Vikas Joshi
Building English ASR model with regional language support
Mar 10, 2025
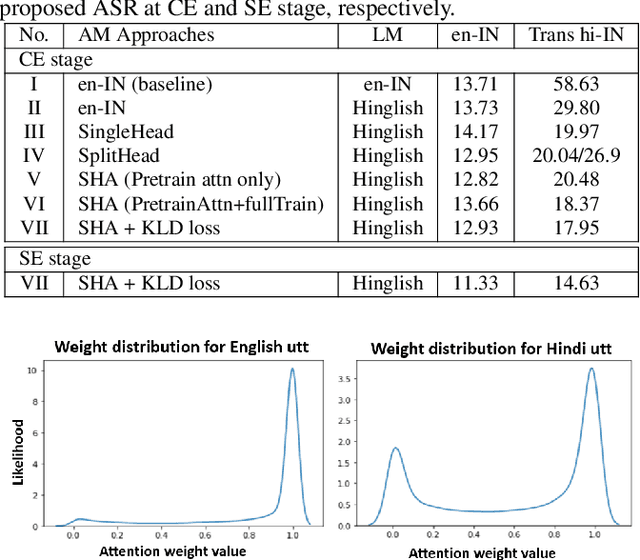

Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel approach to developing an English Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) system that can effectively handle Hindi queries, without compromising its performance on English. We propose a novel acoustic model (AM), referred to as SplitHead with Attention (SHA) model, features shared hidden layers across languages and language-specific projection layers combined via a self-attention mechanism. This mechanism estimates the weight for each language based on input data and weighs the corresponding language-specific projection layers accordingly. Additionally, we propose a language modeling approach that interpolates n-gram models from both English and transliterated Hindi text corpora. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, with a 69.3% and 5.7% relative reduction in word error rate on Hindi and English test sets respectively when compared to a monolingual English model.
Addressing speaker gender bias in large scale speech translation systems
Jan 10, 2025



Abstract:This study addresses the issue of speaker gender bias in Speech Translation (ST) systems, which can lead to offensive and inaccurate translations. The masculine bias often found in large-scale ST systems is typically perpetuated through training data derived from Machine Translation (MT) systems. Our approach involves two key steps. First, we employ Large Language Models (LLMs) to rectify translations based on the speaker's gender in a cost-effective manner. Second, we fine-tune the ST model with the corrected data, enabling the model to generate gender-specific translations directly from audio cues, without the need for explicit gender input. Additionally, we propose a three-mode fine-tuned model for scenarios where the speaker's gender is either predefined or should not be inferred from speech cues. We demonstrate a 70% improvement in translations for female speakers compared to our baseline and other large-scale ST systems, such as Seamless M4T and Canary, on the MuST-SHE test set.
Streaming Bilingual End-to-End ASR model using Attention over Multiple Softmax
Jan 22, 2024



Abstract:Even with several advancements in multilingual modeling, it is challenging to recognize multiple languages using a single neural model, without knowing the input language and most multilingual models assume the availability of the input language. In this work, we propose a novel bilingual end-to-end (E2E) modeling approach, where a single neural model can recognize both languages and also support switching between the languages, without any language input from the user. The proposed model has shared encoder and prediction networks, with language-specific joint networks that are combined via a self-attention mechanism. As the language-specific posteriors are combined, it produces a single posterior probability over all the output symbols, enabling a single beam search decoding and also allowing dynamic switching between the languages. The proposed approach outperforms the conventional bilingual baseline with 13.3%, 8.23% and 1.3% word error rate relative reduction on Hindi, English and code-mixed test sets, respectively.
* Published in IEEE's Spoken Language Technology (SLT) 2022, 8 pages (6 + 2 for references), 5 figures
Can AI Put Gamma-Ray Astrophysicists Out of a Job?
Apr 04, 2023

Abstract:In what will likely be a litany of generative-model-themed arXiv submissions celebrating April the 1st, we evaluate the capacity of state-of-the-art transformer models to create a paper detailing the detection of a Pulsar Wind Nebula with a non-existent Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescope (IACT) Array. We do this to evaluate the ability of such models to interpret astronomical observations and sources based on language information alone, and to assess potential means by which fraudulently generated scientific papers could be identified during peer review (given that reliable generative model watermarking has yet to be deployed for these tools). We conclude that our jobs as astronomers are safe for the time being. From this point on, prompts given to ChatGPT and Stable Diffusion are shown in orange, text generated by ChatGPT is shown in black, whereas analysis by the (human) authors is in blue.
WavFT: Acoustic model finetuning with labelled and unlabelled data
Apr 01, 2022

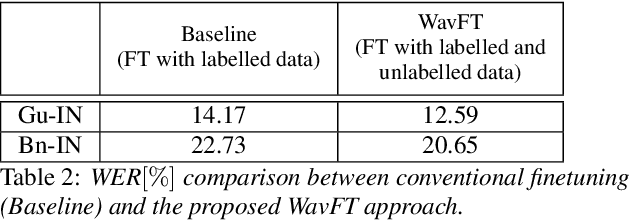
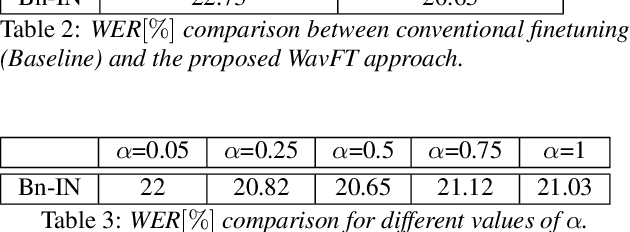
Abstract:Unsupervised and self-supervised learning methods have leveraged unlabelled data to improve the pretrained models. However, these methods need significantly large amount of unlabelled data and the computational cost of training models with such large amount of data can be prohibitively high. We address this issue by using unlabelled data during finetuning, instead of pretraining. We propose acoustic model finetuning (FT) using labelled and unlabelled data. The model is jointly trained to learn representations to classify senones, as well as learn contextual acoustic representations. Our training objective is a combination of cross entropy loss, suitable for classification task, and contrastive loss, suitable to learn acoustic representations. The proposed approach outperforms conventional finetuning with 11.2% and 9.19% word error rate relative (WERR) reduction on Gujarati and Bengali languages respectively.
Transfer Learning Approaches for Streaming End-to-End Speech Recognition System
Aug 17, 2020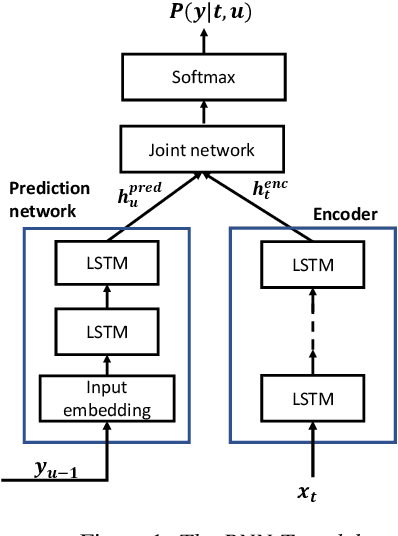
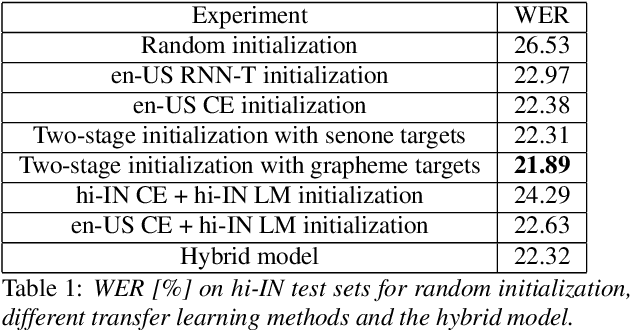
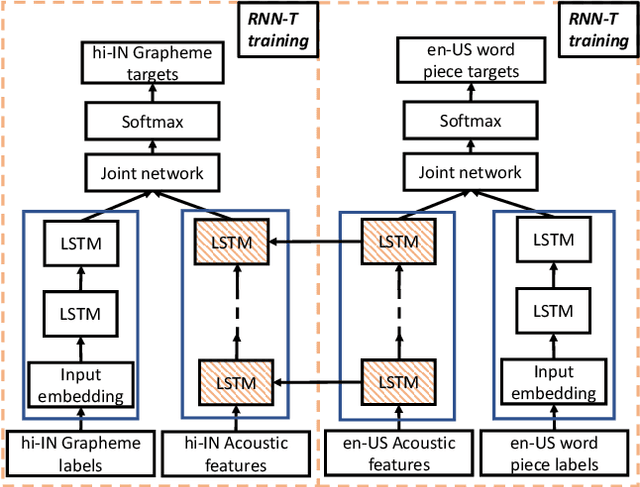
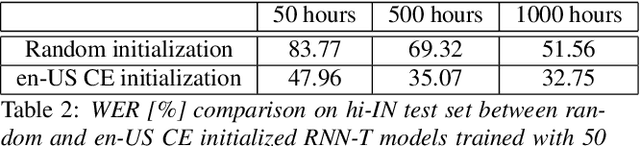
Abstract:Transfer learning (TL) is widely used in conventional hybrid automatic speech recognition (ASR) system, to transfer the knowledge from source to target language. TL can be applied to end-to-end (E2E) ASR system such as recurrent neural network transducer (RNN-T) models, by initializing the encoder and/or prediction network of the target language with the pre-trained models from source language. In the hybrid ASR system, transfer learning is typically done by initializing the target language acoustic model (AM) with source language AM. Several transfer learning strategies exist in the case of the RNN-T framework, depending upon the choice of the initialization model for encoder and prediction networks. This paper presents a comparative study of four different TL methods for RNN-T framework. We show 17% relative word error rate reduction with different TL methods over randomly initialized RNN-T model. We also study the impact of TL with varying amount of training data ranging from 50 hours to 1000 hours and show the efficacy of TL for languages with small amount of training data.
Learning not to Discriminate: Task Agnostic Learning for Improving Monolingual and Code-switched Speech Recognition
Jun 09, 2020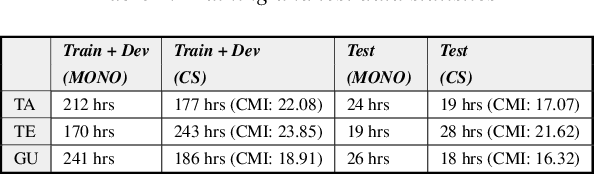
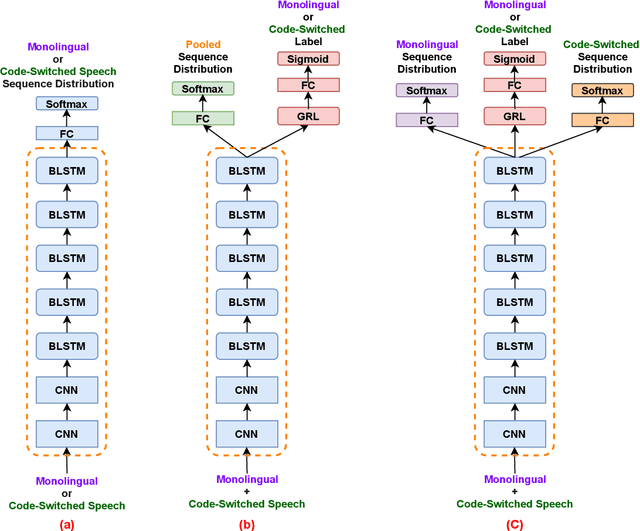
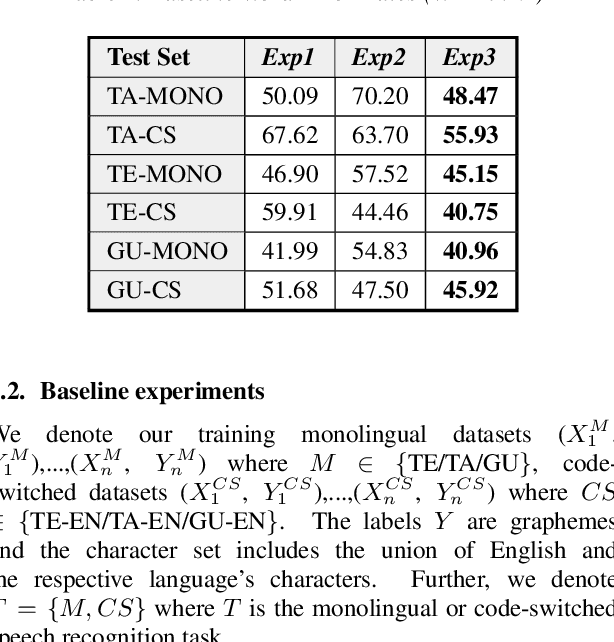
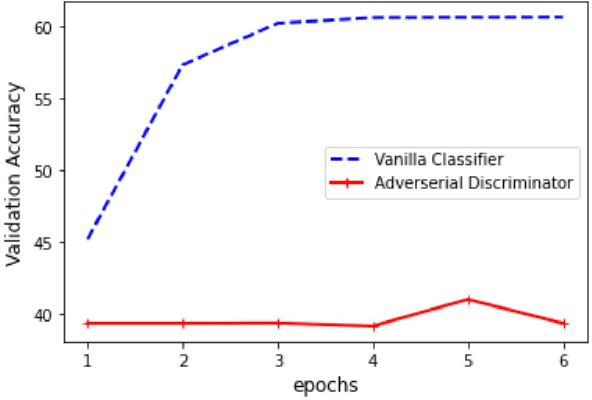
Abstract:Recognizing code-switched speech is challenging for Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) for a variety of reasons, including the lack of code-switched training data. Recently, we showed that monolingual ASR systems fine-tuned on code-switched data deteriorate in performance on monolingual speech recognition, which is not desirable as ASR systems deployed in multilingual scenarios should recognize both monolingual and code-switched speech with high accuracy. Our experiments indicated that this loss in performance could be mitigated by using certain strategies for fine-tuning and regularization, leading to improvements in both monolingual and code-switched ASR. In this work, we present further improvements over our previous work by using domain adversarial learning to train task agnostic models. We evaluate the classification accuracy of an adversarial discriminator and show that it can learn shared layer parameters that are task agnostic. We train end-to-end ASR systems starting with a pooled model that uses monolingual and code-switched data along with the adversarial discriminator. Our proposed technique leads to reductions in Word Error Rates (WER) in monolingual and code-switched test sets across three language pairs.
Learning to Recognize Code-switched Speech Without Forgetting Monolingual Speech Recognition
Jun 01, 2020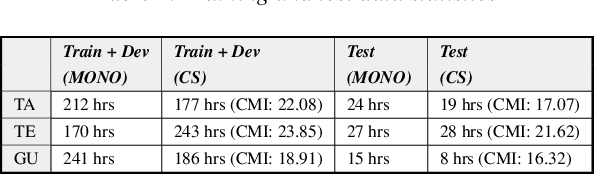
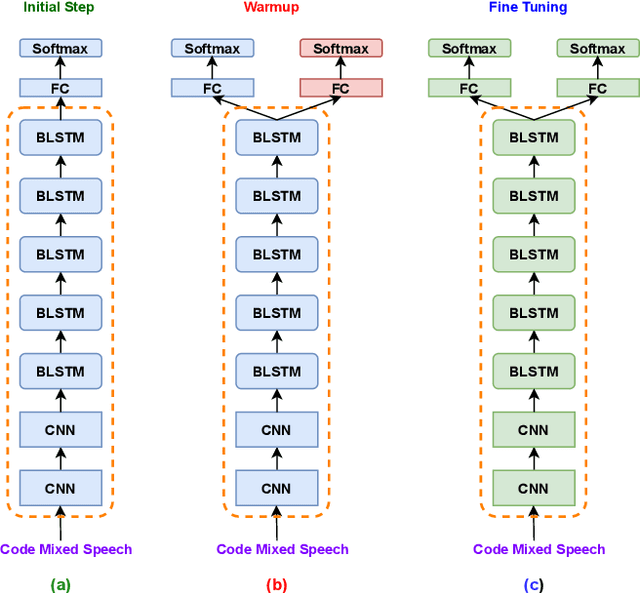
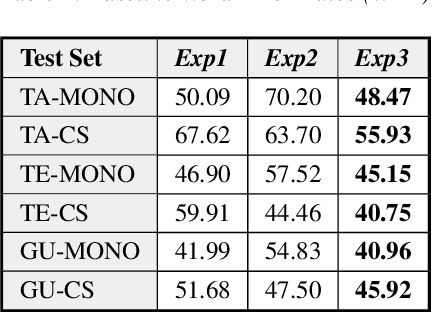
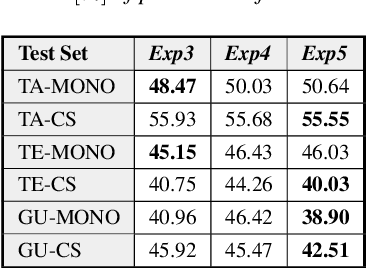
Abstract:Recently, there has been significant progress made in Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) of code-switched speech, leading to gains in accuracy on code-switched datasets in many language pairs. Code-switched speech co-occurs with monolingual speech in one or both languages being mixed. In this work, we show that fine-tuning ASR models on code-switched speech harms performance on monolingual speech. We point out the need to optimize models for code-switching while also ensuring that monolingual performance is not sacrificed. Monolingual models may be trained on thousands of hours of speech which may not be available for re-training a new model. We propose using the Learning Without Forgetting (LWF) framework for code-switched ASR when we only have access to a monolingual model and do not have the data it was trained on. We show that it is possible to train models using this framework that perform well on both code-switched and monolingual test sets. In cases where we have access to monolingual training data as well, we propose regularization strategies for fine-tuning models for code-switching without sacrificing monolingual accuracy. We report improvements in Word Error Rate (WER) in monolingual and code-switched test sets compared to baselines that use pooled data and simple fine-tuning.
Modified SPLICE and its Extension to Non-Stereo Data for Noise Robust Speech Recognition
Jul 15, 2013
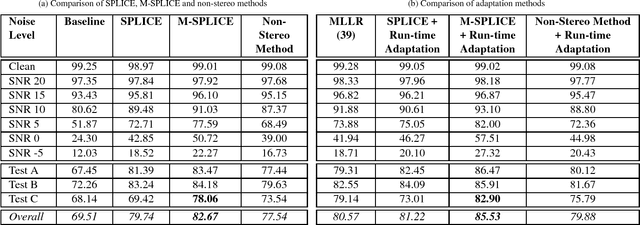
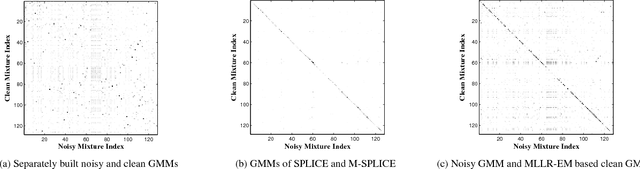
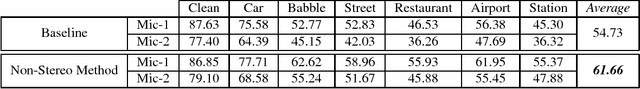
Abstract:In this paper, a modification to the training process of the popular SPLICE algorithm has been proposed for noise robust speech recognition. The modification is based on feature correlations, and enables this stereo-based algorithm to improve the performance in all noise conditions, especially in unseen cases. Further, the modified framework is extended to work for non-stereo datasets where clean and noisy training utterances, but not stereo counterparts, are required. Finally, an MLLR-based computationally efficient run-time noise adaptation method in SPLICE framework has been proposed. The modified SPLICE shows 8.6% absolute improvement over SPLICE in Test C of Aurora-2 database, and 2.93% overall. Non-stereo method shows 10.37% and 6.93% absolute improvements over Aurora-2 and Aurora-4 baseline models respectively. Run-time adaptation shows 9.89% absolute improvement in modified framework as compared to SPLICE for Test C, and 4.96% overall w.r.t. standard MLLR adaptation on HMMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge