Xiangchu Feng
Towards Robust 2D Convolution for Reliable Visual Recognition
Mar 18, 2022



Abstract:2D convolution (Conv2d), which is responsible for extracting features from the input image, is one of the key modules of a convolutional neural network (CNN). However, Conv2d is vulnerable to image corruptions and adversarial samples. It is an important yet rarely investigated problem that whether we can design a more robust alternative of Conv2d for more reliable feature extraction. In this paper, inspired by the recently developed learnable sparse transform that learns to convert the CNN features into a compact and sparse latent space, we design a novel building block, denoted by RConv-MK, to strengthen the robustness of extracted convolutional features. Our method leverages a set of learnable kernels of different sizes to extract features at different frequencies and employs a normalized soft thresholding operator to adaptively remove noises and trivial features at different corruption levels. Extensive experiments on clean images, corrupted images as well as adversarial samples validate the effectiveness of the proposed robust module for reliable visual recognition. The source codes are enclosed in the submission.
Multi-channel Weighted Nuclear Norm Minimization for Real Color Image Denoising
May 28, 2017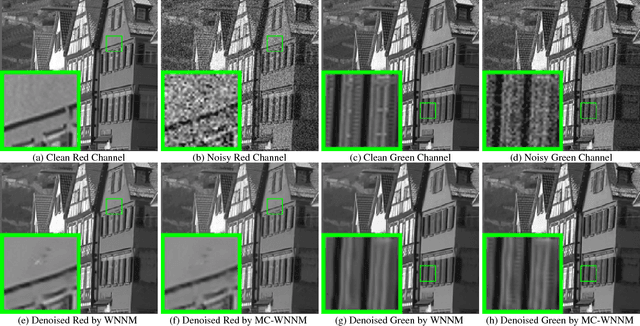
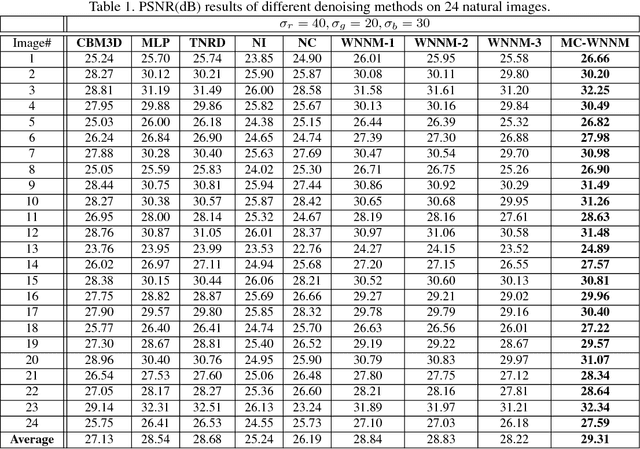

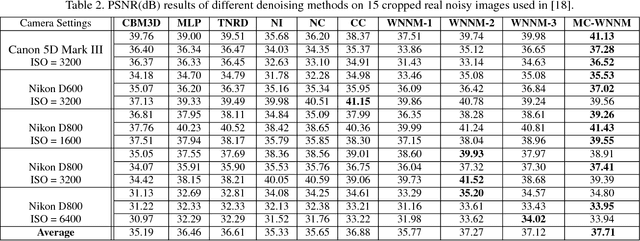
Abstract:Most of the existing denoising algorithms are developed for grayscale images, while it is not a trivial work to extend them for color image denoising because the noise statistics in R, G, B channels can be very different for real noisy images. In this paper, we propose a multi-channel (MC) optimization model for real color image denoising under the weighted nuclear norm minimization (WNNM) framework. We concatenate the RGB patches to make use of the channel redundancy, and introduce a weight matrix to balance the data fidelity of the three channels in consideration of their different noise statistics. The proposed MC-WNNM model does not have an analytical solution. We reformulate it into a linear equality-constrained problem and solve it with the alternating direction method of multipliers. Each alternative updating step has closed-form solution and the convergence can be guaranteed. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real noisy image datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed MC-WNNM over state-of-the-art denoising methods.
Cross-Domain Visual Matching via Generalized Similarity Measure and Feature Learning
May 13, 2016



Abstract:Cross-domain visual data matching is one of the fundamental problems in many real-world vision tasks, e.g., matching persons across ID photos and surveillance videos. Conventional approaches to this problem usually involves two steps: i) projecting samples from different domains into a common space, and ii) computing (dis-)similarity in this space based on a certain distance. In this paper, we present a novel pairwise similarity measure that advances existing models by i) expanding traditional linear projections into affine transformations and ii) fusing affine Mahalanobis distance and Cosine similarity by a data-driven combination. Moreover, we unify our similarity measure with feature representation learning via deep convolutional neural networks. Specifically, we incorporate the similarity measure matrix into the deep architecture, enabling an end-to-end way of model optimization. We extensively evaluate our generalized similarity model in several challenging cross-domain matching tasks: person re-identification under different views and face verification over different modalities (i.e., faces from still images and videos, older and younger faces, and sketch and photo portraits). The experimental results demonstrate superior performance of our model over other state-of-the-art methods.
On the Optimal Solution of Weighted Nuclear Norm Minimization
May 23, 2014Abstract:In recent years, the nuclear norm minimization (NNM) problem has been attracting much attention in computer vision and machine learning. The NNM problem is capitalized on its convexity and it can be solved efficiently. The standard nuclear norm regularizes all singular values equally, which is however not flexible enough to fit real scenarios. Weighted nuclear norm minimization (WNNM) is a natural extension and generalization of NNM. By assigning properly different weights to different singular values, WNNM can lead to state-of-the-art results in applications such as image denoising. Nevertheless, so far the global optimal solution of WNNM problem is not completely solved yet due to its non-convexity in general cases. In this article, we study the theoretical properties of WNNM and prove that WNNM can be equivalently transformed into a quadratic programming problem with linear constraints. This implies that WNNM is equivalent to a convex problem and its global optimum can be readily achieved by off-the-shelf convex optimization solvers. We further show that when the weights are non-descending, the globally optimal solution of WNNM can be obtained in closed-form.
Collaborative Representation based Classification for Face Recognition
Mar 10, 2014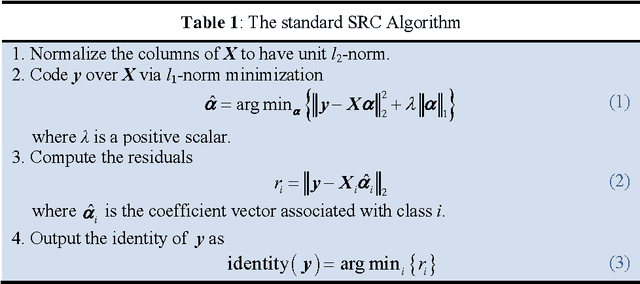
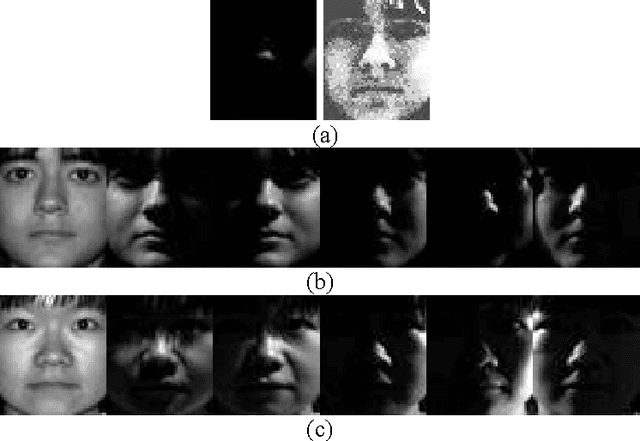

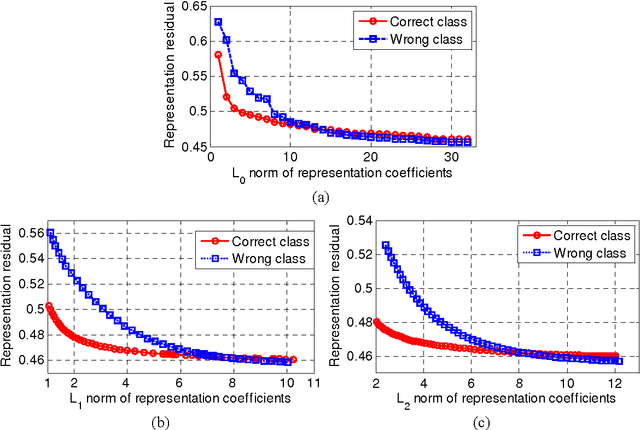
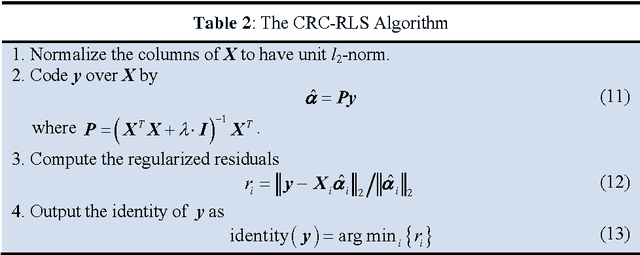
Abstract:By coding a query sample as a sparse linear combination of all training samples and then classifying it by evaluating which class leads to the minimal coding residual, sparse representation based classification (SRC) leads to interesting results for robust face recognition. It is widely believed that the l1- norm sparsity constraint on coding coefficients plays a key role in the success of SRC, while its use of all training samples to collaboratively represent the query sample is rather ignored. In this paper we discuss how SRC works, and show that the collaborative representation mechanism used in SRC is much more crucial to its success of face classification. The SRC is a special case of collaborative representation based classification (CRC), which has various instantiations by applying different norms to the coding residual and coding coefficient. More specifically, the l1 or l2 norm characterization of coding residual is related to the robustness of CRC to outlier facial pixels, while the l1 or l2 norm characterization of coding coefficient is related to the degree of discrimination of facial features. Extensive experiments were conducted to verify the face recognition accuracy and efficiency of CRC with different instantiations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge