Tianchen Liu
Cascade IPG Observer for Underwater Robot State Estimation
Apr 21, 2025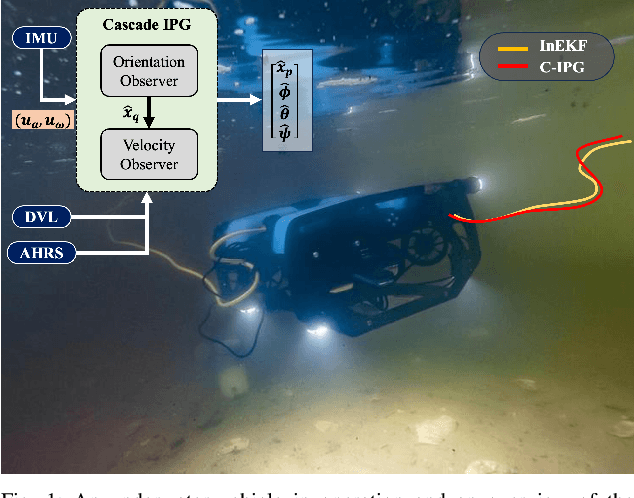
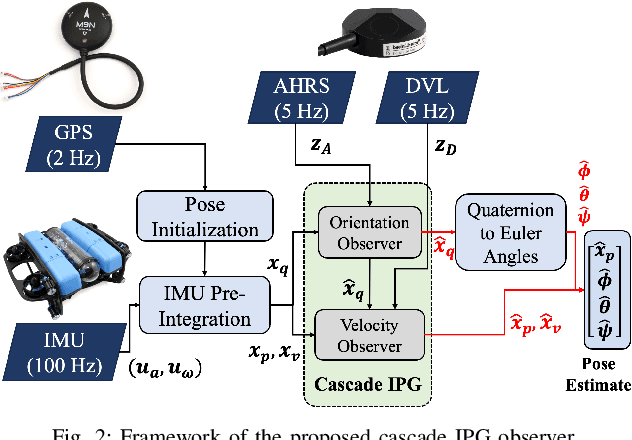
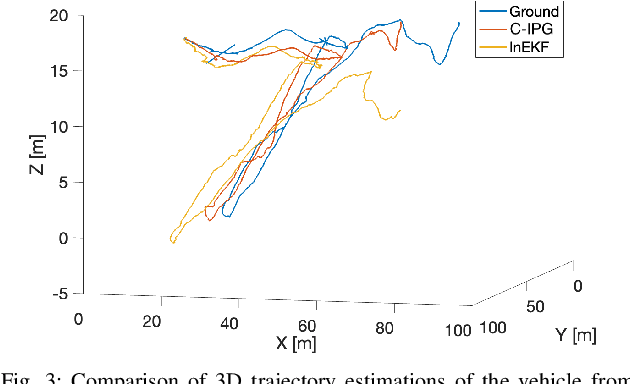
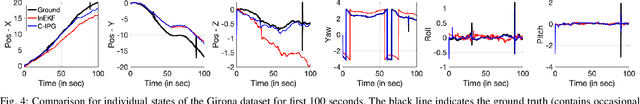
Abstract:This paper presents a novel cascade nonlinear observer framework for inertial state estimation. It tackles the problem of intermediate state estimation when external localization is unavailable or in the event of a sensor outage. The proposed observer comprises two nonlinear observers based on a recently developed iteratively preconditioned gradient descent (IPG) algorithm. It takes the inputs via an IMU preintegration model where the first observer is a quaternion-based IPG. The output for the first observer is the input for the second observer, estimating the velocity and, consequently, the position. The proposed observer is validated on a public underwater dataset and a real-world experiment using our robot platform. The estimation is compared with an extended Kalman filter (EKF) and an invariant extended Kalman filter (InEKF). Results demonstrate that our method outperforms these methods regarding better positional accuracy and lower variance.
3D Water Quality Mapping using Invariant Extended Kalman Filtering for Underwater Robot Localization
Sep 17, 2024Abstract:Water quality mapping for critical parameters such as temperature, salinity, and turbidity is crucial for assessing an aquaculture farm's health and yield capacity. Traditional approaches involve using boats or human divers, which are time-constrained and lack depth variability. This work presents an innovative approach to 3D water quality mapping in shallow water environments using a BlueROV2 equipped with GPS and a water quality sensor. This system allows for accurate location correction by resurfacing when errors occur. This study is being conducted at an oyster farm in the Chesapeake Bay, USA, providing a more comprehensive and precise water quality analysis in aquaculture settings.
Performance Trade-off and Joint Waveform Design for MIMO-OFDM DFRC Systems
Jan 04, 2024Abstract:Dual-functional radar-communication (DFRC) has attracted considerable attention. This paper considers the frequency-selective multipath fading environment and proposes DFRC waveform design strategies based on multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) and orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) techniques. In the proposed waveform design strategies, the Cramer-Rao bound (CRB) of the radar system, the inter-stream interference (ISI) and the achievable rate of the communication system, are respectively considered as the performance metrics. In this paper, we focus on the performance trade-off between the radar system and the communication system, and the optimization problems are formulated. In the ISI minimization based waveform design strategy, the optimization problem is convex and can be easily solved. In the achievable rate maximization based waveform design strategy, we propose a water-filling (WF) and sequential quadratic programming (SQP) based algorithm to derive the covariance matrix and the precoding matrix. Simulation results validate the proposed DFRC waveform designs and show that the achievable rate maximization based strategy has a better performance than the ISI minimization based strategy.
Archiving Body Movements: Collective Generation of Chinese Calligraphy
Nov 27, 2023Abstract:As a communication channel, body movements have been widely explored in behavioral studies and kinesics. Performing and visual arts share the same interests but focus on documenting and representing human body movements, such as for dance notation and visual work creation. This paper investigates body movements in oriental calligraphy and how to apply calligraphy principles to stimulate and archive body movements. Through an artwork (Wushu), the authors experiment with an interactive and generative approach to engage the audience's bodily participation and archive the body movements as a compendium of generated calligraphy. The audience assumes the role of both writers and readers; creating ("writing") and appreciating ("reading") the generated calligraphy becomes a cyclical process within this infinite "Book," which can motivate further attention and discussions concerning Chinese characters and calligraphy.
UIVNAV: Underwater Information-driven Vision-based Navigation via Imitation Learning
Sep 15, 2023Abstract:Autonomous navigation in the underwater environment is challenging due to limited visibility, dynamic changes, and the lack of a cost-efficient accurate localization system. We introduce UIVNav, a novel end-to-end underwater navigation solution designed to drive robots over Objects of Interest (OOI) while avoiding obstacles, without relying on localization. UIVNav uses imitation learning and is inspired by the navigation strategies used by human divers who do not rely on localization. UIVNav consists of the following phases: (1) generating an intermediate representation (IR), and (2) training the navigation policy based on human-labeled IR. By training the navigation policy on IR instead of raw data, the second phase is domain-invariant -- the navigation policy does not need to be retrained if the domain or the OOI changes. We show this by deploying the same navigation policy for surveying two different OOIs, oyster and rock reefs, in two different domains, simulation, and a real pool. We compared our method with complete coverage and random walk methods which showed that our method is more efficient in gathering information for OOIs while also avoiding obstacles. The results show that UIVNav chooses to visit the areas with larger area sizes of oysters or rocks with no prior information about the environment or localization. Moreover, a robot using UIVNav compared to complete coverage method surveys on average 36% more oysters when traveling the same distances. We also demonstrate the feasibility of real-time deployment of UIVNavin pool experiments with BlueROV underwater robot for surveying a bed of oyster shells.
Iteratively Preconditioned Gradient-Descent Approach for Moving Horizon Estimation Problems
Jun 22, 2023


Abstract:Moving horizon estimation (MHE) is a widely studied state estimation approach in several practical applications. In the MHE problem, the state estimates are obtained via the solution of an approximated nonlinear optimization problem. However, this optimization step is known to be computationally complex. Given this limitation, this paper investigates the idea of iteratively preconditioned gradient-descent (IPG) to solve MHE problem with the aim of an improved performance than the existing solution techniques. To our knowledge, the preconditioning technique is used for the first time in this paper to reduce the computational cost and accelerate the crucial optimization step for MHE. The convergence guarantee of the proposed iterative approach for a class of MHE problems is presented. Additionally, sufficient conditions for the MHE problem to be convex are also derived. Finally, the proposed method is implemented on a unicycle localization example. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed approach can achieve better accuracy with reduced computational costs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge