Xintao Zhao
RobustSVC: HuBERT-based Melody Extractor and Adversarial Learning for Robust Singing Voice Conversion
Sep 10, 2024



Abstract:Singing voice conversion (SVC) is hindered by noise sensitivity due to the use of non-robust methods for extracting pitch and energy during the inference. As clean signals are key for the source audio in SVC, music source separation preprocessing offers a viable solution for handling noisy audio, like singing with background music (BGM). However, current separating methods struggle to fully remove noise or excessively suppress signal components, affecting the naturalness and similarity of the processed audio. To tackle this, our study introduces RobustSVC, a novel any-to-one SVC framework that converts noisy vocals into clean vocals sung by the target singer. We replace the non-robust feature with a HuBERT-based melody extractor and use adversarial training mechanisms with three discriminators to reduce information leakage in self-supervised representations. Experimental results show that RobustSVC is noise-robust and achieves higher similarity and naturalness than baseline methods in both noisy and clean vocal conditions.
Adversarial Speaker Disentanglement Using Unannotated External Data for Self-supervised Representation Based Voice Conversion
May 16, 2023Abstract:Nowadays, recognition-synthesis-based methods have been quite popular with voice conversion (VC). By introducing linguistics features with good disentangling characters extracted from an automatic speech recognition (ASR) model, the VC performance achieved considerable breakthroughs. Recently, self-supervised learning (SSL) methods trained with a large-scale unannotated speech corpus have been applied to downstream tasks focusing on the content information, which is suitable for VC tasks. However, a huge amount of speaker information in SSL representations degrades timbre similarity and the quality of converted speech significantly. To address this problem, we proposed a high-similarity any-to-one voice conversion method with the input of SSL representations. We incorporated adversarial training mechanisms in the synthesis module using external unannotated corpora. Two auxiliary discriminators were trained to distinguish whether a sequence of mel-spectrograms has been converted by the acoustic model and whether a sequence of content embeddings contains speaker information from external corpora. Experimental results show that our proposed method achieves comparable similarity and higher naturalness than the supervised method, which needs a huge amount of annotated corpora for training and is applicable to improve similarity for VC methods with other SSL representations as input.
Speech Representation Disentanglement with Adversarial Mutual Information Learning for One-shot Voice Conversion
Aug 18, 2022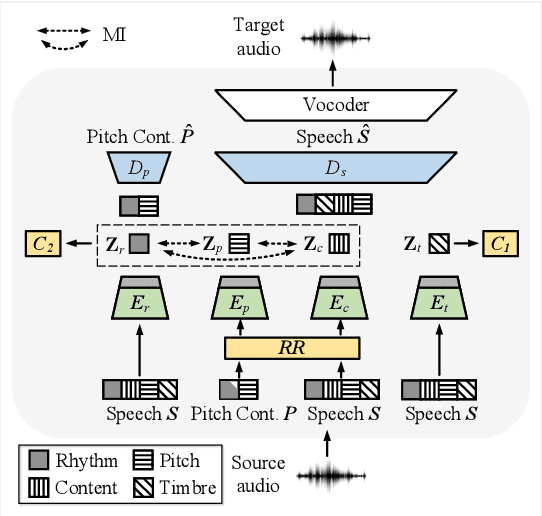
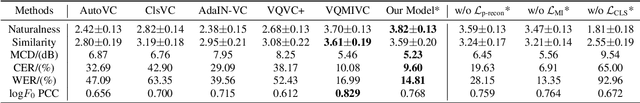
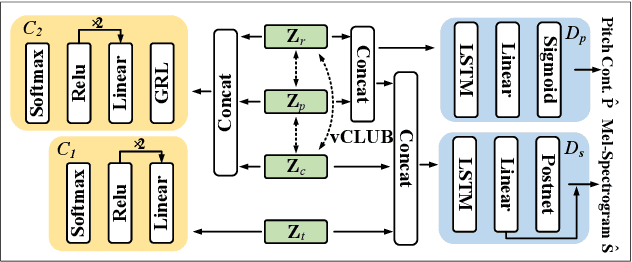
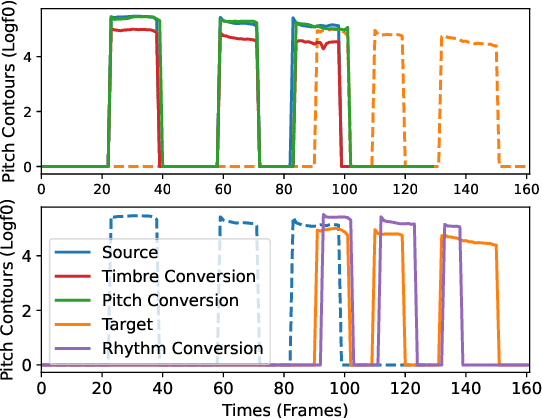
Abstract:One-shot voice conversion (VC) with only a single target speaker's speech for reference has become a hot research topic. Existing works generally disentangle timbre, while information about pitch, rhythm and content is still mixed together. To perform one-shot VC effectively with further disentangling these speech components, we employ random resampling for pitch and content encoder and use the variational contrastive log-ratio upper bound of mutual information and gradient reversal layer based adversarial mutual information learning to ensure the different parts of the latent space containing only the desired disentangled representation during training. Experiments on the VCTK dataset show the model achieves state-of-the-art performance for one-shot VC in terms of naturalness and intellgibility. In addition, we can transfer characteristics of one-shot VC on timbre, pitch and rhythm separately by speech representation disentanglement. Our code, pre-trained models and demo are available at https://im1eon.github.io/IS2022-SRDVC/.
Disentangleing Content and Fine-grained Prosody Information via Hybrid ASR Bottleneck Features for Voice Conversion
Mar 24, 2022



Abstract:Non-parallel data voice conversion (VC) have achieved considerable breakthroughs recently through introducing bottleneck features (BNFs) extracted by the automatic speech recognition(ASR) model. However, selection of BNFs have a significant impact on VC result. For example, when extracting BNFs from ASR trained with Cross Entropy loss (CE-BNFs) and feeding into neural network to train a VC system, the timbre similarity of converted speech is significantly degraded. If BNFs are extracted from ASR trained using Connectionist Temporal Classification loss (CTC-BNFs), the naturalness of the converted speech may decrease. This phenomenon is caused by the difference of information contained in BNFs. In this paper, we proposed an any-to-one VC method using hybrid bottleneck features extracted from CTC-BNFs and CE-BNFs to complement each other advantages. Gradient reversal layer and instance normalization were used to extract prosody information from CE-BNFs and content information from CTC-BNFs. Auto-regressive decoder and Hifi-GAN vocoder were used to generate high-quality waveform. Experimental results show that our proposed method achieves higher similarity, naturalness, quality than baseline method and reveals the differences between the information contained in CE-BNFs and CTC-BNFs as well as the influence they have on the converted speech.
Adversarially learning disentangled speech representations for robust multi-factor voice conversion
Jan 30, 2021



Abstract:Factorizing speech as disentangled speech representations is vital to achieve highly controllable style transfer in voice conversion (VC). Conventional speech representation learning methods in VC only factorize speech as speaker and content, lacking controllability on other prosody-related factors. State-of-the-art speech representation learning methods for more speech factors are using primary disentangle algorithms such as random resampling and ad-hoc bottleneck layer size adjustment, which however is hard to ensure robust speech representation disentanglement. To increase the robustness of highly controllable style transfer on multiple factors in VC, we propose a disentangled speech representation learning framework based on adversarial learning. Four speech representations characterizing content, timbre, rhythm and pitch are extracted, and further disentangled by an adversarial network inspired by BERT. The adversarial network is used to minimize the correlations between the speech representations, by randomly masking and predicting one of the representations from the others. A word prediction network is also adopted to learn a more informative content representation. Experimental results show that the proposed speech representation learning framework significantly improves the robustness of VC on multiple factors by increasing conversion rate from 48.2% to 57.1% and ABX preference exceeding by 31.2% compared with state-of-the-art method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge