Xu Lan
Improving Open-Set Semantic Segmentation in 3D Point Clouds by Conditional Channel Capacity Maximization: Preliminary Results
May 09, 2025Abstract:Point-cloud semantic segmentation underpins a wide range of critical applications. Although recent deep architectures and large-scale datasets have driven impressive closed-set performance, these models struggle to recognize or properly segment objects outside their training classes. This gap has sparked interest in Open-Set Semantic Segmentation (O3S), where models must both correctly label known categories and detect novel, unseen classes. In this paper, we propose a plug and play framework for O3S. By modeling the segmentation pipeline as a conditional Markov chain, we derive a novel regularizer term dubbed Conditional Channel Capacity Maximization (3CM), that maximizes the mutual information between features and predictions conditioned on each class. When incorporated into standard loss functions, 3CM encourages the encoder to retain richer, label-dependent features, thereby enhancing the network's ability to distinguish and segment previously unseen categories. Experimental results demonstrate effectiveness of proposed method on detecting unseen objects. We further outline future directions for dynamic open-world adaptation and efficient information-theoretic estimation.
Batch Group Normalization
Dec 09, 2020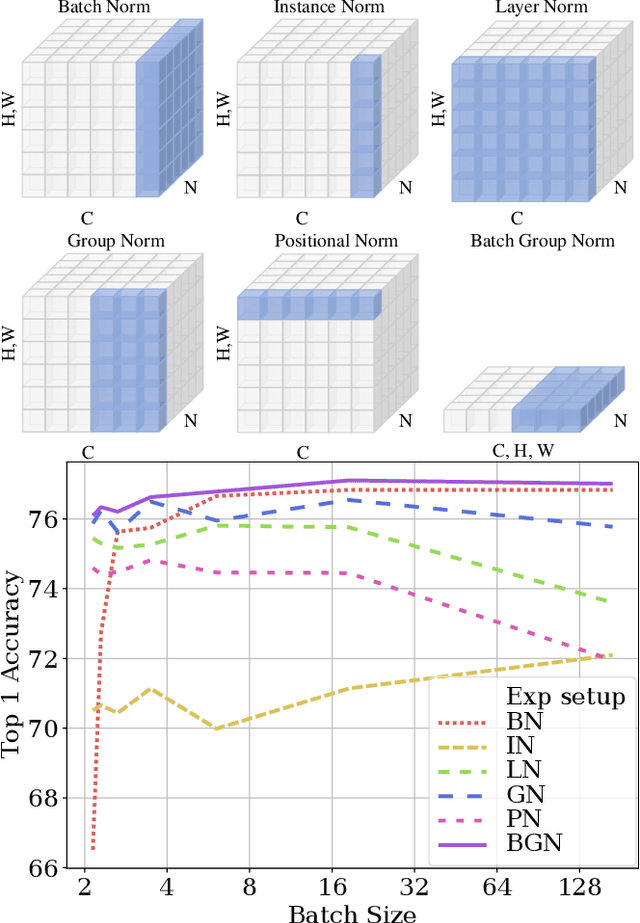
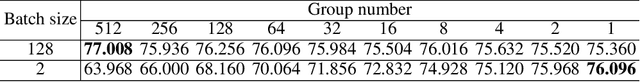

Abstract:Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (DCNNs) are hard and time-consuming to train. Normalization is one of the effective solutions. Among previous normalization methods, Batch Normalization (BN) performs well at medium and large batch sizes and is with good generalizability to multiple vision tasks, while its performance degrades significantly at small batch sizes. In this paper, we find that BN saturates at extreme large batch sizes, i.e., 128 images per worker, i.e., GPU, as well and propose that the degradation/saturation of BN at small/extreme large batch sizes is caused by noisy/confused statistic calculation. Hence without adding new trainable parameters, using multiple-layer or multi-iteration information, or introducing extra computation, Batch Group Normalization (BGN) is proposed to solve the noisy/confused statistic calculation of BN at small/extreme large batch sizes with introducing the channel, height and width dimension to compensate. The group technique in Group Normalization (GN) is used and a hyper-parameter G is used to control the number of feature instances used for statistic calculation, hence to offer neither noisy nor confused statistic for different batch sizes. We empirically demonstrate that BGN consistently outperforms BN, Instance Normalization (IN), Layer Normalization (LN), GN, and Positional Normalization (PN), across a wide spectrum of vision tasks, including image classification, Neural Architecture Search (NAS), adversarial learning, Few Shot Learning (FSL) and Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA), indicating its good performance, robust stability to batch size and wide generalizability. For example, for training ResNet-50 on ImageNet with a batch size of 2, BN achieves Top1 accuracy of 66.512% while BGN achieves 76.096% with notable improvement.
Boosting Few-Shot Learning With Adaptive Margin Loss
May 28, 2020



Abstract:Few-shot learning (FSL) has attracted increasing attention in recent years but remains challenging, due to the intrinsic difficulty in learning to generalize from a few examples. This paper proposes an adaptive margin principle to improve the generalization ability of metric-based meta-learning approaches for few-shot learning problems. Specifically, we first develop a class-relevant additive margin loss, where semantic similarity between each pair of classes is considered to separate samples in the feature embedding space from similar classes. Further, we incorporate the semantic context among all classes in a sampled training task and develop a task-relevant additive margin loss to better distinguish samples from different classes. Our adaptive margin method can be easily extended to a more realistic generalized FSL setting. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method can boost the performance of current metric-based meta-learning approaches, under both the standard FSL and generalized FSL settings.
Universal Person Re-Identification
Jul 22, 2019


Abstract:Most state-of-the-art person re-identification (re-id) methods depend on supervised model learning with a large set of cross-view identity labelled training data. Even worse, such trained models are limited to only the same-domain deployment with significantly degraded cross-domain generalization capability, i.e. "domain specific". To solve this limitation, there are a number of recent unsupervised domain adaptation and unsupervised learning methods that leverage unlabelled target domain training data. However, these methods need to train a separate model for each target domain as supervised learning methods. This conventional "{\em train once, run once}" pattern is unscalable to a large number of target domains typically encountered in real-world deployments. We address this problem by presenting a "train once, run everywhere" pattern industry-scale systems are desperate for. We formulate a "universal model learning' approach enabling domain-generic person re-id using only limited training data of a "{\em single}" seed domain. Specifically, we train a universal re-id deep model to discriminate between a set of transformed person identity classes. Each of such classes is formed by applying a variety of random appearance transformations to the images of that class, where the transformations simulate the camera viewing conditions of any domains for making the model training domain generic. Extensive evaluations show the superiority of our method for universal person re-id over a wide variety of state-of-the-art unsupervised domain adaptation and unsupervised learning re-id methods on five standard benchmarks: Market-1501, DukeMTMC, CUHK03, MSMT17, and VIPeR.
Self-Referenced Deep Learning
Nov 19, 2018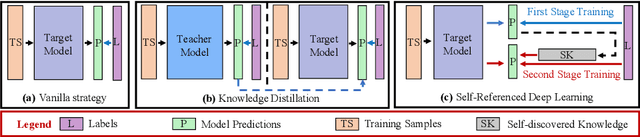

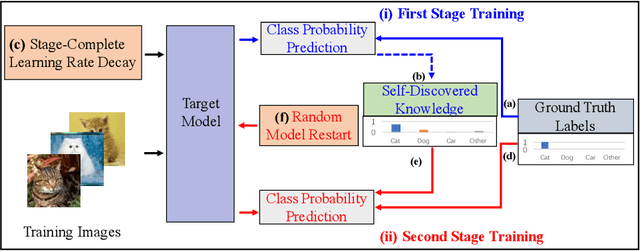

Abstract:Knowledge distillation is an effective approach to transferring knowledge from a teacher neural network to a student target network for satisfying the low-memory and fast running requirements in practice use. Whilst being able to create stronger target networks compared to the vanilla non-teacher based learning strategy, this scheme needs to train additionally a large teacher model with expensive computational cost. In this work, we present a Self-Referenced Deep Learning (SRDL) strategy. Unlike both vanilla optimisation and existing knowledge distillation, SRDL distils the knowledge discovered by the in-training target model back to itself to regularise the subsequent learning procedure therefore eliminating the need for training a large teacher model. SRDL improves the model generalisation performance compared to vanilla learning and conventional knowledge distillation approaches with negligible extra computational cost. Extensive evaluations show that a variety of deep networks benefit from SRDL resulting in enhanced deployment performance on both coarse-grained object categorisation tasks (CIFAR10, CIFAR100, Tiny ImageNet, and ImageNet) and fine-grained person instance identification tasks (Market-1501).
Collaborative Deep Learning Across Multiple Data Centers
Oct 16, 2018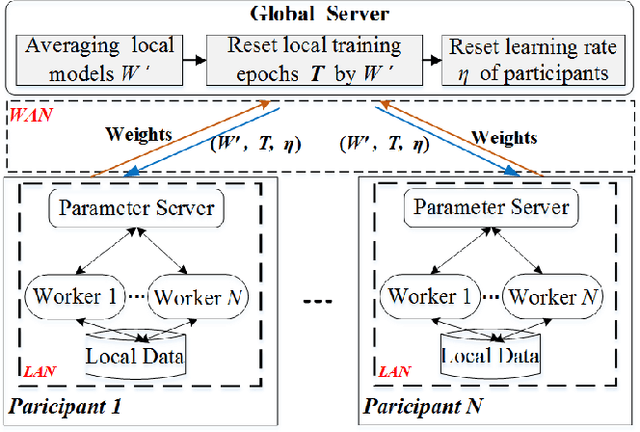
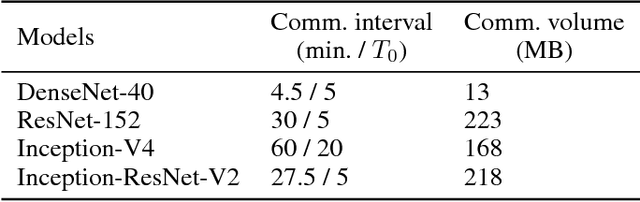
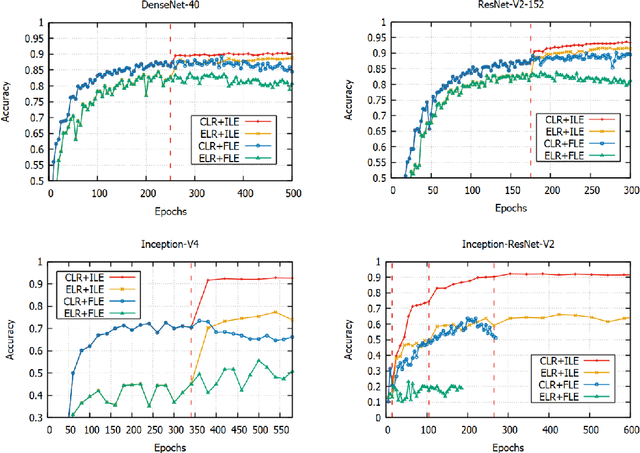
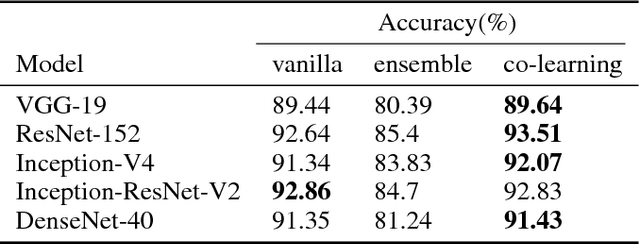
Abstract:Valuable training data is often owned by independent organizations and located in multiple data centers. Most deep learning approaches require to centralize the multi-datacenter data for performance purpose. In practice, however, it is often infeasible to transfer all data to a centralized data center due to not only bandwidth limitation but also the constraints of privacy regulations. Model averaging is a conventional choice for data parallelized training, but its ineffectiveness is claimed by previous studies as deep neural networks are often non-convex. In this paper, we argue that model averaging can be effective in the decentralized environment by using two strategies, namely, the cyclical learning rate and the increased number of epochs for local model training. With the two strategies, we show that model averaging can provide competitive performance in the decentralized mode compared to the data-centralized one. In a practical environment with multiple data centers, we conduct extensive experiments using state-of-the-art deep network architectures on different types of data. Results demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed method.
Knowledge Distillation by On-the-Fly Native Ensemble
Sep 08, 2018



Abstract:Knowledge distillation is effective to train small and generalisable network models for meeting the low-memory and fast running requirements. Existing offline distillation methods rely on a strong pre-trained teacher, which enables favourable knowledge discovery and transfer but requires a complex two-phase training procedure. Online counterparts address this limitation at the price of lacking a highcapacity teacher. In this work, we present an On-the-fly Native Ensemble (ONE) strategy for one-stage online distillation. Specifically, ONE trains only a single multi-branch network while simultaneously establishing a strong teacher on-the- fly to enhance the learning of target network. Extensive evaluations show that ONE improves the generalisation performance a variety of deep neural networks more significantly than alternative methods on four image classification dataset: CIFAR10, CIFAR100, SVHN, and ImageNet, whilst having the computational efficiency advantages.
Person Search by Multi-Scale Matching
Jul 23, 2018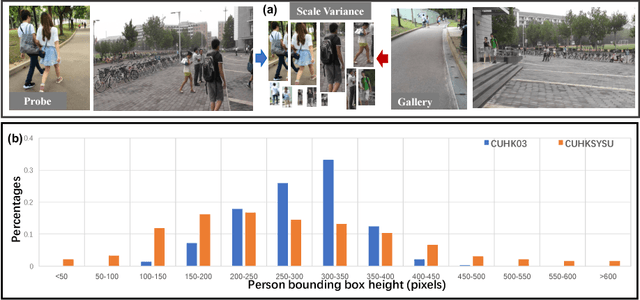

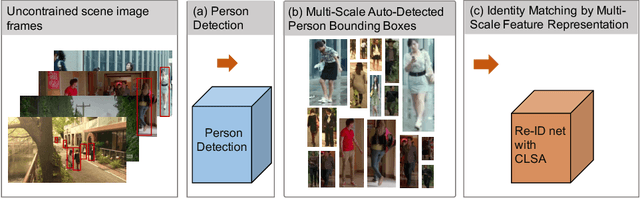
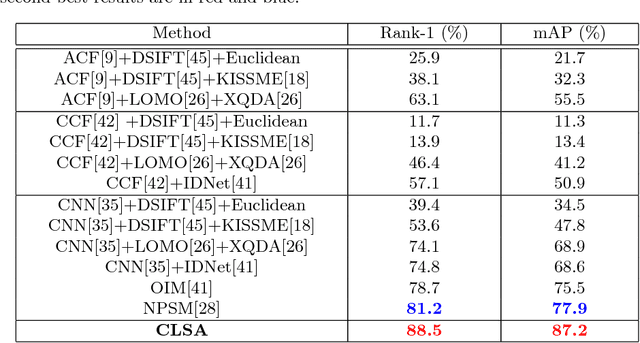
Abstract:We consider the problem of person search in unconstrained scene images. Existing methods usually focus on improving the person detection accuracy to mitigate negative effects imposed by misalignment, mis-detections, and false alarms resulted from noisy people auto-detection. In contrast to previous studies, we show that sufficiently reliable person instance cropping is achievable by slightly improved state-of-the-art deep learning object detectors (e.g. Faster-RCNN), and the under-studied multi-scale matching problem in person search is a more severe barrier. In this work, we address this multi-scale person search challenge by proposing a Cross-Level Semantic Alignment (CLSA) deep learning approach capable of learning more discriminative identity feature representations in a unified end-to-end model. This is realised by exploiting the in-network feature pyramid structure of a deep neural network enhanced by a novel cross pyramid-level semantic alignment loss function. This favourably eliminates the need for constructing a computationally expensive image pyramid and a complex multi-branch network architecture. Extensive experiments show the modelling advantages and performance superiority of CLSA over the state-of-the-art person search and multi-scale matching methods on two large person search benchmarking datasets: CUHK-SYSU and PRW.
Deep Reinforcement Learning Attention Selection for Person Re-Identification
Jul 07, 2018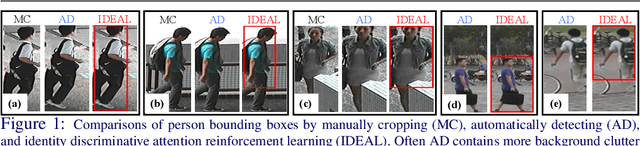

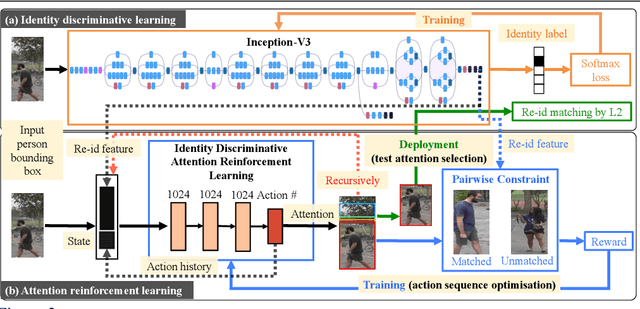

Abstract:Existing person re-identification (re-id) methods assume the provision of accurately cropped person bounding boxes with minimum background noise, mostly by manually cropping. This is significantly breached in practice when person bounding boxes must be detected automatically given a very large number of images and/or videos processed. Compared to carefully cropped manually, auto-detected bounding boxes are far less accurate with random amount of background clutter which can degrade notably person re-id matching accuracy. In this work, we develop a joint learning deep model that optimises person re-id attention selection within any auto-detected person bounding boxes by reinforcement learning of background clutter minimisation subject to re-id label pairwise constraints. Specifically, we formulate a novel unified re-id architecture called Identity DiscriminativE Attention reinforcement Learning (IDEAL) to accurately select re-id attention in auto-detected bounding boxes for optimising re-id performance. Our model can improve re-id accuracy comparable to that from exhaustive human manual cropping of bounding boxes with additional advantages from identity discriminative attention selection that specially benefits re-id tasks beyond human knowledge. Extensive comparative evaluations demonstrate the re-id advantages of the proposed IDEAL model over a wide range of state-of-the-art re-id methods on two auto-detected re-id benchmarks CUHK03 and Market-1501.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge