Gurunath Reddy Madhumani
Automatic Neural Lyrics and Melody Composition
Nov 12, 2020
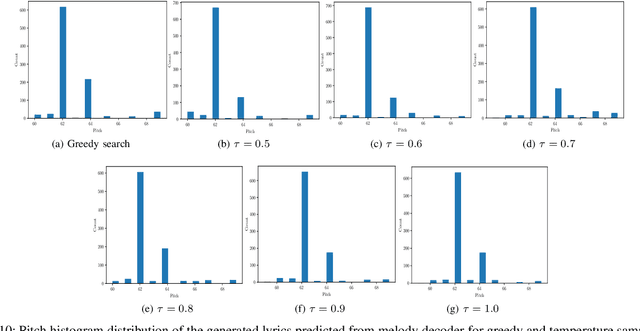
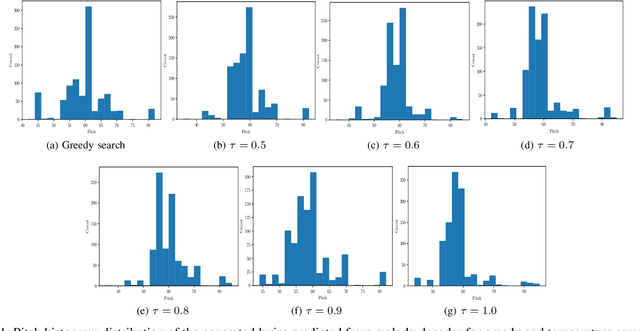
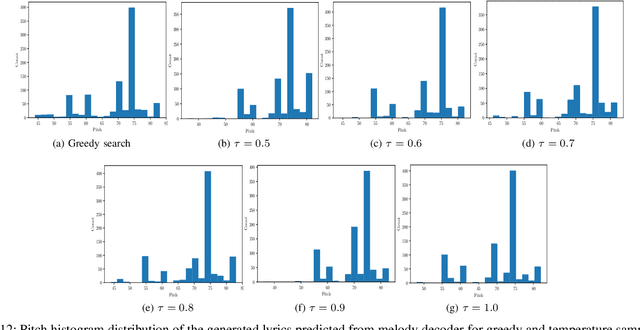
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a technique to address the most challenging aspect of algorithmic songwriting process, which enables the human community to discover original lyrics, and melodies suitable for the generated lyrics. The proposed songwriting system, Automatic Neural Lyrics and Melody Composition (AutoNLMC) is an attempt to make the whole process of songwriting automatic using artificial neural networks. Our lyric to vector (lyric2vec) model trained on a large set of lyric-melody pairs dataset parsed at syllable, word and sentence levels are large scale embedding models enable us to train data driven model such as recurrent neural networks for popular English songs. AutoNLMC is a encoder-decoder sequential recurrent neural network model consisting of a lyric generator, a lyric encoder and melody decoder trained end-to-end. AutoNLMC is designed to generate both lyrics and corresponding melody automatically for an amateur or a person without music knowledge. It can also take lyrics from professional lyric writer to generate matching melodies. The qualitative and quantitative evaluation measures revealed that the proposed method is indeed capable of generating original lyrics and corresponding melody for composing new songs.
Learning not to Discriminate: Task Agnostic Learning for Improving Monolingual and Code-switched Speech Recognition
Jun 09, 2020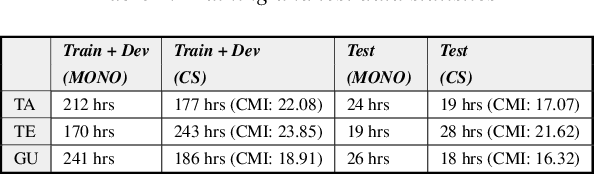
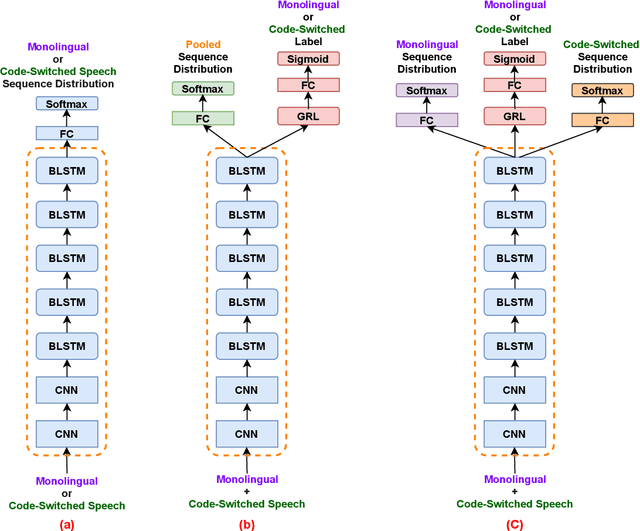
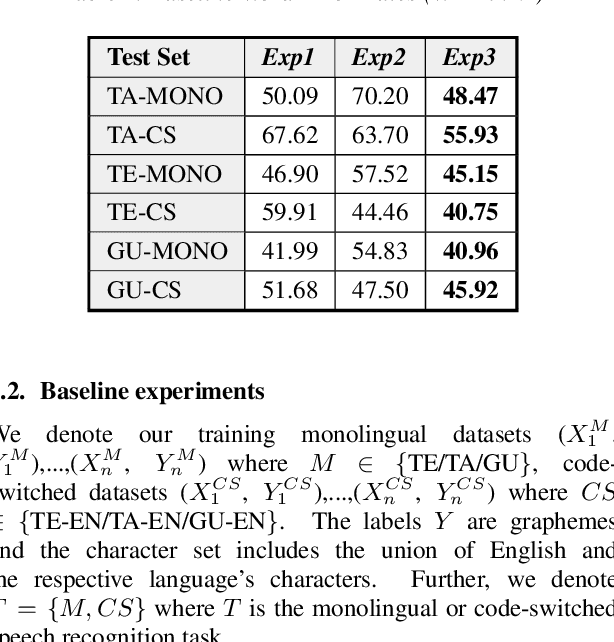
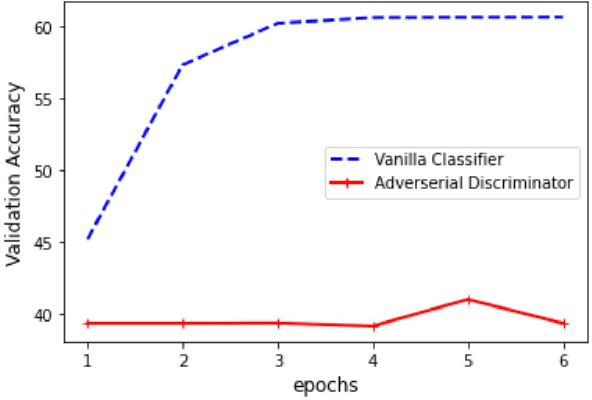
Abstract:Recognizing code-switched speech is challenging for Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) for a variety of reasons, including the lack of code-switched training data. Recently, we showed that monolingual ASR systems fine-tuned on code-switched data deteriorate in performance on monolingual speech recognition, which is not desirable as ASR systems deployed in multilingual scenarios should recognize both monolingual and code-switched speech with high accuracy. Our experiments indicated that this loss in performance could be mitigated by using certain strategies for fine-tuning and regularization, leading to improvements in both monolingual and code-switched ASR. In this work, we present further improvements over our previous work by using domain adversarial learning to train task agnostic models. We evaluate the classification accuracy of an adversarial discriminator and show that it can learn shared layer parameters that are task agnostic. We train end-to-end ASR systems starting with a pooled model that uses monolingual and code-switched data along with the adversarial discriminator. Our proposed technique leads to reductions in Word Error Rates (WER) in monolingual and code-switched test sets across three language pairs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge