Tao Gao
Pangu Ultra MoE: How to Train Your Big MoE on Ascend NPUs
May 07, 2025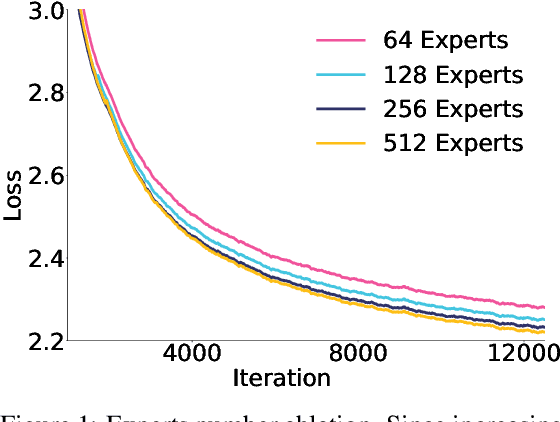

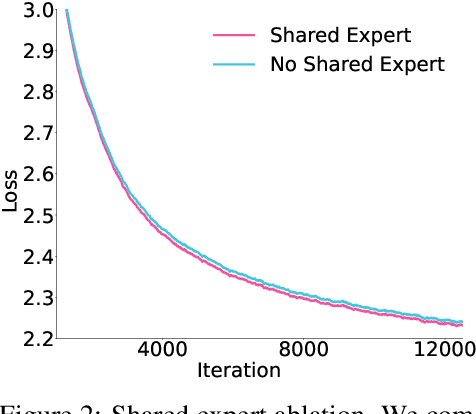
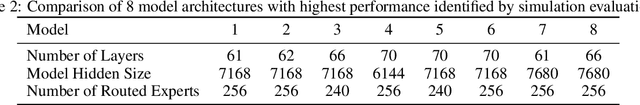
Abstract:Sparse large language models (LLMs) with Mixture of Experts (MoE) and close to a trillion parameters are dominating the realm of most capable language models. However, the massive model scale poses significant challenges for the underlying software and hardware systems. In this paper, we aim to uncover a recipe to harness such scale on Ascend NPUs. The key goals are better usage of the computing resources under the dynamic sparse model structures and materializing the expected performance gain on the actual hardware. To select model configurations suitable for Ascend NPUs without repeatedly running the expensive experiments, we leverage simulation to compare the trade-off of various model hyperparameters. This study led to Pangu Ultra MoE, a sparse LLM with 718 billion parameters, and we conducted experiments on the model to verify the simulation results. On the system side, we dig into Expert Parallelism to optimize the communication between NPU devices to reduce the synchronization overhead. We also optimize the memory efficiency within the devices to further reduce the parameter and activation management overhead. In the end, we achieve an MFU of 30.0% when training Pangu Ultra MoE, with performance comparable to that of DeepSeek R1, on 6K Ascend NPUs, and demonstrate that the Ascend system is capable of harnessing all the training stages of the state-of-the-art language models. Extensive experiments indicate that our recipe can lead to efficient training of large-scale sparse language models with MoE. We also study the behaviors of such models for future reference.
AI-native Memory 2.0: Second Me
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Human interaction with the external world fundamentally involves the exchange of personal memory, whether with other individuals, websites, applications, or, in the future, AI agents. A significant portion of this interaction is redundant, requiring users to repeatedly provide the same information across different contexts. Existing solutions, such as browser-stored credentials, autofill mechanisms, and unified authentication systems, have aimed to mitigate this redundancy by serving as intermediaries that store and retrieve commonly used user data. The advent of large language models (LLMs) presents an opportunity to redefine memory management through an AI-native paradigm: SECOND ME. SECOND ME acts as an intelligent, persistent memory offload system that retains, organizes, and dynamically utilizes user-specific knowledge. By serving as an intermediary in user interactions, it can autonomously generate context-aware responses, prefill required information, and facilitate seamless communication with external systems, significantly reducing cognitive load and interaction friction. Unlike traditional memory storage solutions, SECOND ME extends beyond static data retention by leveraging LLM-based memory parameterization. This enables structured organization, contextual reasoning, and adaptive knowledge retrieval, facilitating a more systematic and intelligent approach to memory management. As AI-driven personal agents like SECOND ME become increasingly integrated into digital ecosystems, SECOND ME further represents a critical step toward augmenting human-world interaction with persistent, contextually aware, and self-optimizing memory systems. We have open-sourced the fully localizable deployment system at GitHub: https://github.com/Mindverse/Second-Me.
APT: Architectural Planning and Text-to-Blueprint Construction Using Large Language Models for Open-World Agents
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:We present APT, an advanced Large Language Model (LLM)-driven framework that enables autonomous agents to construct complex and creative structures within the Minecraft environment. Unlike previous approaches that primarily concentrate on skill-based open-world tasks or rely on image-based diffusion models for generating voxel-based structures, our method leverages the intrinsic spatial reasoning capabilities of LLMs. By employing chain-of-thought decomposition along with multimodal inputs, the framework generates detailed architectural layouts and blueprints that the agent can execute under zero-shot or few-shot learning scenarios. Our agent incorporates both memory and reflection modules to facilitate lifelong learning, adaptive refinement, and error correction throughout the building process. To rigorously evaluate the agent's performance in this emerging research area, we introduce a comprehensive benchmark consisting of diverse construction tasks designed to test creativity, spatial reasoning, adherence to in-game rules, and the effective integration of multimodal instructions. Experimental results using various GPT-based LLM backends and agent configurations demonstrate the agent's capacity to accurately interpret extensive instructions involving numerous items, their positions, and orientations. The agent successfully produces complex structures complete with internal functionalities such as Redstone-powered systems. A/B testing indicates that the inclusion of a memory module leads to a significant increase in performance, emphasizing its role in enabling continuous learning and the reuse of accumulated experience. Additionally, the agent's unexpected emergence of scaffolding behavior highlights the potential of future LLM-driven agents to utilize subroutine planning and leverage the emergence ability of LLMs to autonomously develop human-like problem-solving techniques.
All-in-one Weather-degraded Image Restoration via Adaptive Degradation-aware Self-prompting Model
Nov 12, 2024



Abstract:Existing approaches for all-in-one weather-degraded image restoration suffer from inefficiencies in leveraging degradation-aware priors, resulting in sub-optimal performance in adapting to different weather conditions. To this end, we develop an adaptive degradation-aware self-prompting model (ADSM) for all-in-one weather-degraded image restoration. Specifically, our model employs the contrastive language-image pre-training model (CLIP) to facilitate the training of our proposed latent prompt generators (LPGs), which represent three types of latent prompts to characterize the degradation type, degradation property and image caption. Moreover, we integrate the acquired degradation-aware prompts into the time embedding of diffusion model to improve degradation perception. Meanwhile, we employ the latent caption prompt to guide the reverse sampling process using the cross-attention mechanism, thereby guiding the accurate image reconstruction. Furthermore, to accelerate the reverse sampling procedure of diffusion model and address the limitations of frequency perception, we introduce a wavelet-oriented noise estimating network (WNE-Net). Extensive experiments conducted on eight publicly available datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach in both task-specific and all-in-one applications.
Inverse Attention Agent for Multi-Agent System
Oct 29, 2024
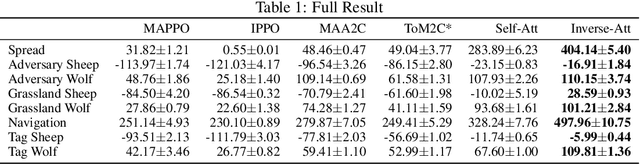

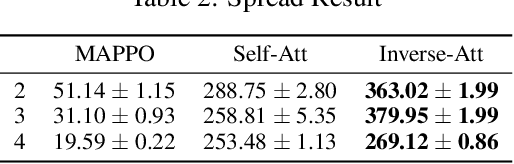
Abstract:A major challenge for Multi-Agent Systems is enabling agents to adapt dynamically to diverse environments in which opponents and teammates may continually change. Agents trained using conventional methods tend to excel only within the confines of their training cohorts; their performance drops significantly when confronting unfamiliar agents. To address this shortcoming, we introduce Inverse Attention Agents that adopt concepts from the Theory of Mind, implemented algorithmically using an attention mechanism and trained in an end-to-end manner. Crucial to determining the final actions of these agents, the weights in their attention model explicitly represent attention to different goals. We furthermore propose an inverse attention network that deduces the ToM of agents based on observations and prior actions. The network infers the attentional states of other agents, thereby refining the attention weights to adjust the agent's final action. We conduct experiments in a continuous environment, tackling demanding tasks encompassing cooperation, competition, and a blend of both. They demonstrate that the inverse attention network successfully infers the attention of other agents, and that this information improves agent performance. Additional human experiments show that, compared to baseline agent models, our inverse attention agents exhibit superior cooperation with humans and better emulate human behaviors.
Testing Large Language Models on Driving Theory Knowledge and Skills for Connected Autonomous Vehicles
Jul 24, 2024


Abstract:Handling long tail corner cases is a major challenge faced by autonomous vehicles (AVs). While large language models (LLMs) hold great potentials to handle the corner cases with excellent generalization and explanation capabilities and received increasing research interest on application to autonomous driving, there are still technical barriers to be tackled, such as strict model performance and huge computing resource requirements of LLMs. In this paper, we investigate a new approach of applying remote or edge LLMs to support autonomous driving. A key issue for such LLM assisted driving system is the assessment of LLMs on their understanding of driving theory and skills, ensuring they are qualified to undertake safety critical driving assistance tasks for CAVs. We design and run driving theory tests for several proprietary LLM models (OpenAI GPT models, Baidu Ernie and Ali QWen) and open-source LLM models (Tsinghua MiniCPM-2B and MiniCPM-Llama3-V2.5) with more than 500 multiple-choices theory test questions. Model accuracy, cost and processing latency are measured from the experiments. Experiment results show that while model GPT-4 passes the test with improved domain knowledge and Ernie has an accuracy of 85% (just below the 86% passing threshold), other LLM models including GPT-3.5 fail the test. For the test questions with images, the multimodal model GPT4-o has an excellent accuracy result of 96%, and the MiniCPM-Llama3-V2.5 achieves an accuracy of 76%. While GPT-4 holds stronger potential for CAV driving assistance applications, the cost of using model GPT4 is much higher, almost 50 times of that of using GPT3.5. The results can help make decision on the use of the existing LLMs for CAV applications and balancing on the model performance and cost.
Unpaired Photo-realistic Image Deraining with Energy-informed Diffusion Model
Jul 24, 2024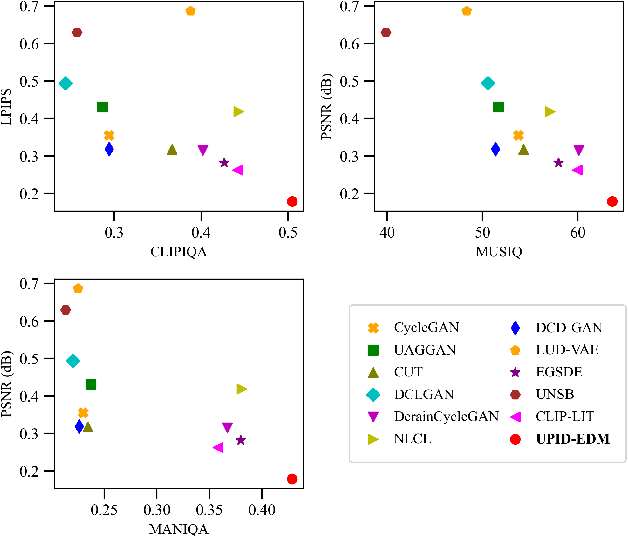
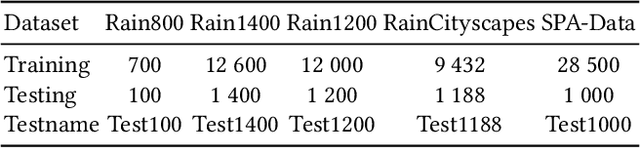
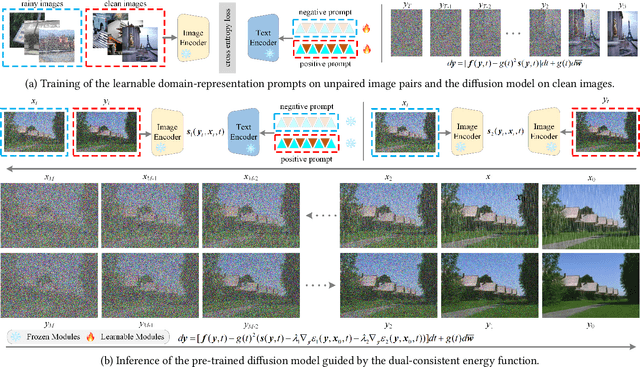
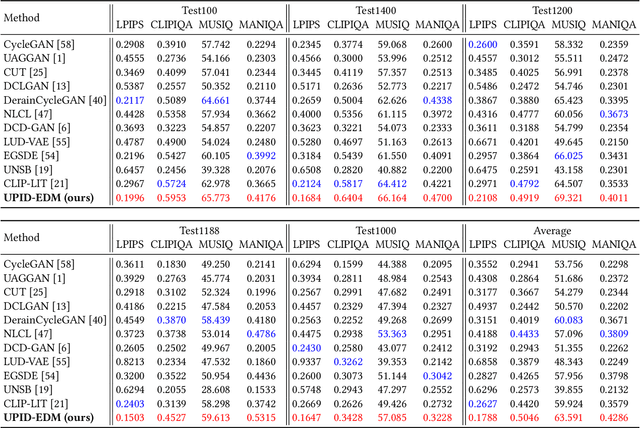
Abstract:Existing unpaired image deraining approaches face challenges in accurately capture the distinguishing characteristics between the rainy and clean domains, resulting in residual degradation and color distortion within the reconstructed images. To this end, we propose an energy-informed diffusion model for unpaired photo-realistic image deraining (UPID-EDM). Initially, we delve into the intricate visual-language priors embedded within the contrastive language-image pre-training model (CLIP), and demonstrate that the CLIP priors aid in the discrimination of rainy and clean images. Furthermore, we introduce a dual-consistent energy function (DEF) that retains the rain-irrelevant characteristics while eliminating the rain-relevant features. This energy function is trained by the non-corresponding rainy and clean images. In addition, we employ the rain-relevance discarding energy function (RDEF) and the rain-irrelevance preserving energy function (RPEF) to direct the reverse sampling procedure of a pre-trained diffusion model, effectively removing the rain streaks while preserving the image contents. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our energy-informed model surpasses the existing unpaired learning approaches in terms of both supervised and no-reference metrics.
Encoder-minimal and Decoder-minimal Framework for Remote Sensing Image Dehazing
Dec 13, 2023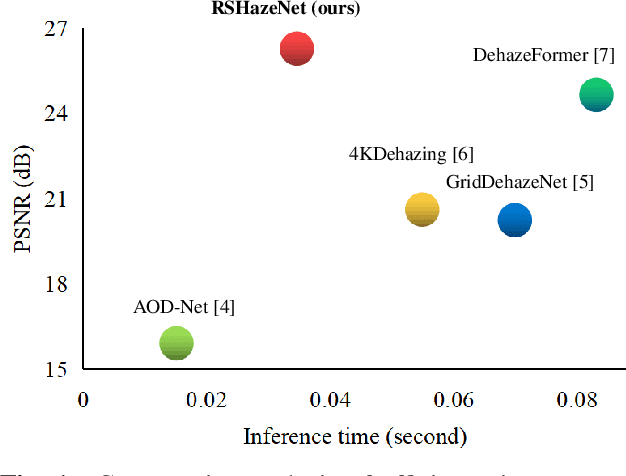
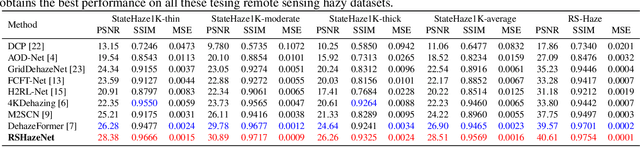
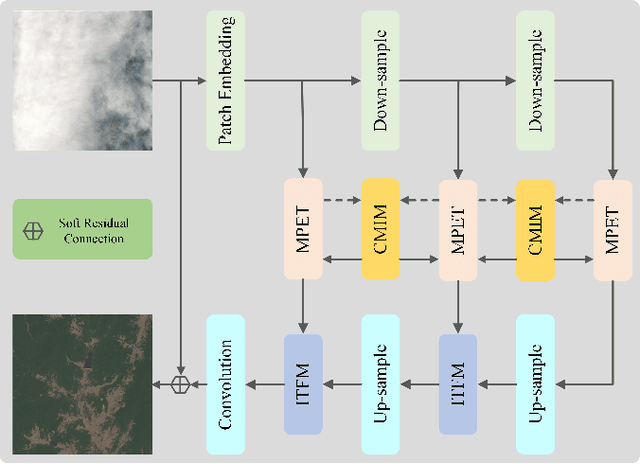
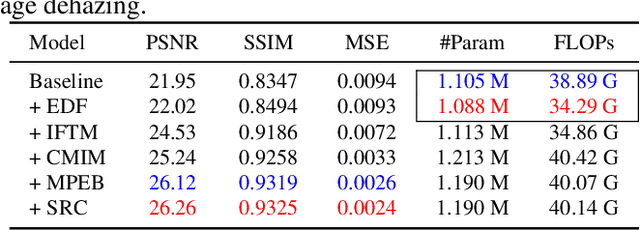
Abstract:Haze obscures remote sensing images, hindering valuable information extraction. To this end, we propose RSHazeNet, an encoder-minimal and decoder-minimal framework for efficient remote sensing image dehazing. Specifically, regarding the process of merging features within the same level, we develop an innovative module called intra-level transposed fusion module (ITFM). This module employs adaptive transposed self-attention to capture comprehensive context-aware information, facilitating the robust context-aware feature fusion. Meanwhile, we present a cross-level multi-view interaction module (CMIM) to enable effective interactions between features from various levels, mitigating the loss of information due to the repeated sampling operations. In addition, we propose a multi-view progressive extraction block (MPEB) that partitions the features into four distinct components and employs convolution with varying kernel sizes, groups, and dilation factors to facilitate view-progressive feature learning. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our proposed RSHazeNet. We release the source code and all pre-trained models at \url{https://github.com/chdwyb/RSHazeNet}.
LRRU: Long-short Range Recurrent Updating Networks for Depth Completion
Oct 13, 2023Abstract:Existing deep learning-based depth completion methods generally employ massive stacked layers to predict the dense depth map from sparse input data. Although such approaches greatly advance this task, their accompanied huge computational complexity hinders their practical applications. To accomplish depth completion more efficiently, we propose a novel lightweight deep network framework, the Long-short Range Recurrent Updating (LRRU) network. Without learning complex feature representations, LRRU first roughly fills the sparse input to obtain an initial dense depth map, and then iteratively updates it through learned spatially-variant kernels. Our iterative update process is content-adaptive and highly flexible, where the kernel weights are learned by jointly considering the guidance RGB images and the depth map to be updated, and large-to-small kernel scopes are dynamically adjusted to capture long-to-short range dependencies. Our initial depth map has coarse but complete scene depth information, which helps relieve the burden of directly regressing the dense depth from sparse ones, while our proposed method can effectively refine it to an accurate depth map with less learnable parameters and inference time. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed LRRU variants achieve state-of-the-art performance across different parameter regimes. In particular, the LRRU-Base model outperforms competing approaches on the NYUv2 dataset, and ranks 1st on the KITTI depth completion benchmark at the time of submission. Project page: https://npucvr.github.io/LRRU/.
Multi-dimension Queried and Interacting Network for Stereo Image Deraining
Sep 19, 2023Abstract:Eliminating the rain degradation in stereo images poses a formidable challenge, which necessitates the efficient exploitation of mutual information present between the dual views. To this end, we devise MQINet, which employs multi-dimension queries and interactions for stereo image deraining. More specifically, our approach incorporates a context-aware dimension-wise queried block (CDQB). This module leverages dimension-wise queries that are independent of the input features and employs global context-aware attention (GCA) to capture essential features while avoiding the entanglement of redundant or irrelevant information. Meanwhile, we introduce an intra-view physics-aware attention (IPA) based on the inverse physical model of rainy images. IPA extracts shallow features that are sensitive to the physics of rain degradation, facilitating the reduction of rain-related artifacts during the early learning period. Furthermore, we integrate a cross-view multi-dimension interacting attention mechanism (CMIA) to foster comprehensive feature interaction between the two views across multiple dimensions. Extensive experimental evaluations demonstrate the superiority of our model over EPRRNet and StereoIRR, achieving respective improvements of 4.18 dB and 0.45 dB in PSNR. Code and models are available at \url{https://github.com/chdwyb/MQINet}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge