Duo Chai
Description Based Text Classification with Reinforcement Learning
Feb 08, 2020

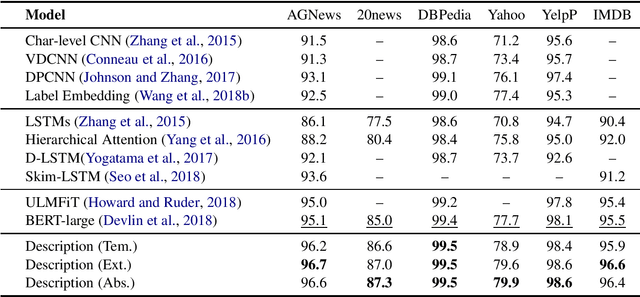
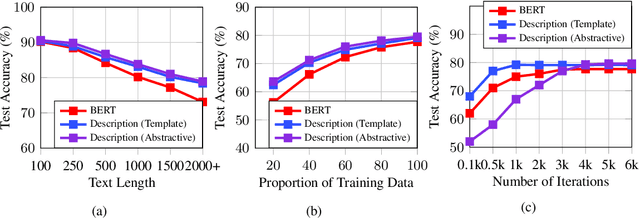
Abstract:The task of text classification is usually divided into two stages: {\it text feature extraction} and {\it classification}. In this standard formalization categories are merely represented as indexes in the label vocabulary, and the model lacks for explicit instructions on what to classify. Inspired by the current trend of formalizing NLP problems as question answering tasks, we propose a new framework for text classification, in which each category label is associated with a category description. Descriptions are generated by hand-crafted templates or using abstractive/extractive models from reinforcement learning. The concatenation of the description and the text is fed to the classifier to decide whether or not the current label should be assigned to the text. The proposed strategy forces the model to attend to the most salient texts with respect to the label, which can be regarded as a hard version of attention, leading to better performances. We observe significant performance boosts over strong baselines on a wide range of text classification tasks including single-label classification, multi-label classification and multi-aspect sentiment analysis.
Entity-Relation Extraction as Multi-Turn Question Answering
May 24, 2019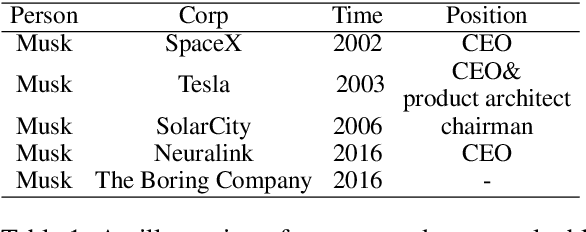
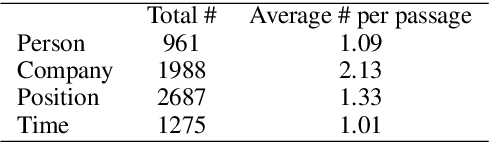
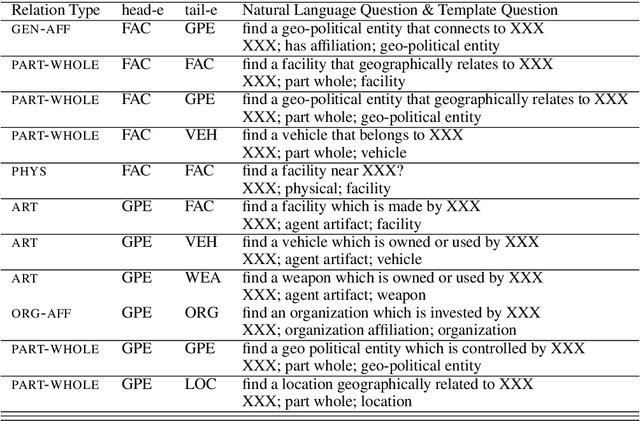

Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new paradigm for the task of entity-relation extraction. We cast the task as a multi-turn question answering problem, i.e., the extraction of entities and relations is transformed to the task of identifying answer spans from the context. This multi-turn QA formalization comes with several key advantages: firstly, the question query encodes important information for the entity/relation class we want to identify; secondly, QA provides a natural way of jointly modeling entity and relation; and thirdly, it allows us to exploit the well developed machine reading comprehension (MRC) models. Experiments on the ACE and the CoNLL04 corpora demonstrate that the proposed paradigm significantly outperforms previous best models. We are able to obtain the state-of-the-art results on all of the ACE04, ACE05 and CoNLL04 datasets, increasing the SOTA results on the three datasets to 49.4 (+1.0), 60.2 (+0.6) and 68.9 (+2.1), respectively. Additionally, we construct a newly developed dataset RESUME in Chinese, which requires multi-step reasoning to construct entity dependencies, as opposed to the single-step dependency extraction in the triplet exaction in previous datasets. The proposed multi-turn QA model also achieves the best performance on the RESUME dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge