Nick Stracke
What If : Understanding Motion Through Sparse Interactions
Oct 14, 2025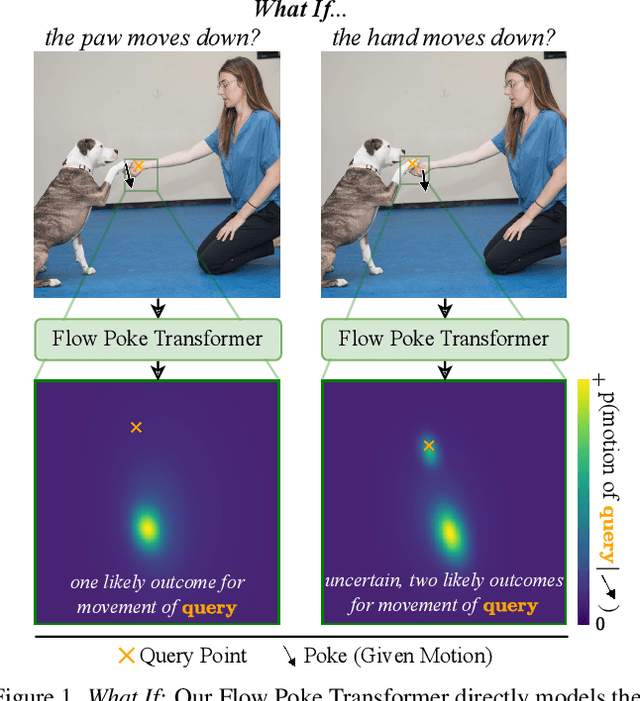
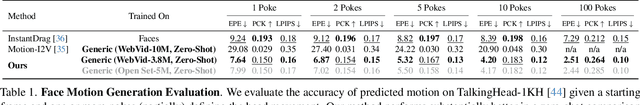
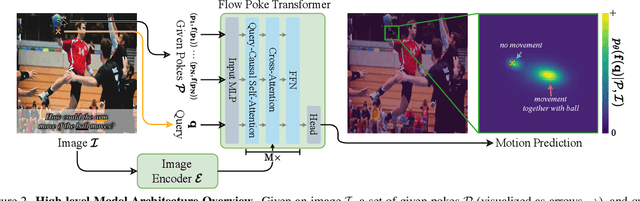
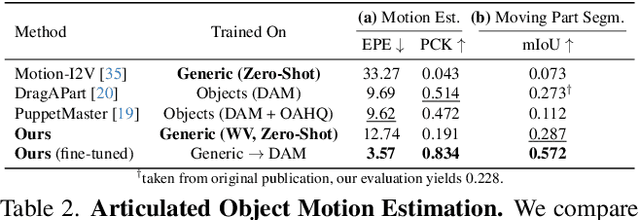
Abstract:Understanding the dynamics of a physical scene involves reasoning about the diverse ways it can potentially change, especially as a result of local interactions. We present the Flow Poke Transformer (FPT), a novel framework for directly predicting the distribution of local motion, conditioned on sparse interactions termed "pokes". Unlike traditional methods that typically only enable dense sampling of a single realization of scene dynamics, FPT provides an interpretable directly accessible representation of multi-modal scene motion, its dependency on physical interactions and the inherent uncertainties of scene dynamics. We also evaluate our model on several downstream tasks to enable comparisons with prior methods and highlight the flexibility of our approach. On dense face motion generation, our generic pre-trained model surpasses specialized baselines. FPT can be fine-tuned in strongly out-of-distribution tasks such as synthetic datasets to enable significant improvements over in-domain methods in articulated object motion estimation. Additionally, predicting explicit motion distributions directly enables our method to achieve competitive performance on tasks like moving part segmentation from pokes which further demonstrates the versatility of our FPT. Code and models are publicly available at https://compvis.github.io/flow-poke-transformer.
CleanDIFT: Diffusion Features without Noise
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Internal features from large-scale pre-trained diffusion models have recently been established as powerful semantic descriptors for a wide range of downstream tasks. Works that use these features generally need to add noise to images before passing them through the model to obtain the semantic features, as the models do not offer the most useful features when given images with little to no noise. We show that this noise has a critical impact on the usefulness of these features that cannot be remedied by ensembling with different random noises. We address this issue by introducing a lightweight, unsupervised fine-tuning method that enables diffusion backbones to provide high-quality, noise-free semantic features. We show that these features readily outperform previous diffusion features by a wide margin in a wide variety of extraction setups and downstream tasks, offering better performance than even ensemble-based methods at a fraction of the cost.
CTRLorALTer: Conditional LoRAdapter for Efficient 0-Shot Control & Altering of T2I Models
May 13, 2024Abstract:Text-to-image generative models have become a prominent and powerful tool that excels at generating high-resolution realistic images. However, guiding the generative process of these models to consider detailed forms of conditioning reflecting style and/or structure information remains an open problem. In this paper, we present LoRAdapter, an approach that unifies both style and structure conditioning under the same formulation using a novel conditional LoRA block that enables zero-shot control. LoRAdapter is an efficient, powerful, and architecture-agnostic approach to condition text-to-image diffusion models, which enables fine-grained control conditioning during generation and outperforms recent state-of-the-art approaches
Continuous, Subject-Specific Attribute Control in T2I Models by Identifying Semantic Directions
Mar 25, 2024Abstract:In recent years, advances in text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have substantially elevated the quality of their generated images. However, achieving fine-grained control over attributes remains a challenge due to the limitations of natural language prompts (such as no continuous set of intermediate descriptions existing between ``person'' and ``old person''). Even though many methods were introduced that augment the model or generation process to enable such control, methods that do not require a fixed reference image are limited to either enabling global fine-grained attribute expression control or coarse attribute expression control localized to specific subjects, not both simultaneously. We show that there exist directions in the commonly used token-level CLIP text embeddings that enable fine-grained subject-specific control of high-level attributes in text-to-image models. Based on this observation, we introduce one efficient optimization-free and one robust optimization-based method to identify these directions for specific attributes from contrastive text prompts. We demonstrate that these directions can be used to augment the prompt text input with fine-grained control over attributes of specific subjects in a compositional manner (control over multiple attributes of a single subject) without having to adapt the diffusion model. Project page: https://compvis.github.io/attribute-control. Code is available at https://github.com/CompVis/attribute-control.
Boosting Latent Diffusion with Flow Matching
Dec 12, 2023



Abstract:Recently, there has been tremendous progress in visual synthesis and the underlying generative models. Here, diffusion models (DMs) stand out particularly, but lately, flow matching (FM) has also garnered considerable interest. While DMs excel in providing diverse images, they suffer from long training and slow generation. With latent diffusion, these issues are only partially alleviated. Conversely, FM offers faster training and inference but exhibits less diversity in synthesis. We demonstrate that introducing FM between the Diffusion model and the convolutional decoder offers high-resolution image synthesis with reduced computational cost and model size. Diffusion can then efficiently provide the necessary generation diversity. FM compensates for the lower resolution, mapping the small latent space to a high-dimensional one. Subsequently, the convolutional decoder of the LDM maps these latents to high-resolution images. By combining the diversity of DMs, the efficiency of FMs, and the effectiveness of convolutional decoders, we achieve state-of-the-art high-resolution image synthesis at $1024^2$ with minimal computational cost. Importantly, our approach is orthogonal to recent approximation and speed-up strategies for the underlying DMs, making it easily integrable into various DM frameworks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge