Xiayu Li
Fengshenbang 1.0: Being the Foundation of Chinese Cognitive Intelligence
Sep 07, 2022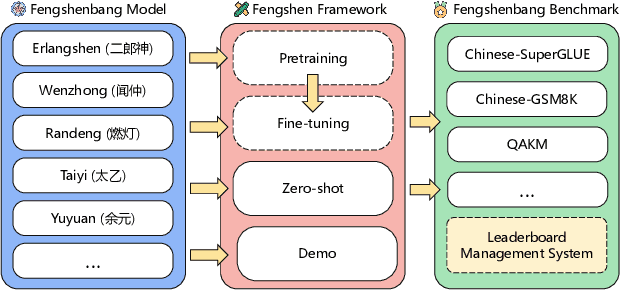
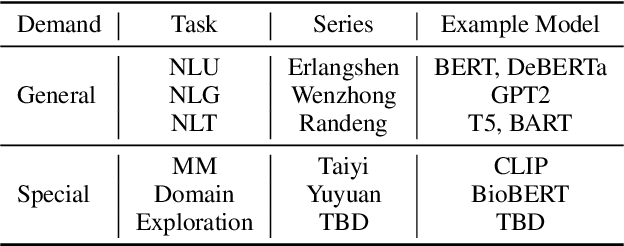
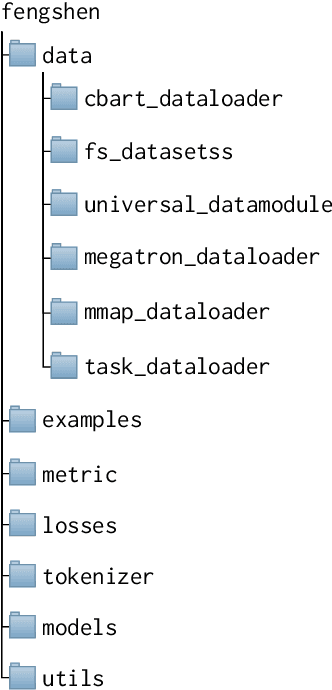
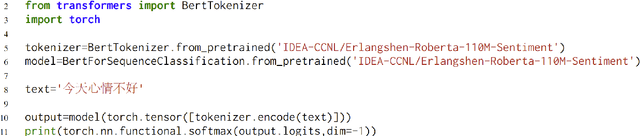
Abstract:Nowadays, foundation models become one of fundamental infrastructures in artificial intelligence, paving ways to the general intelligence. However, the reality presents two urgent challenges: existing foundation models are dominated by the English-language community; users are often given limited resources and thus cannot always use foundation models. To support the development of the Chinese-language community, we introduce an open-source project, called Fengshenbang, which leads by the research center for Cognitive Computing and Natural Language (CCNL). Our project has comprehensive capabilities, including large pre-trained models, user-friendly APIs, benchmarks, datasets, and others. We wrap all these in three sub-projects: the Fengshenbang Model, the Fengshen Framework, and the Fengshen Benchmark. An open-source roadmap, Fengshenbang, aims to re-evaluate the open-source community of Chinese pre-trained large-scale models, prompting the development of the entire Chinese large-scale model community. We also want to build a user-centered open-source ecosystem to allow individuals to access the desired models to match their computing resources. Furthermore, we invite companies, colleges, and research institutions to collaborate with us to build the large-scale open-source model-based ecosystem. We hope that this project will be the foundation of Chinese cognitive intelligence.
Entity-Relation Extraction as Multi-Turn Question Answering
May 24, 2019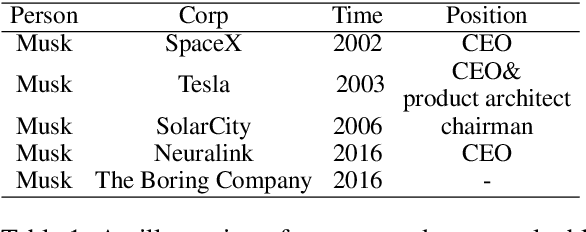
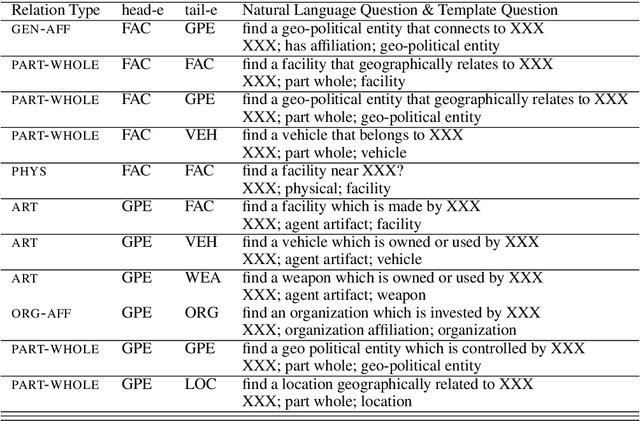

Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new paradigm for the task of entity-relation extraction. We cast the task as a multi-turn question answering problem, i.e., the extraction of entities and relations is transformed to the task of identifying answer spans from the context. This multi-turn QA formalization comes with several key advantages: firstly, the question query encodes important information for the entity/relation class we want to identify; secondly, QA provides a natural way of jointly modeling entity and relation; and thirdly, it allows us to exploit the well developed machine reading comprehension (MRC) models. Experiments on the ACE and the CoNLL04 corpora demonstrate that the proposed paradigm significantly outperforms previous best models. We are able to obtain the state-of-the-art results on all of the ACE04, ACE05 and CoNLL04 datasets, increasing the SOTA results on the three datasets to 49.4 (+1.0), 60.2 (+0.6) and 68.9 (+2.1), respectively. Additionally, we construct a newly developed dataset RESUME in Chinese, which requires multi-step reasoning to construct entity dependencies, as opposed to the single-step dependency extraction in the triplet exaction in previous datasets. The proposed multi-turn QA model also achieves the best performance on the RESUME dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge