNet LoRA, whose abduction can encode all the image details. Second, we abduct another exogenous variable parameterized by a text encoder LoRA, which recovers the lost editability caused by the overfitted first abduction. Thanks to the second abduction, which exclusively encodes the visual transition from post-edit to pre-edit, its inversion -- subtracting the LoRA -- effectively reverts pre-edit back to post-edit, thereby accomplishing the edit. Through extensive experiments, our DAC achieves a good trade-off between editability and fidelity. Thus, we can support a wide spectrum of user editing intents, including addition, removal, manipulation, replacement, style transfer, and facial change, which are extensively validated in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations. Codes are in https://github.com/xuesong39/DAC.
Text-driven Video Prediction
Oct 06, 2022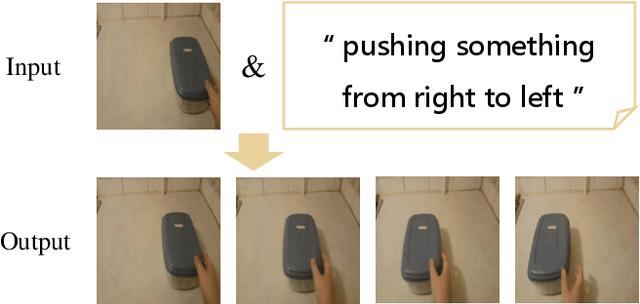
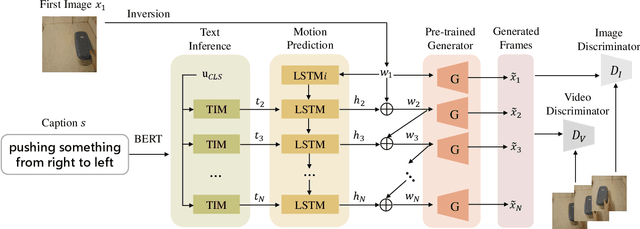
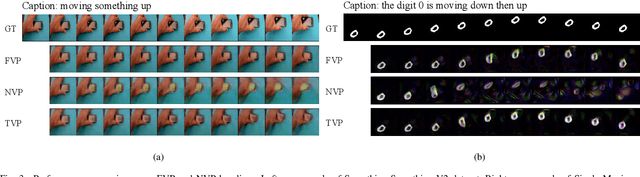
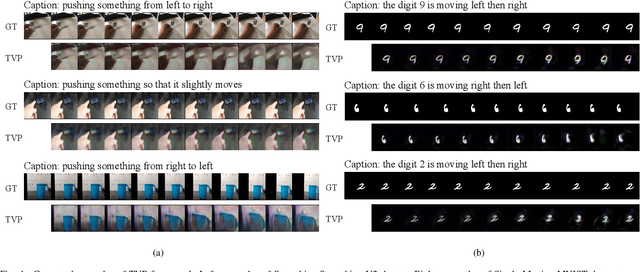
Abstract:Current video generation models usually convert signals indicating appearance and motion received from inputs (e.g., image, text) or latent spaces (e.g., noise vectors) into consecutive frames, fulfilling a stochastic generation process for the uncertainty introduced by latent code sampling. However, this generation pattern lacks deterministic constraints for both appearance and motion, leading to uncontrollable and undesirable outcomes. To this end, we propose a new task called Text-driven Video Prediction (TVP). Taking the first frame and text caption as inputs, this task aims to synthesize the following frames. Specifically, appearance and motion components are provided by the image and caption separately. The key to addressing the TVP task depends on fully exploring the underlying motion information in text descriptions, thus facilitating plausible video generation. In fact, this task is intrinsically a cause-and-effect problem, as the text content directly influences the motion changes of frames. To investigate the capability of text in causal inference for progressive motion information, our TVP framework contains a Text Inference Module (TIM), producing step-wise embeddings to regulate motion inference for subsequent frames. In particular, a refinement mechanism incorporating global motion semantics guarantees coherent generation. Extensive experiments are conducted on Something-Something V2 and Single Moving MNIST datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves better results over other baselines, verifying the effectiveness of the proposed framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge