Wenzhe Wang
Effects of Prompt Length on Domain-specific Tasks for Large Language Models
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:In recent years, Large Language Models have garnered significant attention for their strong performance in various natural language tasks, such as machine translation and question answering. These models demonstrate an impressive ability to generalize across diverse tasks. However, their effectiveness in tackling domain-specific tasks, such as financial sentiment analysis and monetary policy understanding, remains a topic of debate, as these tasks often require specialized knowledge and precise reasoning. To address such challenges, researchers design various prompts to unlock the models' abilities. By carefully crafting input prompts, researchers can guide these models to produce more accurate responses. Consequently, prompt engineering has become a key focus of study. Despite the advancements in both models and prompt engineering, the relationship between the two-specifically, how prompt design impacts models' ability to perform domain-specific tasks-remains underexplored. This paper aims to bridge this research gap.
High-Order Tensor Recovery with A Tensor $U_1$ Norm
Nov 23, 2023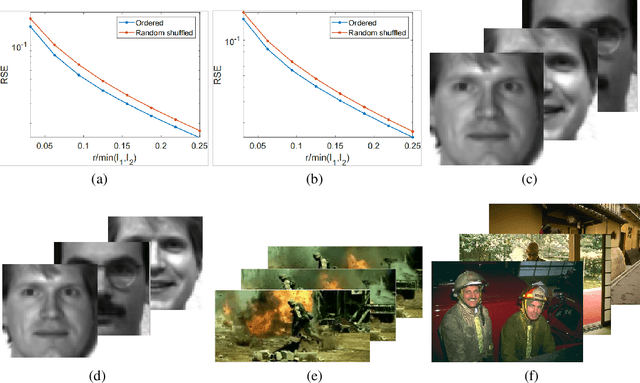
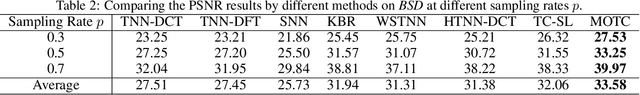
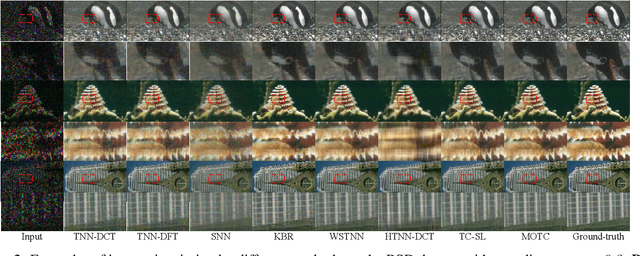
Abstract:Recently, numerous tensor SVD (t-SVD)-based tensor recovery methods have emerged, showing promise in processing visual data. However, these methods often suffer from performance degradation when confronted with high-order tensor data exhibiting non-smooth changes, commonly observed in real-world scenarios but ignored by the traditional t-SVD-based methods. Our objective in this study is to provide an effective tensor recovery technique for handling non-smooth changes in tensor data and efficiently explore the correlations of high-order tensor data across its various dimensions without introducing numerous variables and weights. To this end, we introduce a new tensor decomposition and a new tensor norm called the Tensor $U_1$ norm. We utilize these novel techniques in solving the problem of high-order tensor completion problem and provide theoretical guarantees for the exact recovery of the resulting tensor completion models. An optimization algorithm is proposed to solve the resulting tensor completion model iteratively by combining the proximal algorithm with the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers. Theoretical analysis showed the convergence of the algorithm to the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) point of the optimization problem. Numerical experiments demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed method in high-order tensor completion, especially for tensor data with non-smooth changes.
A Novel Tensor Factorization-Based Method with Robustness to Inaccurate Rank Estimation
May 19, 2023



Abstract:This study aims to solve the over-reliance on the rank estimation strategy in the standard tensor factorization-based tensor recovery and the problem of a large computational cost in the standard t-SVD-based tensor recovery. To this end, we proposes a new tensor norm with a dual low-rank constraint, which utilizes the low-rank prior and rank information at the same time. In the proposed tensor norm, a series of surrogate functions of the tensor tubal rank can be used to achieve better performance in harness low-rankness within tensor data. It is proven theoretically that the resulting tensor completion model can effectively avoid performance degradation caused by inaccurate rank estimation. Meanwhile, attributed to the proposed dual low-rank constraint, the t-SVD of a smaller tensor instead of the original big one is computed by using a sample trick. Based on this, the total cost at each iteration of the optimization algorithm is reduced to $\mathcal{O}(n^3\log n +kn^3)$ from $\mathcal{O}(n^4)$ achieved with standard methods, where $k$ is the estimation of the true tensor rank and far less than $n$. Our method was evaluated on synthetic and real-world data, and it demonstrated superior performance and efficiency over several existing state-of-the-art tensor completion methods.
PR-Net: Preference Reasoning for Personalized Video Highlight Detection
Sep 04, 2021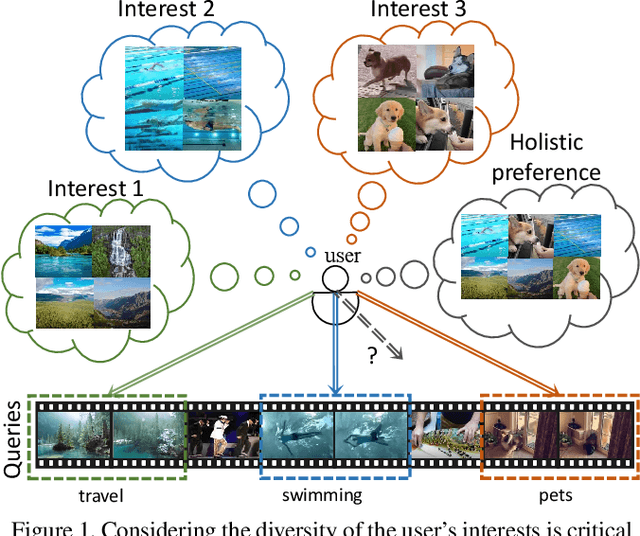
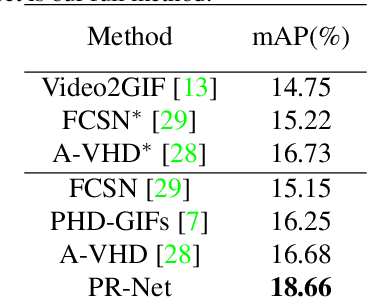
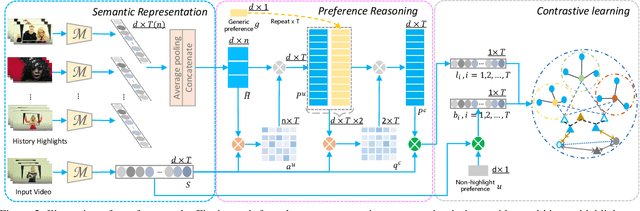
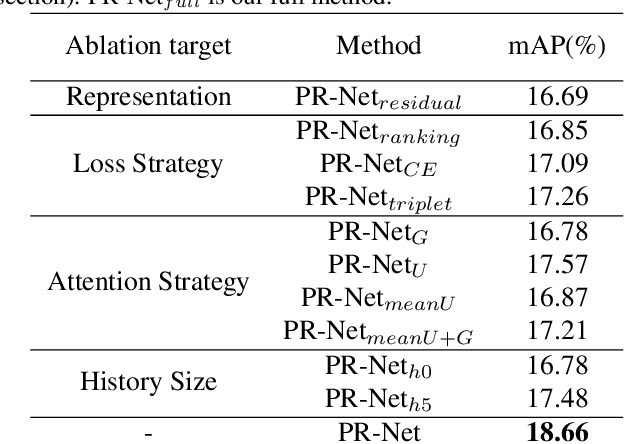
Abstract:Personalized video highlight detection aims to shorten a long video to interesting moments according to a user's preference, which has recently raised the community's attention. Current methods regard the user's history as holistic information to predict the user's preference but negating the inherent diversity of the user's interests, resulting in vague preference representation. In this paper, we propose a simple yet efficient preference reasoning framework (PR-Net) to explicitly take the diverse interests into account for frame-level highlight prediction. Specifically, distinct user-specific preferences for each input query frame are produced, presented as the similarity weighted sum of history highlights to the corresponding query frame. Next, distinct comprehensive preferences are formed by the user-specific preferences and a learnable generic preference for more overall highlight measurement. Lastly, the degree of highlight and non-highlight for each query frame is calculated as semantic similarity to its comprehensive and non-highlight preferences, respectively. Besides, to alleviate the ambiguity due to the incomplete annotation, a new bi-directional contrastive loss is proposed to ensure a compact and differentiable metric space. In this way, our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods with a relative improvement of 12% in mean accuracy precision.
Frame Aggregation and Multi-Modal Fusion Framework for Video-Based Person Recognition
Oct 19, 2020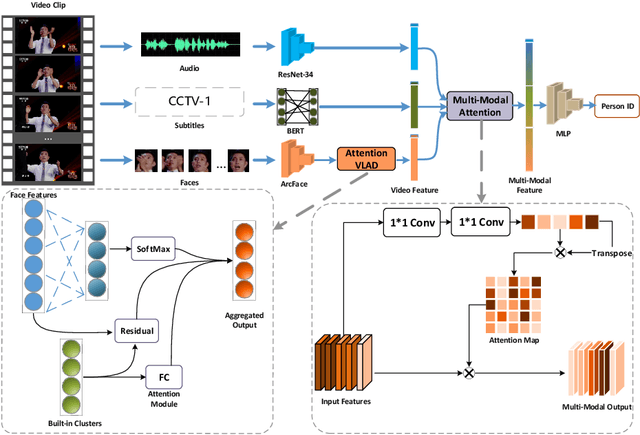
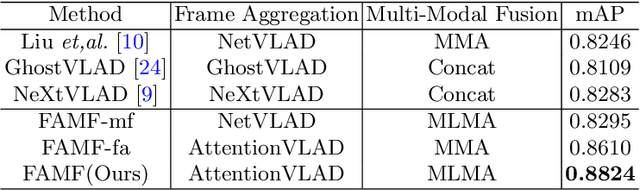
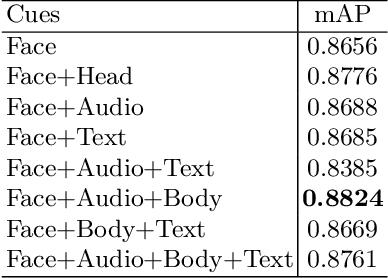
Abstract:Video-based person recognition is challenging due to persons being blocked and blurred, and the variation of shooting angle. Previous research always focused on person recognition on still images, ignoring similarity and continuity between video frames. To tackle the challenges above, we propose a novel Frame Aggregation and Multi-Modal Fusion (FAMF) framework for video-based person recognition, which aggregates face features and incorporates them with multi-modal information to identify persons in videos. For frame aggregation, we propose a novel trainable layer based on NetVLAD (named AttentionVLAD), which takes arbitrary number of features as input and computes a fixed-length aggregation feature based on feature quality. We show that introducing an attention mechanism to NetVLAD can effectively decrease the impact of low-quality frames. For the multi-model information of videos, we propose a Multi-Layer Multi-Modal Attention (MLMA) module to learn the correlation of multi-modality by adaptively updating Gram matrix. Experimental results on iQIYI-VID-2019 dataset show that our framework outperforms other state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge