Xingyue Chen
Text2Street: Controllable Text-to-image Generation for Street Views
Feb 07, 2024Abstract:Text-to-image generation has made remarkable progress with the emergence of diffusion models. However, it is still a difficult task to generate images for street views based on text, mainly because the road topology of street scenes is complex, the traffic status is diverse and the weather condition is various, which makes conventional text-to-image models difficult to deal with. To address these challenges, we propose a novel controllable text-to-image framework, named \textbf{Text2Street}. In the framework, we first introduce the lane-aware road topology generator, which achieves text-to-map generation with the accurate road structure and lane lines armed with the counting adapter, realizing the controllable road topology generation. Then, the position-based object layout generator is proposed to obtain text-to-layout generation through an object-level bounding box diffusion strategy, realizing the controllable traffic object layout generation. Finally, the multiple control image generator is designed to integrate the road topology, object layout and weather description to realize controllable street-view image generation. Extensive experiments show that the proposed approach achieves controllable street-view text-to-image generation and validates the effectiveness of the Text2Street framework for street views.
Perceive, Excavate and Purify: A Novel Object Mining Framework for Instance Segmentation
Apr 18, 2023Abstract:Recently, instance segmentation has made great progress with the rapid development of deep neural networks. However, there still exist two main challenges including discovering indistinguishable objects and modeling the relationship between instances. To deal with these difficulties, we propose a novel object mining framework for instance segmentation. In this framework, we first introduce the semantics perceiving subnetwork to capture pixels that may belong to an obvious instance from the bottom up. Then, we propose an object excavating mechanism to discover indistinguishable objects. In the mechanism, preliminary perceived semantics are regarded as original instances with classifications and locations, and then indistinguishable objects around these original instances are mined, which ensures that hard objects are fully excavated. Next, an instance purifying strategy is put forward to model the relationship between instances, which pulls the similar instances close and pushes away different instances to keep intra-instance similarity and inter-instance discrimination. In this manner, the same objects are combined as the one instance and different objects are distinguished as independent instances. Extensive experiments on the COCO dataset show that the proposed approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods, which validates the effectiveness of the proposed object mining framework.
Artificial Intelligence System for Detection and Screening of Cardiac Abnormalities using Electrocardiogram Images
Feb 10, 2023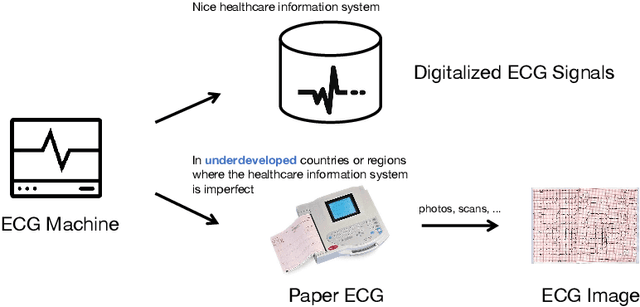



Abstract:The artificial intelligence (AI) system has achieved expert-level performance in electrocardiogram (ECG) signal analysis. However, in underdeveloped countries or regions where the healthcare information system is imperfect, only paper ECGs can be provided. Analysis of real-world ECG images (photos or scans of paper ECGs) remains challenging due to complex environments or interference. In this study, we present an AI system developed to detect and screen cardiac abnormalities (CAs) from real-world ECG images. The system was evaluated on a large dataset of 52,357 patients from multiple regions and populations across the world. On the detection task, the AI system obtained area under the receiver operating curve (AUC) of 0.996 (hold-out test), 0.994 (external test 1), 0.984 (external test 2), and 0.979 (external test 3), respectively. Meanwhile, the detection results of AI system showed a strong correlation with the diagnosis of cardiologists (cardiologist 1 (R=0.794, p<1e-3), cardiologist 2 (R=0.812, p<1e-3)). On the screening task, the AI system achieved AUCs of 0.894 (hold-out test) and 0.850 (external test). The screening performance of the AI system was better than that of the cardiologists (AI system (0.846) vs. cardiologist 1 (0.520) vs. cardiologist 2 (0.480)). Our study demonstrates the feasibility of an accurate, objective, easy-to-use, fast, and low-cost AI system for CA detection and screening. The system has the potential to be used by healthcare professionals, caregivers, and general users to assess CAs based on real-world ECG images.
Visual and Textual Sentiment Analysis Using Deep Fusion Convolutional Neural Networks
Nov 21, 2017



Abstract:Sentiment analysis is attracting more and more attentions and has become a very hot research topic due to its potential applications in personalized recommendation, opinion mining, etc. Most of the existing methods are based on either textual or visual data and can not achieve satisfactory results, as it is very hard to extract sufficient information from only one single modality data. Inspired by the observation that there exists strong semantic correlation between visual and textual data in social medias, we propose an end-to-end deep fusion convolutional neural network to jointly learn textual and visual sentiment representations from training examples. The two modality information are fused together in a pooling layer and fed into fully-connected layers to predict the sentiment polarity. We evaluate the proposed approach on two widely used data sets. Results show that our method achieves promising result compared with the state-of-the-art methods which clearly demonstrate its competency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge