Syrine Krichene
Faithful Chart Summarization with ChaTS-Pi
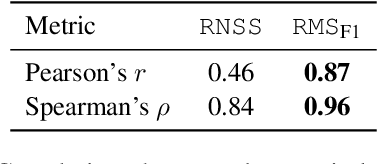
May 29, 2024Abstract:Chart-to-summary generation can help explore data, communicate insights, and help the visually impaired people. Multi-modal generative models have been used to produce fluent summaries, but they can suffer from factual and perceptual errors. In this work we present CHATS-CRITIC, a reference-free chart summarization metric for scoring faithfulness. CHATS-CRITIC is composed of an image-to-text model to recover the table from a chart, and a tabular entailment model applied to score the summary sentence by sentence. We find that CHATS-CRITIC evaluates the summary quality according to human ratings better than reference-based metrics, either learned or n-gram based, and can be further used to fix candidate summaries by removing not supported sentences. We then introduce CHATS-PI, a chart-to-summary pipeline that leverages CHATS-CRITIC during inference to fix and rank sampled candidates from any chart-summarization model. We evaluate CHATS-PI and CHATS-CRITIC using human raters, establishing state-of-the-art results on two popular chart-to-summary datasets.
DePlot: One-shot visual language reasoning by plot-to-table translation
Dec 20, 2022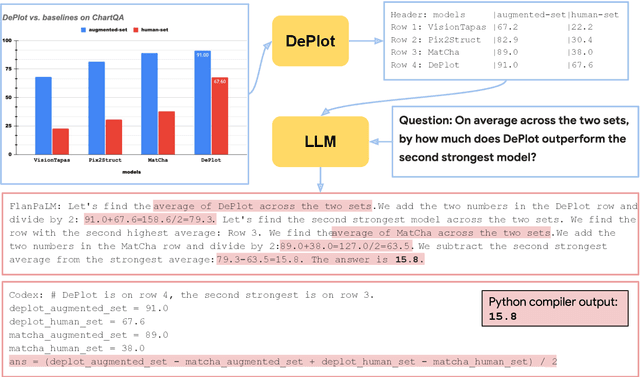
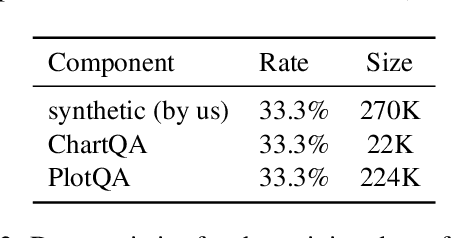
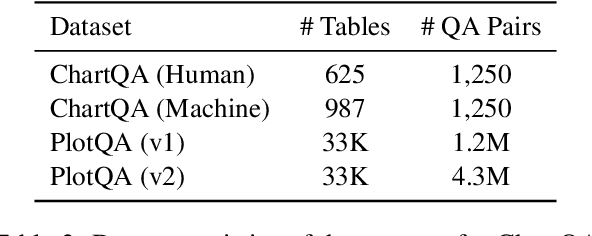
Abstract:Visual language such as charts and plots is ubiquitous in the human world. Comprehending plots and charts requires strong reasoning skills. Prior state-of-the-art (SOTA) models require at least tens of thousands of training examples and their reasoning capabilities are still much limited, especially on complex human-written queries. This paper presents the first one-shot solution to visual language reasoning. We decompose the challenge of visual language reasoning into two steps: (1) plot-to-text translation, and (2) reasoning over the translated text. The key in this method is a modality conversion module, named as DePlot, which translates the image of a plot or chart to a linearized table. The output of DePlot can then be directly used to prompt a pretrained large language model (LLM), exploiting the few-shot reasoning capabilities of LLMs. To obtain DePlot, we standardize the plot-to-table task by establishing unified task formats and metrics, and train DePlot end-to-end on this task. DePlot can then be used off-the-shelf together with LLMs in a plug-and-play fashion. Compared with a SOTA model finetuned on more than >28k data points, DePlot+LLM with just one-shot prompting achieves a 24.0% improvement over finetuned SOTA on human-written queries from the task of chart QA.
MatCha: Enhancing Visual Language Pretraining with Math Reasoning and Chart Derendering
Dec 19, 2022



Abstract:Visual language data such as plots, charts, and infographics are ubiquitous in the human world. However, state-of-the-art vision-language models do not perform well on these data. We propose MatCha (Math reasoning and Chart derendering pretraining) to enhance visual language models' capabilities in jointly modeling charts/plots and language data. Specifically, we propose several pretraining tasks that cover plot deconstruction and numerical reasoning which are the key capabilities in visual language modeling. We perform the MatCha pretraining starting from Pix2Struct, a recently proposed image-to-text visual language model. On standard benchmarks such as PlotQA and ChartQA, the MatCha model outperforms state-of-the-art methods by as much as nearly 20%. We also examine how well MatCha pretraining transfers to domains such as screenshots, textbook diagrams, and document figures and observe overall improvement, verifying the usefulness of MatCha pretraining on broader visual language tasks.
Table-To-Text generation and pre-training with TabT5
Oct 17, 2022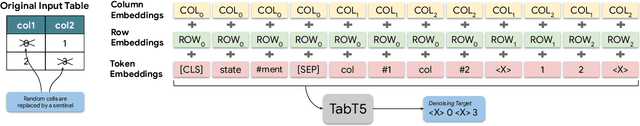
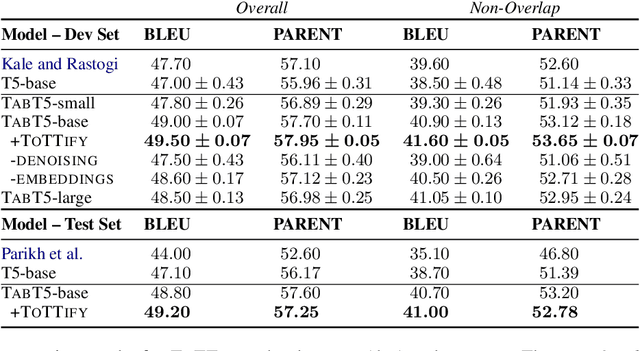
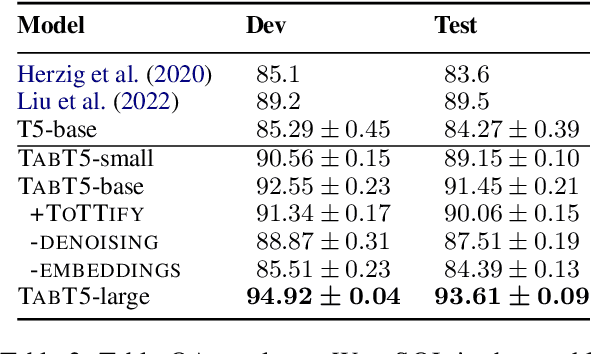
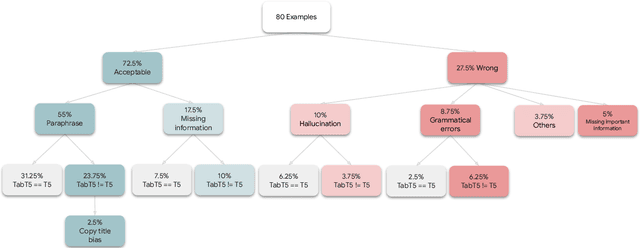
Abstract:Encoder-only transformer models have been successfully applied to different table understanding tasks, as in TAPAS (Herzig et al., 2020). A major limitation of these architectures is that they are constrained to classification-like tasks such as cell selection or entailment detection. We present TABT5, an encoder-decoder model that generates natural language text based on tables and textual inputs. TABT5 overcomes the encoder-only limitation by incorporating a decoder component and leverages the input structure with table specific embeddings and pre-training. TABT5 achieves new state-of-the-art results on several domains, including spreadsheet formula prediction with a 15% increase in sequence accuracy, QA with a 2.5% increase in sequence accuracy and data-to-text generation with a 2.5% increase in BLEU.
DoT: An efficient Double Transformer for NLP tasks with tables
Jun 01, 2021



Abstract:Transformer-based approaches have been successfully used to obtain state-of-the-art accuracy on natural language processing (NLP) tasks with semi-structured tables. These model architectures are typically deep, resulting in slow training and inference, especially for long inputs. To improve efficiency while maintaining a high accuracy, we propose a new architecture, DoT, a double transformer model, that decomposes the problem into two sub-tasks: A shallow pruning transformer that selects the top-K tokens, followed by a deep task-specific transformer that takes as input those K tokens. Additionally, we modify the task-specific attention to incorporate the pruning scores. The two transformers are jointly trained by optimizing the task-specific loss. We run experiments on three benchmarks, including entailment and question-answering. We show that for a small drop of accuracy, DoT improves training and inference time by at least 50%. We also show that the pruning transformer effectively selects relevant tokens enabling the end-to-end model to maintain similar accuracy as slower baseline models. Finally, we analyse the pruning and give some insight into its impact on the task model.
TAPAS at SemEval-2021 Task 9: Reasoning over tables with intermediate pre-training
Apr 02, 2021



Abstract:We present the TAPAS contribution to the Shared Task on Statement Verification and Evidence Finding with Tables (SemEval 2021 Task 9, Wang et al. (2021)). SEM TAB FACT Task A is a classification task of recognizing if a statement is entailed, neutral or refuted by the content of a given table. We adopt the binary TAPAS model of Eisenschlos et al. (2020) to this task. We learn two binary classification models: A first model to predict if a statement is neutral or non-neutral and a second one to predict if it is entailed or refuted. As the shared task training set contains only entailed or refuted examples, we generate artificial neutral examples to train the first model. Both models are pre-trained using a MASKLM objective, intermediate counter-factual and synthetic data (Eisenschlos et al., 2020) and TABFACT (Chen et al., 2020), a large table entailment dataset. We find that the artificial neutral examples are somewhat effective at training the first model, achieving 68.03 test F1 versus the 60.47 of a majority baseline. For the second stage, we find that the pre-training on the intermediate data and TABFACT improves the results over MASKLM pre-training (68.03 vs 57.01).
Open Domain Question Answering over Tables via Dense Retrieval
Mar 22, 2021



Abstract:Recent advances in open-domain QA have led to strong models based on dense retrieval, but only focused on retrieving textual passages. In this work, we tackle open-domain QA over tables for the first time, and show that retrieval can be improved by a retriever designed to handle tabular context. We present an effective pre-training procedure for our retriever and improve retrieval quality with mined hard negatives. As relevant datasets are missing, we extract a subset of Natural Questions (Kwiatkowski et al., 2019) into a Table QA dataset. We find that our retriever improves retrieval results from 72.0 to 81.1 recall@10 and end-to-end QA results from 33.8 to 37.7 exact match, over a BERT based retriever.
Understanding tables with intermediate pre-training
Oct 05, 2020



Abstract:Table entailment, the binary classification task of finding if a sentence is supported or refuted by the content of a table, requires parsing language and table structure as well as numerical and discrete reasoning. While there is extensive work on textual entailment, table entailment is less well studied. We adapt TAPAS (Herzig et al., 2020), a table-based BERT model, to recognize entailment. Motivated by the benefits of data augmentation, we create a balanced dataset of millions of automatically created training examples which are learned in an intermediate step prior to fine-tuning. This new data is not only useful for table entailment, but also for SQA (Iyyer et al., 2017), a sequential table QA task. To be able to use long examples as input of BERT models, we evaluate table pruning techniques as a pre-processing step to drastically improve the training and prediction efficiency at a moderate drop in accuracy. The different methods set the new state-of-the-art on the TabFact (Chen et al., 2020) and SQA datasets.
Embedding models for recommendation under contextual constraints
Jun 21, 2019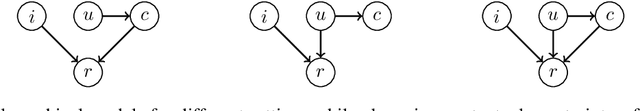
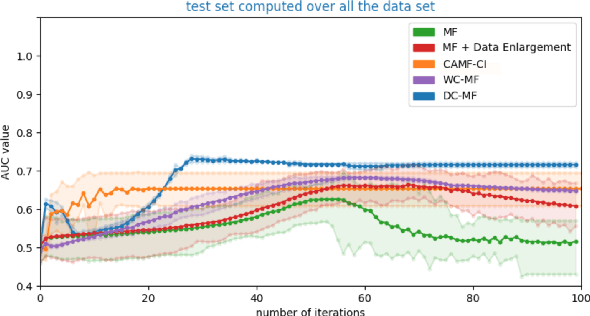
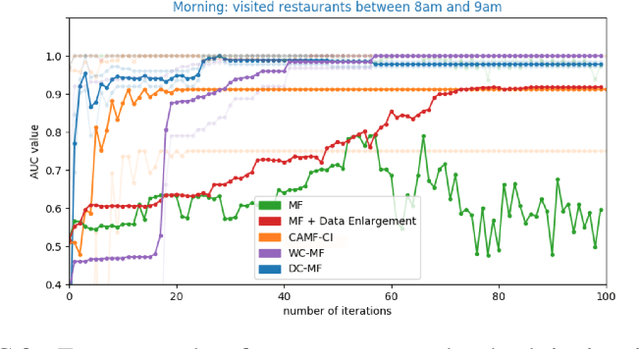
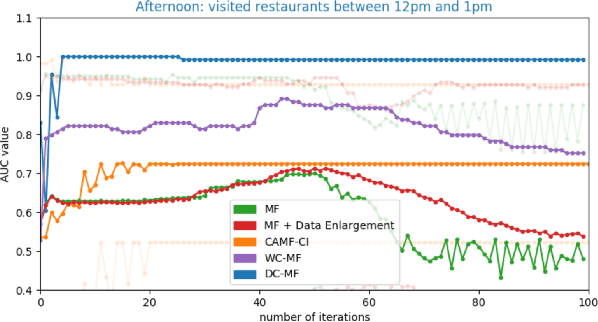
Abstract:Embedding models, which learn latent representations of users and items based on user-item interaction patterns, are a key component of recommendation systems. In many applications, contextual constraints need to be applied to refine recommendations, e.g. when a user specifies a price range or product category filter. The conventional approach, for both context-aware and standard models, is to retrieve items and apply the constraints as independent operations. The order in which these two steps are executed can induce significant problems. For example, applying constraints a posteriori can result in incomplete recommendations or low-quality results for the tail of the distribution (i.e., less popular items). As a result, the additional information that the constraint brings about user intent may not be accurately captured. In this paper we propose integrating the information provided by the contextual constraint into the similarity computation, by merging constraint application and retrieval into one operation in the embedding space. This technique allows us to generate high-quality recommendations for the specified constraint. Our approach learns constraints representations jointly with the user and item embeddings. We incorporate our methods into a matrix factorization model, and perform an experimental evaluation on one internal and two real-world datasets. Our results show significant improvements in predictive performance compared to context-aware and standard models.
Learning Nonsymmetric Determinantal Point Processes
May 30, 2019



Abstract:Determinantal point processes (DPPs) have attracted substantial attention as an elegant probabilistic model that captures the balance between quality and diversity within sets. DPPs are conventionally parameterized by a positive semi-definite kernel matrix, and this symmetric kernel encodes only repulsive interactions between items. These so-called symmetric DPPs have significant expressive power, and have been successfully applied to a variety of machine learning tasks, including recommendation systems, information retrieval, and automatic summarization, among many others. Efficient algorithms for learning symmetric DPPs and sampling from these models have been reasonably well studied. However, relatively little attention has been given to nonsymmetric DPPs, which relax the symmetric constraint on the kernel. Nonsymmetric DPPs allow for both repulsive and attractive item interactions, which can significantly improve modeling power, resulting in a model that may better fit for some applications. We present a method that enables a tractable algorithm, based on maximum likelihood estimation, for learning nonsymmetric DPPs from data composed of observed subsets. Our method imposes a particular decomposition of the nonsymmetric kernel that enables such tractable learning algorithms, which we analyze both theoretically and experimentally. We evaluate our model on synthetic and real-world datasets, demonstrating improved predictive performance compared to symmetric DPPs, which have previously shown strong performance on modeling tasks associated with these datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge