Xiangchen Wu
Solving the Min-Max Multiple Traveling Salesmen Problem via Learning-Based Path Generation and Optimal Splitting
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:This study addresses the Min-Max Multiple Traveling Salesmen Problem ($m^3$-TSP), which aims to coordinate tours for multiple salesmen such that the length of the longest tour is minimized. Due to its NP-hard nature, exact solvers become impractical under the assumption that $P \ne NP$. As a result, learning-based approaches have gained traction for their ability to rapidly generate high-quality approximate solutions. Among these, two-stage methods combine learning-based components with classical solvers, simplifying the learning objective. However, this decoupling often disrupts consistent optimization, potentially degrading solution quality. To address this issue, we propose a novel two-stage framework named \textbf{Generate-and-Split} (GaS), which integrates reinforcement learning (RL) with an optimal splitting algorithm in a joint training process. The splitting algorithm offers near-linear scalability with respect to the number of cities and guarantees optimal splitting in Euclidean space for any given path. To facilitate the joint optimization of the RL component with the algorithm, we adopt an LSTM-enhanced model architecture to address partial observability. Extensive experiments show that the proposed GaS framework significantly outperforms existing learning-based approaches in both solution quality and transferability.
CVM-Cervix: A Hybrid Cervical Pap-Smear Image Classification Framework Using CNN, Visual Transformer and Multilayer Perceptron
Jun 02, 2022

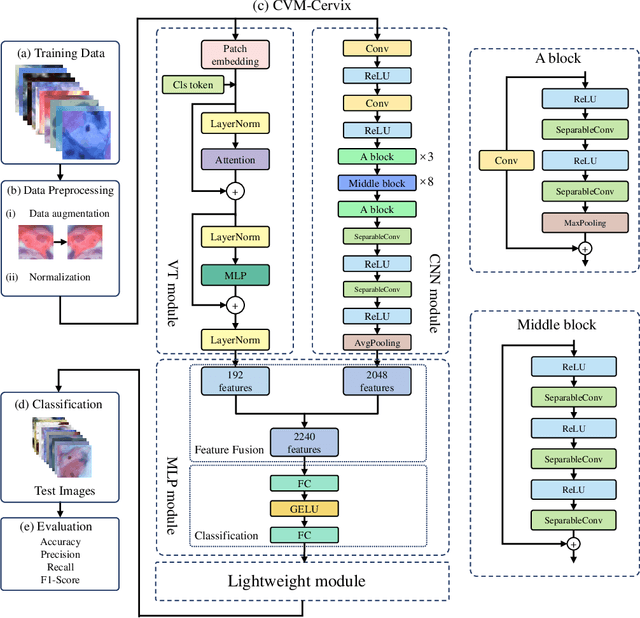

Abstract:Cervical cancer is the seventh most common cancer among all the cancers worldwide and the fourth most common cancer among women. Cervical cytopathology image classification is an important method to diagnose cervical cancer. Manual screening of cytopathology images is time-consuming and error-prone. The emergence of the automatic computer-aided diagnosis system solves this problem. This paper proposes a framework called CVM-Cervix based on deep learning to perform cervical cell classification tasks. It can analyze pap slides quickly and accurately. CVM-Cervix first proposes a Convolutional Neural Network module and a Visual Transformer module for local and global feature extraction respectively, then a Multilayer Perceptron module is designed to fuse the local and global features for the final classification. Experimental results show the effectiveness and potential of the proposed CVM-Cervix in the field of cervical Pap smear image classification. In addition, according to the practical needs of clinical work, we perform a lightweight post-processing to compress the model.
DeepCervix: A Deep Learning-based Framework for the Classification of Cervical Cells Using Hybrid Deep Feature Fusion Techniques
Feb 24, 2021



Abstract:Cervical cancer, one of the most common fatal cancers among women, can be prevented by regular screening to detect any precancerous lesions at early stages and treat them. Pap smear test is a widely performed screening technique for early detection of cervical cancer, whereas this manual screening method suffers from high false-positive results because of human errors. To improve the manual screening practice, machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) based computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) systems have been investigated widely to classify cervical pap cells. Most of the existing researches require pre-segmented images to obtain good classification results, whereas accurate cervical cell segmentation is challenging because of cell clustering. Some studies rely on handcrafted features, which cannot guarantee the classification stage's optimality. Moreover, DL provides poor performance for a multiclass classification task when there is an uneven distribution of data, which is prevalent in the cervical cell dataset. This investigation has addressed those limitations by proposing DeepCervix, a hybrid deep feature fusion (HDFF) technique based on DL to classify the cervical cells accurately. Our proposed method uses various DL models to capture more potential information to enhance classification performance. Our proposed HDFF method is tested on the publicly available SIPAKMED dataset and compared the performance with base DL models and the LF method. For the SIPAKMED dataset, we have obtained the state-of-the-art classification accuracy of 99.85%, 99.38%, and 99.14% for 2-class, 3-class, and 5-class classification. Moreover, our method is tested on the Herlev dataset and achieves an accuracy of 98.32% for binary class and 90.32% for 7-class classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge