Purvi Agrawal
Building English ASR model with regional language support
Mar 10, 2025
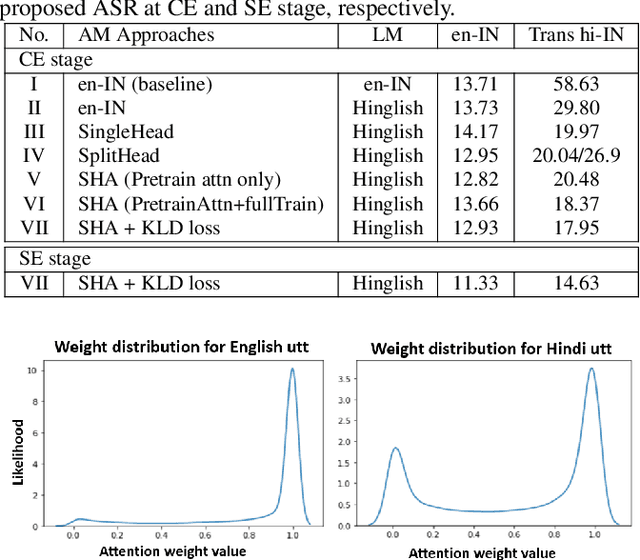

Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel approach to developing an English Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) system that can effectively handle Hindi queries, without compromising its performance on English. We propose a novel acoustic model (AM), referred to as SplitHead with Attention (SHA) model, features shared hidden layers across languages and language-specific projection layers combined via a self-attention mechanism. This mechanism estimates the weight for each language based on input data and weighs the corresponding language-specific projection layers accordingly. Additionally, we propose a language modeling approach that interpolates n-gram models from both English and transliterated Hindi text corpora. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, with a 69.3% and 5.7% relative reduction in word error rate on Hindi and English test sets respectively when compared to a monolingual English model.
Streaming Bilingual End-to-End ASR model using Attention over Multiple Softmax
Jan 22, 2024



Abstract:Even with several advancements in multilingual modeling, it is challenging to recognize multiple languages using a single neural model, without knowing the input language and most multilingual models assume the availability of the input language. In this work, we propose a novel bilingual end-to-end (E2E) modeling approach, where a single neural model can recognize both languages and also support switching between the languages, without any language input from the user. The proposed model has shared encoder and prediction networks, with language-specific joint networks that are combined via a self-attention mechanism. As the language-specific posteriors are combined, it produces a single posterior probability over all the output symbols, enabling a single beam search decoding and also allowing dynamic switching between the languages. The proposed approach outperforms the conventional bilingual baseline with 13.3%, 8.23% and 1.3% word error rate relative reduction on Hindi, English and code-mixed test sets, respectively.
* Published in IEEE's Spoken Language Technology (SLT) 2022, 8 pages (6 + 2 for references), 5 figures
A Multi-Head Relevance Weighting Framework For Learning Raw Waveform Audio Representations
Jul 30, 2021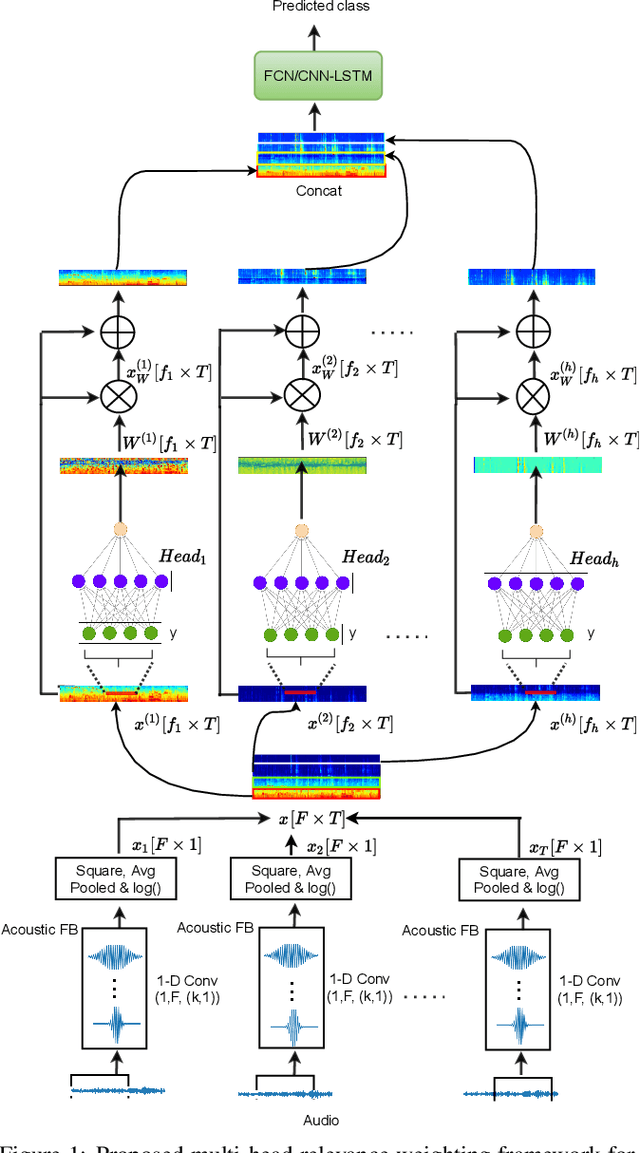
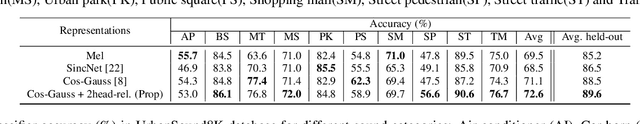
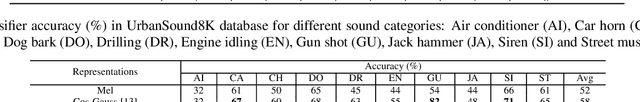
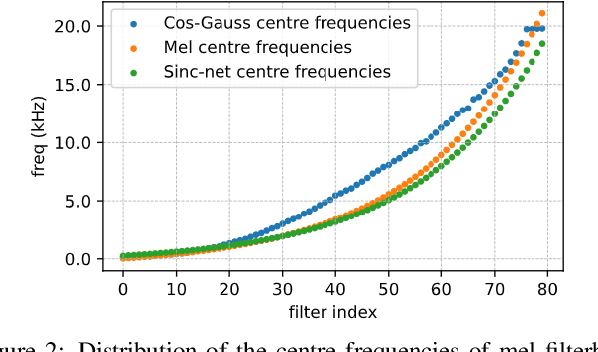
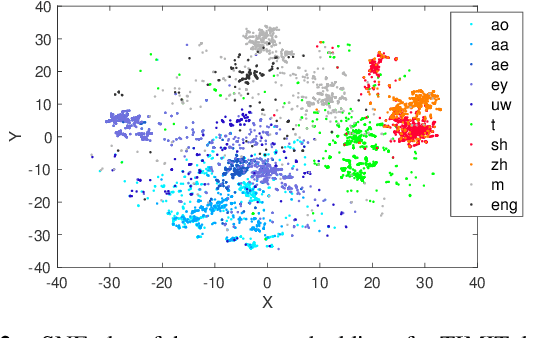
Abstract:In this work, we propose a multi-head relevance weighting framework to learn audio representations from raw waveforms. The audio waveform, split into windows of short duration, are processed with a 1-D convolutional layer of cosine modulated Gaussian filters acting as a learnable filterbank. The key novelty of the proposed framework is the introduction of multi-head relevance on the learnt filterbank representations. Each head of the relevance network is modelled as a separate sub-network. These heads perform representation enhancement by generating weight masks for different parts of the time-frequency representation learnt by the parametric acoustic filterbank layer. The relevance weighted representations are fed to a neural classifier and the whole system is trained jointly for the audio classification objective. Experiments are performed on the DCASE2020 Task 1A challenge as well as the Urban Sound Classification (USC) tasks. In these experiments, the proposed approach yields relative improvements of 10% and 23% respectively for the DCASE2020 and USC datasets over the mel-spectrogram baseline. Also, the analysis of multi-head relevance weights provides insights on the learned representations.
Representation Learning For Speech Recognition Using Feedback Based Relevance Weighting
Feb 15, 2021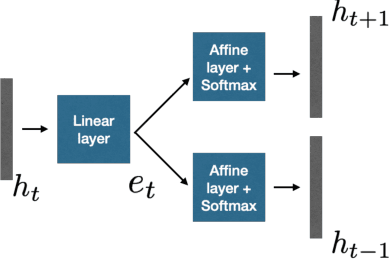
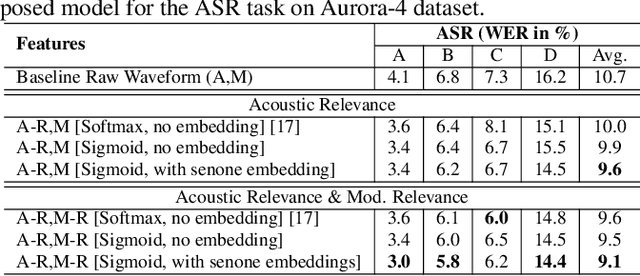

Abstract:In this work, we propose an acoustic embedding based approach for representation learning in speech recognition. The proposed approach involves two stages comprising of acoustic filterbank learning from raw waveform, followed by modulation filterbank learning. In each stage, a relevance weighting operation is employed that acts as a feature selection module. In particular, the relevance weighting network receives embeddings of the model outputs from the previous time instants as feedback. The proposed relevance weighting scheme allows the respective feature representations to be adaptively selected before propagation to the higher layers. The application of the proposed approach for the task of speech recognition on Aurora-4 and CHiME-3 datasets gives significant performance improvements over baseline systems on raw waveform signal as well as those based on mel representations (average relative improvement of 15% over the mel baseline on Aurora-4 dataset and 7% on CHiME-3 dataset).
* arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2011.00721, arXiv:2011.02136, arXiv:2001.07067
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge