Shih-Yuan Liu
SLAM with Objects using a Nonparametric Pose Graph
Apr 19, 2017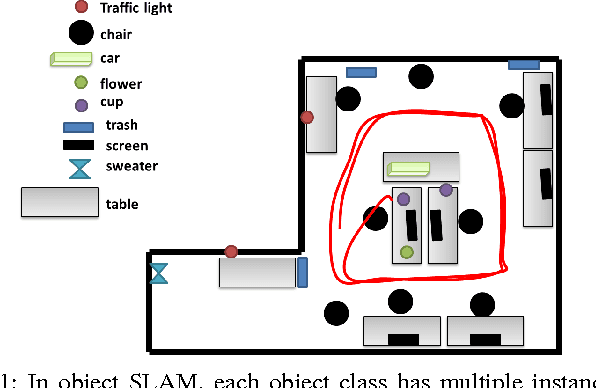
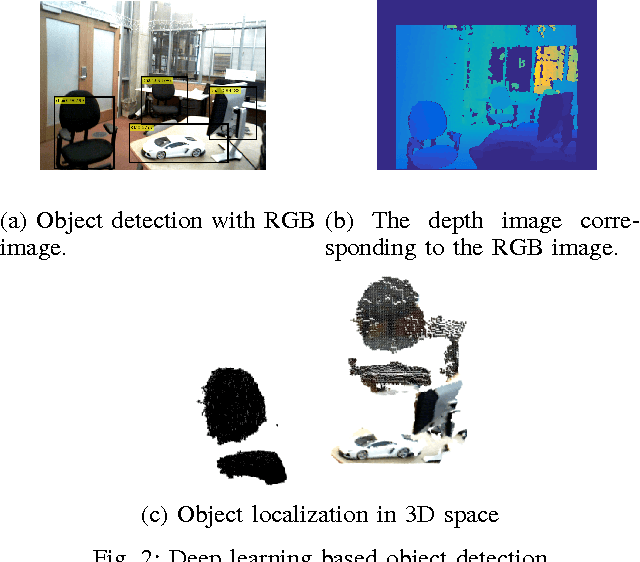
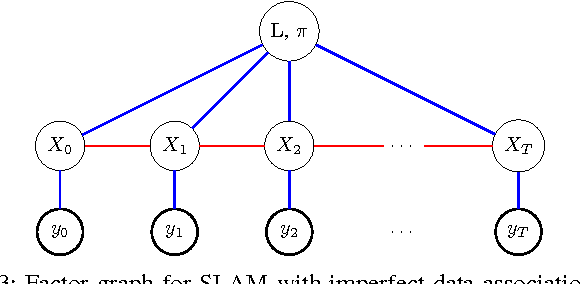
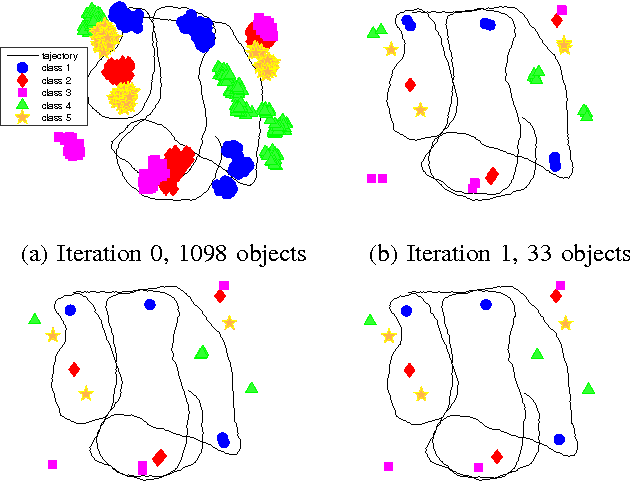
Abstract:Mapping and self-localization in unknown environments are fundamental capabilities in many robotic applications. These tasks typically involve the identification of objects as unique features or landmarks, which requires the objects both to be detected and then assigned a unique identifier that can be maintained when viewed from different perspectives and in different images. The \textit{data association} and \textit{simultaneous localization and mapping} (SLAM) problems are, individually, well-studied in the literature. But these two problems are inherently tightly coupled, and that has not been well-addressed. Without accurate SLAM, possible data associations are combinatorial and become intractable easily. Without accurate data association, the error of SLAM algorithms diverge easily. This paper proposes a novel nonparametric pose graph that models data association and SLAM in a single framework. An algorithm is further introduced to alternate between inferring data association and performing SLAM. Experimental results show that our approach has the new capability of associating object detections and localizing objects at the same time, leading to significantly better performance on both the data association and SLAM problems than achieved by considering only one and ignoring imperfections in the other.
Semantic-level Decentralized Multi-Robot Decision-Making using Probabilistic Macro-Observations
Mar 16, 2017
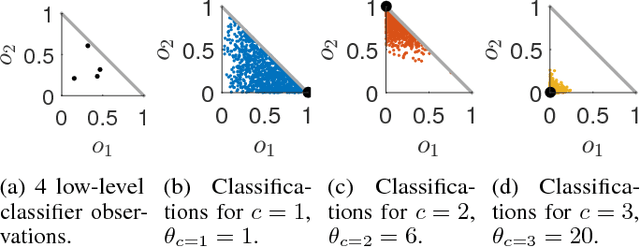


Abstract:Robust environment perception is essential for decision-making on robots operating in complex domains. Intelligent task execution requires principled treatment of uncertainty sources in a robot's observation model. This is important not only for low-level observations (e.g., accelerometer data), but also for high-level observations such as semantic object labels. This paper formalizes the concept of macro-observations in Decentralized Partially Observable Semi-Markov Decision Processes (Dec-POSMDPs), allowing scalable semantic-level multi-robot decision making. A hierarchical Bayesian approach is used to model noise statistics of low-level classifier outputs, while simultaneously allowing sharing of domain noise characteristics between classes. Classification accuracy of the proposed macro-observation scheme, called Hierarchical Bayesian Noise Inference (HBNI), is shown to exceed existing methods. The macro-observation scheme is then integrated into a Dec-POSMDP planner, with hardware experiments running onboard a team of dynamic quadrotors in a challenging domain where noise-agnostic filtering fails. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of a real-time, convolutional neural net-based classification framework running fully onboard a team of quadrotors in a multi-robot decision-making domain.
Dynamic Arrival Rate Estimation for Campus Mobility on Demand Network Graphs
Mar 06, 2017



Abstract:Mobility On Demand (MOD) systems are revolutionizing transportation in urban settings by improving vehicle utilization and reducing parking congestion. A key factor in the success of an MOD system is the ability to measure and respond to real-time customer arrival data. Real time traffic arrival rate data is traditionally difficult to obtain due to the need to install fixed sensors throughout the MOD network. This paper presents a framework for measuring pedestrian traffic arrival rates using sensors onboard the vehicles that make up the MOD fleet. A novel distributed fusion algorithm is presented which combines onboard LIDAR and camera sensor measurements to detect trajectories of pedestrians with a 90% detection hit rate with 1.5 false positives per minute. A novel moving observer method is introduced to estimate pedestrian arrival rates from pedestrian trajectories collected from mobile sensors. The moving observer method is evaluated in both simulation and hardware and is shown to achieve arrival rate estimates comparable to those that would be obtained with multiple stationary sensors.
* Appears in 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7759357/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge