Stefan Andreas Baumann
Guiding Token-Sparse Diffusion Models
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Diffusion models deliver high quality in image synthesis but remain expensive during training and inference. Recent works have leveraged the inherent redundancy in visual content to make training more affordable by training only on a subset of visual information. While these methods were successful in providing cheaper and more effective training, sparsely trained diffusion models struggle in inference. This is due to their lacking response to Classifier-free Guidance (CFG) leading to underwhelming performance during inference. To overcome this, we propose Sparse Guidance (SG). Instead of using conditional dropout as a signal to guide diffusion models, SG uses token-level sparsity. As a result, SG preserves the high-variance of the conditional prediction better, achieving good quality and high variance outputs. Leveraging token-level sparsity at inference, SG improves fidelity at lower compute, achieving 1.58 FID on the commonly used ImageNet-256 benchmark with 25% fewer FLOPs, and yields up to 58% FLOP savings at matched baseline quality. To demonstrate the effectiveness of Sparse Guidance, we train a 2.5B text-to-image diffusion model using training time sparsity and leverage SG during inference. SG achieves improvements in composition and human preference score while increasing throughput at the same time.
What If : Understanding Motion Through Sparse Interactions
Oct 14, 2025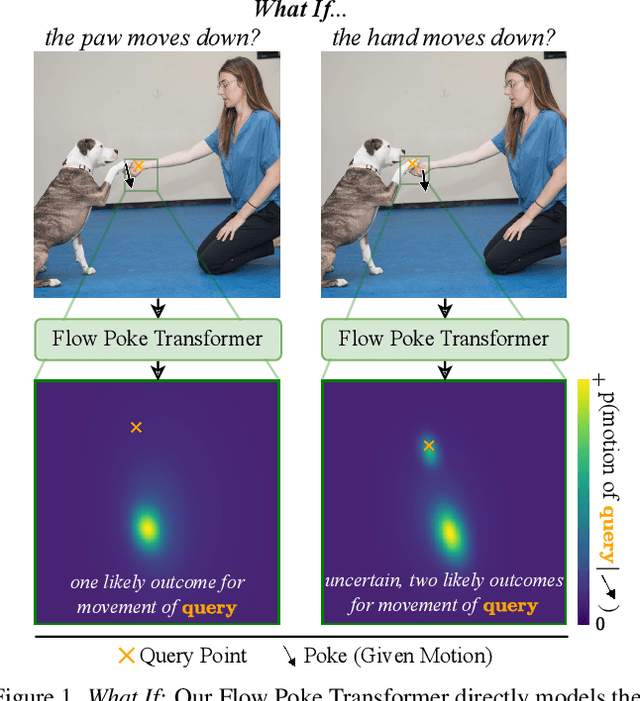
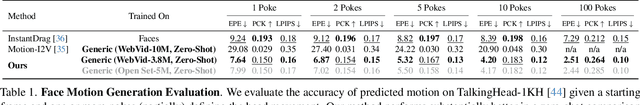
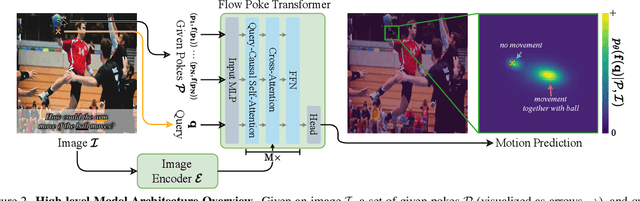
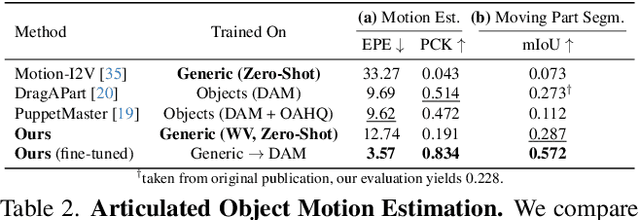
Abstract:Understanding the dynamics of a physical scene involves reasoning about the diverse ways it can potentially change, especially as a result of local interactions. We present the Flow Poke Transformer (FPT), a novel framework for directly predicting the distribution of local motion, conditioned on sparse interactions termed "pokes". Unlike traditional methods that typically only enable dense sampling of a single realization of scene dynamics, FPT provides an interpretable directly accessible representation of multi-modal scene motion, its dependency on physical interactions and the inherent uncertainties of scene dynamics. We also evaluate our model on several downstream tasks to enable comparisons with prior methods and highlight the flexibility of our approach. On dense face motion generation, our generic pre-trained model surpasses specialized baselines. FPT can be fine-tuned in strongly out-of-distribution tasks such as synthetic datasets to enable significant improvements over in-domain methods in articulated object motion estimation. Additionally, predicting explicit motion distributions directly enables our method to achieve competitive performance on tasks like moving part segmentation from pokes which further demonstrates the versatility of our FPT. Code and models are publicly available at https://compvis.github.io/flow-poke-transformer.
CleanDIFT: Diffusion Features without Noise
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Internal features from large-scale pre-trained diffusion models have recently been established as powerful semantic descriptors for a wide range of downstream tasks. Works that use these features generally need to add noise to images before passing them through the model to obtain the semantic features, as the models do not offer the most useful features when given images with little to no noise. We show that this noise has a critical impact on the usefulness of these features that cannot be remedied by ensembling with different random noises. We address this issue by introducing a lightweight, unsupervised fine-tuning method that enables diffusion backbones to provide high-quality, noise-free semantic features. We show that these features readily outperform previous diffusion features by a wide margin in a wide variety of extraction setups and downstream tasks, offering better performance than even ensemble-based methods at a fraction of the cost.
CTRLorALTer: Conditional LoRAdapter for Efficient 0-Shot Control & Altering of T2I Models
May 13, 2024Abstract:Text-to-image generative models have become a prominent and powerful tool that excels at generating high-resolution realistic images. However, guiding the generative process of these models to consider detailed forms of conditioning reflecting style and/or structure information remains an open problem. In this paper, we present LoRAdapter, an approach that unifies both style and structure conditioning under the same formulation using a novel conditional LoRA block that enables zero-shot control. LoRAdapter is an efficient, powerful, and architecture-agnostic approach to condition text-to-image diffusion models, which enables fine-grained control conditioning during generation and outperforms recent state-of-the-art approaches
Continuous, Subject-Specific Attribute Control in T2I Models by Identifying Semantic Directions
Mar 25, 2024Abstract:In recent years, advances in text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have substantially elevated the quality of their generated images. However, achieving fine-grained control over attributes remains a challenge due to the limitations of natural language prompts (such as no continuous set of intermediate descriptions existing between ``person'' and ``old person''). Even though many methods were introduced that augment the model or generation process to enable such control, methods that do not require a fixed reference image are limited to either enabling global fine-grained attribute expression control or coarse attribute expression control localized to specific subjects, not both simultaneously. We show that there exist directions in the commonly used token-level CLIP text embeddings that enable fine-grained subject-specific control of high-level attributes in text-to-image models. Based on this observation, we introduce one efficient optimization-free and one robust optimization-based method to identify these directions for specific attributes from contrastive text prompts. We demonstrate that these directions can be used to augment the prompt text input with fine-grained control over attributes of specific subjects in a compositional manner (control over multiple attributes of a single subject) without having to adapt the diffusion model. Project page: https://compvis.github.io/attribute-control. Code is available at https://github.com/CompVis/attribute-control.
DepthFM: Fast Monocular Depth Estimation with Flow Matching
Mar 20, 2024



Abstract:Monocular depth estimation is crucial for numerous downstream vision tasks and applications. Current discriminative approaches to this problem are limited due to blurry artifacts, while state-of-the-art generative methods suffer from slow sampling due to their SDE nature. Rather than starting from noise, we seek a direct mapping from input image to depth map. We observe that this can be effectively framed using flow matching, since its straight trajectories through solution space offer efficiency and high quality. Our study demonstrates that a pre-trained image diffusion model can serve as an adequate prior for a flow matching depth model, allowing efficient training on only synthetic data to generalize to real images. We find that an auxiliary surface normals loss further improves the depth estimates. Due to the generative nature of our approach, our model reliably predicts the confidence of its depth estimates. On standard benchmarks of complex natural scenes, our lightweight approach exhibits state-of-the-art performance at favorable low computational cost despite only being trained on little synthetic data.
ZigMa: Zigzag Mamba Diffusion Model
Mar 20, 2024



Abstract:The diffusion model has long been plagued by scalability and quadratic complexity issues, especially within transformer-based structures. In this study, we aim to leverage the long sequence modeling capability of a State-Space Model called Mamba to extend its applicability to visual data generation. Firstly, we identify a critical oversight in most current Mamba-based vision methods, namely the lack of consideration for spatial continuity in the scan scheme of Mamba. Secondly, building upon this insight, we introduce a simple, plug-and-play, zero-parameter method named Zigzag Mamba, which outperforms Mamba-based baselines and demonstrates improved speed and memory utilization compared to transformer-based baselines. Lastly, we integrate Zigzag Mamba with the Stochastic Interpolant framework to investigate the scalability of the model on large-resolution visual datasets, such as FacesHQ $1024\times 1024$ and UCF101, MultiModal-CelebA-HQ, and MS COCO $256\times 256$. Code will be released at https://taohu.me/zigma/
Scalable High-Resolution Pixel-Space Image Synthesis with Hourglass Diffusion Transformers
Jan 21, 2024Abstract:We present the Hourglass Diffusion Transformer (HDiT), an image generative model that exhibits linear scaling with pixel count, supporting training at high-resolution (e.g. $1024 \times 1024$) directly in pixel-space. Building on the Transformer architecture, which is known to scale to billions of parameters, it bridges the gap between the efficiency of convolutional U-Nets and the scalability of Transformers. HDiT trains successfully without typical high-resolution training techniques such as multiscale architectures, latent autoencoders or self-conditioning. We demonstrate that HDiT performs competitively with existing models on ImageNet $256^2$, and sets a new state-of-the-art for diffusion models on FFHQ-$1024^2$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge