Shira Wein
When Does Meaning Backfire? Investigating the Role of AMRs in NLI
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Natural Language Inference (NLI) relies heavily on adequately parsing the semantic content of the premise and hypothesis. In this work, we investigate whether adding semantic information in the form of an Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR) helps pretrained language models better generalize in NLI. Our experiments integrating AMR into NLI in both fine-tuning and prompting settings show that the presence of AMR in fine-tuning hinders model generalization while prompting with AMR leads to slight gains in \texttt{GPT-4o}. However, an ablation study reveals that the improvement comes from amplifying surface-level differences rather than aiding semantic reasoning. This amplification can mislead models to predict non-entailment even when the core meaning is preserved.
Generating Text from Uniform Meaning Representation
Feb 17, 2025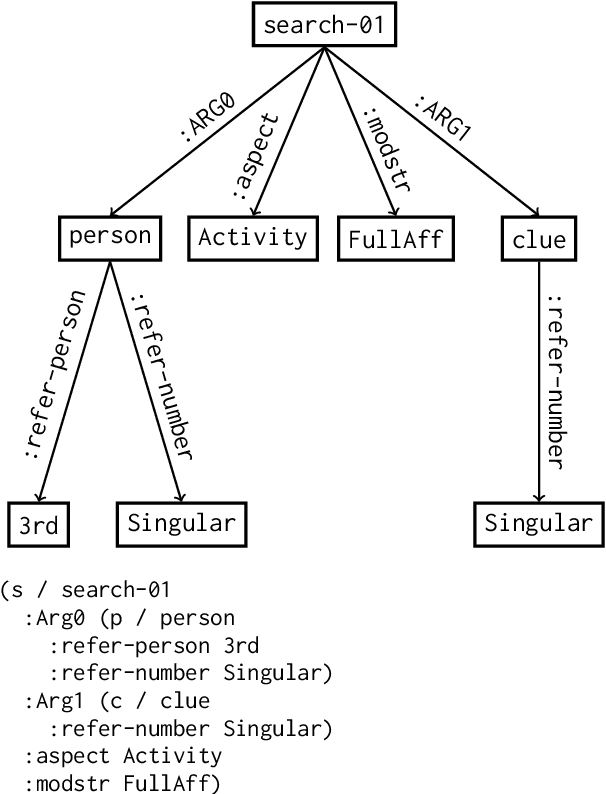

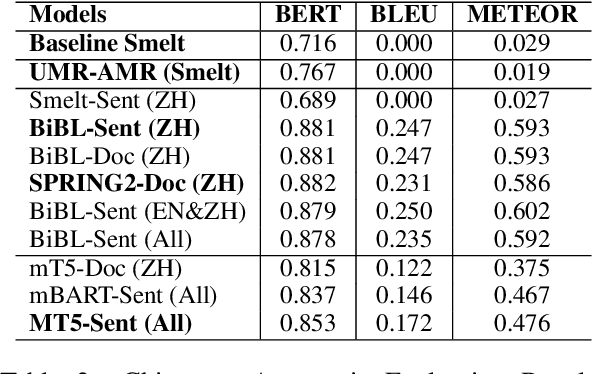
Abstract:Uniform Meaning Representation (UMR) is a recently developed graph-based semantic representation, which expands on Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR) in a number of ways, in particular through the inclusion of document-level information and multilingual flexibility. In order to effectively adopt and leverage UMR for downstream tasks, efforts must be placed toward developing a UMR technological ecosystem. Though still limited amounts of UMR annotations have been produced to date, in this work, we investigate the first approaches to producing text from multilingual UMR graphs: (1) a pipeline conversion of UMR to AMR, then using AMR-to-text generation models, (2) fine-tuning large language models with UMR data, and (3) fine-tuning existing AMR-to-text generation models with UMR data. Our best performing model achieves a multilingual BERTscore of 0.825 for English and 0.882 for Chinese when compared to the reference, which is a promising indication of the effectiveness of fine-tuning approaches for UMR-to-text generation with even limited amounts of UMR data.
Can Uniform Meaning Representation Help GPT-4 Translate from Indigenous Languages?
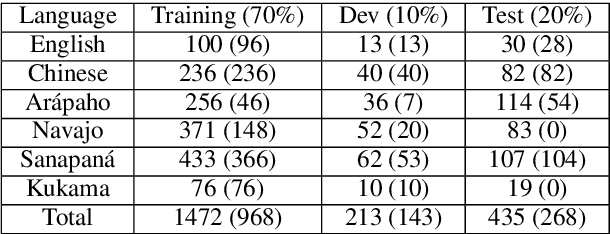
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:While ChatGPT and GPT-based models are able to effectively perform many tasks without additional fine-tuning, they struggle with related to extremely low-resource languages and indigenous languages. Uniform Meaning Representation (UMR), a semantic representation designed to capture the meaning of texts in many languages, is well-poised to be leveraged in the development of low-resource language technologies. In this work, we explore the downstream technical utility of UMR for low-resource languages by incorporating it into GPT-4 prompts. Specifically, we examine the ability of GPT-4 to perform translation from three indigenous languages (Navajo, Ar\'apaho, and Kukama), with and without demonstrations, as well as with and without UMR annotations. Ultimately we find that in the majority of our test cases, integrating UMR into the prompt results in a statistically significant increase in performance, which is a promising indication of future applications of the UMR formalism.
MASSIVE Multilingual Abstract Meaning Representation: A Dataset and Baselines for Hallucination Detection
May 29, 2024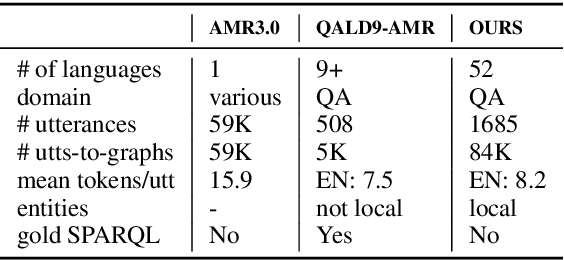
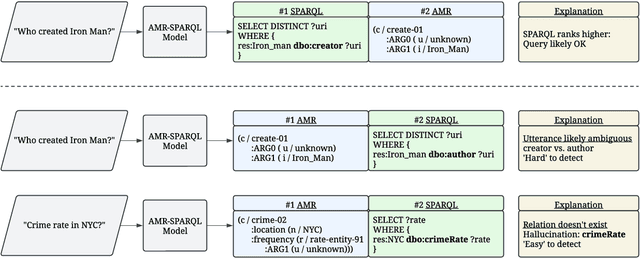
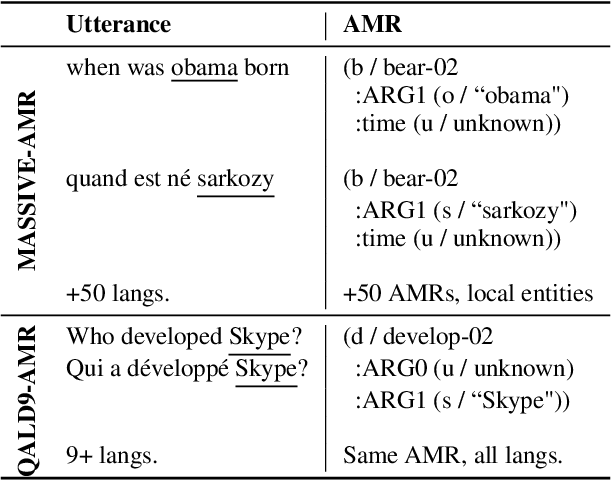

Abstract:Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR) is a semantic formalism that captures the core meaning of an utterance. There has been substantial work developing AMR corpora in English and more recently across languages, though the limited size of existing datasets and the cost of collecting more annotations are prohibitive. With both engineering and scientific questions in mind, we introduce MASSIVE-AMR, a dataset with more than 84,000 text-to-graph annotations, currently the largest and most diverse of its kind: AMR graphs for 1,685 information-seeking utterances mapped to 50+ typologically diverse languages. We describe how we built our resource and its unique features before reporting on experiments using large language models for multilingual AMR and SPARQL parsing as well as applying AMRs for hallucination detection in the context of knowledge base question answering, with results shedding light on persistent issues using LLMs for structured parsing.
Natural Language Processing RELIES on Linguistics
May 09, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have become capable of generating highly fluent text in certain languages, without modules specially designed to capture grammar or semantic coherence. What does this mean for the future of linguistic expertise in NLP? We highlight several aspects in which NLP (still) relies on linguistics, or where linguistic thinking can illuminate new directions. We argue our case around the acronym $RELIES$ that encapsulates six major facets where linguistics contributes to NLP: $R$esources, $E$valuation, $L$ow-resource settings, $I$nterpretability, $E$xplanation, and the $S$tudy of language. This list is not exhaustive, nor is linguistics the main point of reference for every effort under these themes; but at a macro level, these facets highlight the enduring importance of studying machine systems vis-a-vis systems of human language.
AMR4NLI: Interpretable and robust NLI measures from semantic graphs
Jun 01, 2023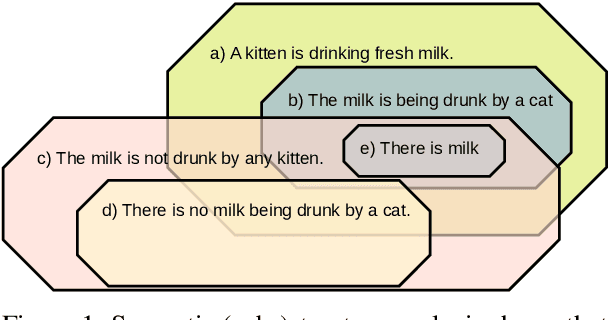
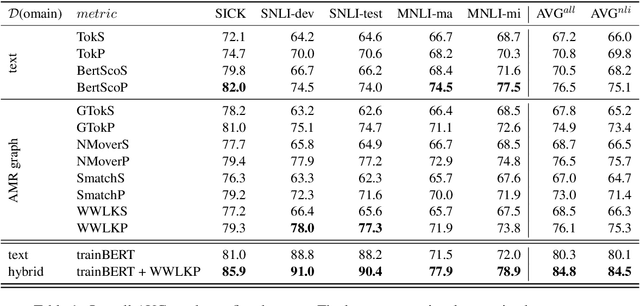
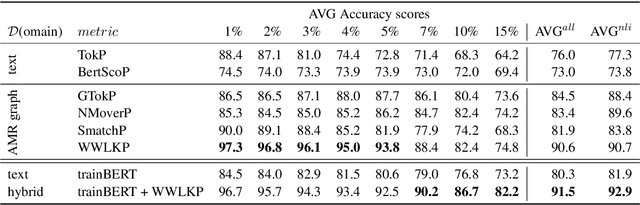
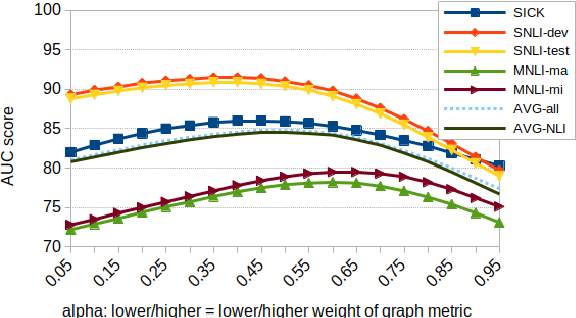
Abstract:The task of natural language inference (NLI) asks whether a given premise (expressed in NL) entails a given NL hypothesis. NLI benchmarks contain human ratings of entailment, but the meaning relationships driving these ratings are not formalized. Can the underlying sentence pair relationships be made more explicit in an interpretable yet robust fashion? We compare semantic structures to represent premise and hypothesis, including sets of contextualized embeddings and semantic graphs (Abstract Meaning Representations), and measure whether the hypothesis is a semantic substructure of the premise, utilizing interpretable metrics. Our evaluation on three English benchmarks finds value in both contextualized embeddings and semantic graphs; moreover, they provide complementary signals, and can be leveraged together in a hybrid model.
Translationese Reduction using Abstract Meaning Representation
Apr 23, 2023Abstract:Translated texts or utterances bear several hallmarks distinct from texts originating in the language. This phenomenon, known as translationese, is well-documented, and when found in training or test sets can affect model performance. Still, work to mitigate the effect of translationese in human translated text is understudied. We hypothesize that Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR), a semantic representation which abstracts away from the surface form, can be used as an interlingua to reduce the amount of translationese in translated texts. By parsing English translations into an AMR graph and then generating text from that AMR, we obtain texts that more closely resemble non-translationese by macro-level measures. We show that across four metrics, and qualitatively, using AMR as an interlingua enables the reduction of translationese and we compare our results to two additional approaches: one based on round-trip machine translation and one based on syntactically controlled generation.
Measuring Fine-Grained Semantic Equivalence with Abstract Meaning Representation
Oct 06, 2022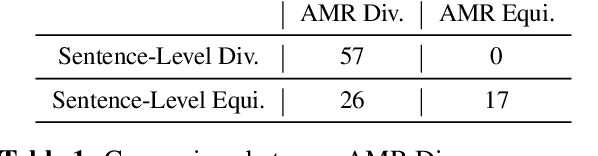
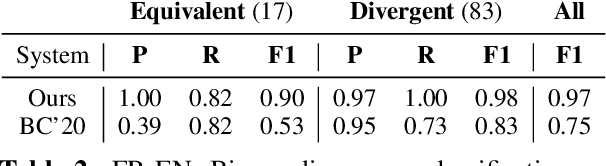

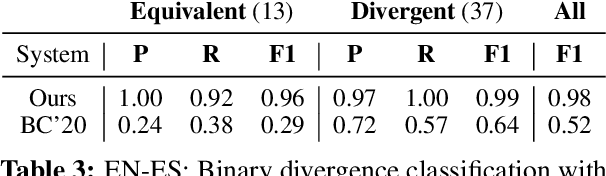
Abstract:Identifying semantically equivalent sentences is important for many cross-lingual and mono-lingual NLP tasks. Current approaches to semantic equivalence take a loose, sentence-level approach to "equivalence," despite previous evidence that fine-grained differences and implicit content have an effect on human understanding (Roth and Anthonio, 2021) and system performance (Briakou and Carpuat, 2021). In this work, we introduce a novel, more sensitive method of characterizing semantic equivalence that leverages Abstract Meaning Representation graph structures. We develop an approach, which can be used with either gold or automatic AMR annotations, and demonstrate that our solution is in fact finer-grained than existing corpus filtering methods and more accurate at predicting strictly equivalent sentences than existing semantic similarity metrics. We suggest that our finer-grained measure of semantic equivalence could limit the workload in the task of human post-edited machine translation and in human evaluation of sentence similarity.
Spanish Abstract Meaning Representation: Annotation of a General Corpus
Apr 15, 2022


Abstract:The Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR) formalism, designed originally for English, has been adapted to a number of languages. We build on previous work proposing the annotation of AMR in Spanish, which resulted in the release of 50 Spanish AMR annotations for the fictional text "The Little Prince." In this work, we present the first sizable, general annotation project for Spanish Abstract Meaning Representation. Our approach to annotation makes use of Spanish rolesets from the AnCora-Net lexicon and extends English AMR with semantic features specific to Spanish. In addition to our guidelines, we release an annotated corpus (586 annotations total, for 486 unique sentences) of multiple genres of documents from the "Abstract Meaning Representation 2.0 - Four Translations" sembank. This corpus is commonly used for evaluation of AMR parsing and generation, but does not include gold AMRs; we hope that providing gold annotations for this dataset can result in a more complete approach to cross-lingual AMR parsing. Finally, we perform a disagreement analysis and discuss the implications of our work on the adaptability of AMR to languages other than English.
PASTRIE: A Corpus of Prepositions Annotated with Supersense Tags in Reddit International English
Oct 23, 2021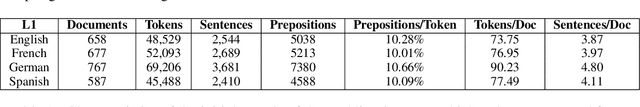
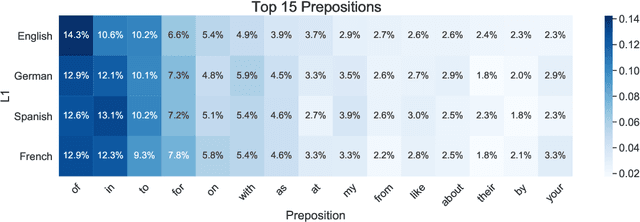
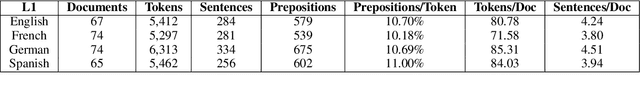

Abstract:We present the Prepositions Annotated with Supersense Tags in Reddit International English ("PASTRIE") corpus, a new dataset containing manually annotated preposition supersenses of English data from presumed speakers of four L1s: English, French, German, and Spanish. The annotations are comprehensive, covering all preposition types and tokens in the sample. Along with the corpus, we provide analysis of distributional patterns across the included L1s and a discussion of the influence of L1s on L2 preposition choice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge