Weilun Xu
Accuracy of Wearable ECG Parameter Calculation Method for Long QT and First-Degree A-V Block Detection: A Multi-Center Real-World Study with External Validations Compared to Standard ECG Machines and Cardiologist Assessments
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:In recent years, wearable devices have revolutionized cardiac monitoring by enabling continuous, non-invasive ECG recording in real-world settings. Despite these advances, the accuracy of ECG parameter calculations (PR interval, QRS interval, QT interval, etc.) from wearables remains to be rigorously validated against conventional ECG machines and expert clinician assessments. In this large-scale, multicenter study, we evaluated FeatureDB, a novel algorithm for automated computation of ECG parameters from wearable single-lead signals Three diverse datasets were employed: the AHMU-FH dataset (n=88,874), the CSE dataset (n=106), and the HeartVoice-ECG-lite dataset (n=369) with annotations provided by two experienced cardiologists. FeatureDB demonstrates a statistically significant correlation with key parameters (PR interval, QRS duration, QT interval, and QTc) calculated by standard ECG machines and annotated by clinical doctors. Bland-Altman analysis confirms a high level of agreement.Moreover,FeatureDB exhibited robust diagnostic performance in detecting Long QT syndrome (LQT) and atrioventricular block interval abnormalities (AVBI),with excellent area under the ROC curve (LQT: 0.836, AVBI: 0.861),accuracy (LQT: 0.856, AVBI: 0.845),sensitivity (LQT: 0.815, AVBI: 0.877),and specificity (LQT: 0.856, AVBI: 0.845).This further validates its clinical reliability. These results validate the clinical applicability of FeatureDB for wearable ECG analysis and highlight its potential to bridge the gap between traditional diagnostic methods and emerging wearable technologies.Ultimately,this study supports integrating wearable ECG devices into large-scale cardiovascular disease management and early intervention strategies,and it highlights the potential of wearable ECG technologies to deliver accurate,clinically relevant cardiac monitoring while advancing broader applications in cardiovascular care.
Artificial Intelligence System for Detection and Screening of Cardiac Abnormalities using Electrocardiogram Images
Feb 10, 2023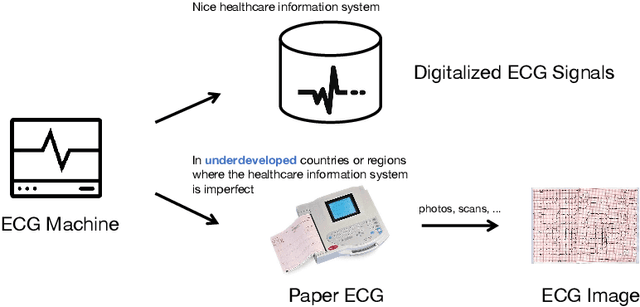



Abstract:The artificial intelligence (AI) system has achieved expert-level performance in electrocardiogram (ECG) signal analysis. However, in underdeveloped countries or regions where the healthcare information system is imperfect, only paper ECGs can be provided. Analysis of real-world ECG images (photos or scans of paper ECGs) remains challenging due to complex environments or interference. In this study, we present an AI system developed to detect and screen cardiac abnormalities (CAs) from real-world ECG images. The system was evaluated on a large dataset of 52,357 patients from multiple regions and populations across the world. On the detection task, the AI system obtained area under the receiver operating curve (AUC) of 0.996 (hold-out test), 0.994 (external test 1), 0.984 (external test 2), and 0.979 (external test 3), respectively. Meanwhile, the detection results of AI system showed a strong correlation with the diagnosis of cardiologists (cardiologist 1 (R=0.794, p<1e-3), cardiologist 2 (R=0.812, p<1e-3)). On the screening task, the AI system achieved AUCs of 0.894 (hold-out test) and 0.850 (external test). The screening performance of the AI system was better than that of the cardiologists (AI system (0.846) vs. cardiologist 1 (0.520) vs. cardiologist 2 (0.480)). Our study demonstrates the feasibility of an accurate, objective, easy-to-use, fast, and low-cost AI system for CA detection and screening. The system has the potential to be used by healthcare professionals, caregivers, and general users to assess CAs based on real-world ECG images.
Defending Against Adversarial Attack in ECG Classification with Adversarial Distillation Training
Mar 14, 2022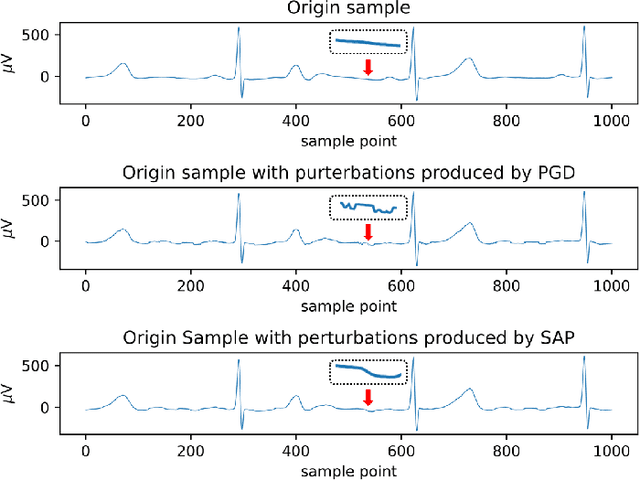
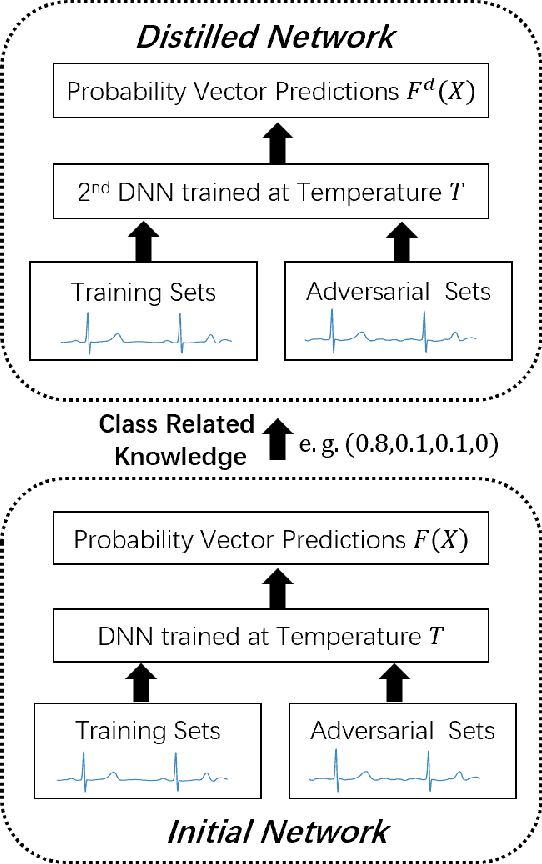
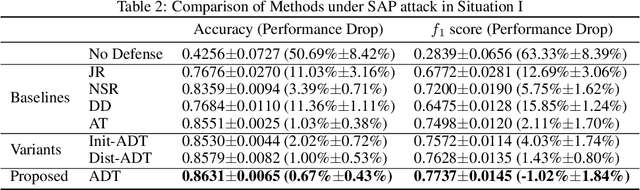
Abstract:In clinics, doctors rely on electrocardiograms (ECGs) to assess severe cardiac disorders. Owing to the development of technology and the increase in health awareness, ECG signals are currently obtained by using medical and commercial devices. Deep neural networks (DNNs) can be used to analyze these signals because of their high accuracy rate. However, researchers have found that adversarial attacks can significantly reduce the accuracy of DNNs. Studies have been conducted to defend ECG-based DNNs against traditional adversarial attacks, such as projected gradient descent (PGD), and smooth adversarial perturbation (SAP) which targets ECG classification; however, to the best of our knowledge, no study has completely explored the defense against adversarial attacks targeting ECG classification. Thus, we did different experiments to explore the effects of defense methods against white-box adversarial attack and black-box adversarial attack targeting ECG classification, and we found that some common defense methods performed well against these attacks. Besides, we proposed a new defense method called Adversarial Distillation Training (ADT) which comes from defensive distillation and can effectively improve the generalization performance of DNNs. The results show that our method performed more effectively against adversarial attacks targeting on ECG classification than the other baseline methods, namely, adversarial training, defensive distillation, Jacob regularization, and noise-to-signal ratio regularization. Furthermore, we found that our method performed better against PGD attacks with low noise levels, which means that our method has stronger robustness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge