Seyed Mahed Mousavi
What Does Loss Optimization Actually Teach, If Anything? Knowledge Dynamics in Continual Pre-training of LLMs
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Continual Pre-Training (CPT) is widely used for acquiring and updating factual knowledge in LLMs. This practice treats loss as a proxy for knowledge learning, while offering no grounding into how it changes during training. We study CPT as a knowledge learning process rather than a solely optimization problem. We construct a controlled, distribution-matched benchmark of factual documents and interleave diagnostic probes directly into the CPT loop, enabling epoch-level measurement of knowledge acquisition dynamics and changes in Out-Of-Domain (OOD) general skills (e.g., math). We further analyze how CPT reshapes knowledge circuits during training. Across three instruction-tuned LLMs and multiple CPT strategies, optimization and learning systematically diverge as loss decreases monotonically while factual learning is unstable and non-monotonic. Acquired facts are rarely consolidated, learning is strongly conditioned on prior exposure, and OOD performance degrades from early epochs. Circuit analysis reveals rapid reconfiguration of knowledge pathways across epochs, providing an explanation for narrow acquisition windows and systematic forgetting. These results show that loss optimization is misaligned with learning progress in CPT and motivate evaluation of stopping criteria based on task-level learning dynamics.
From Synthetic Scenes to Real Performance: Enhancing Spatial Reasoning in VLMs
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Fine-tuning Vision-Language Models (VLMs) is a common strategy to improve performance following an ad-hoc data collection and annotation of real-world scenes. However, this process is often prone to biases, errors, and distribution imbalance, resulting in overfitting and imbalanced performance. Although a few studies have tried to address this problem by generating synthetic data, they lacked control over distribution bias and annotation quality. To address these challenges, we redesign the fine-tuning process in two ways. First, we control the generation of data and its annotations, ensuring it is free from bias, distribution imbalance, and annotation errors. We automatically construct the dataset by comprehensively sampling objects' attributes, including color, shape, size, and position within the scene. Secondly, using this annotated dataset, we fine-tune state-of-the-art VLMs and assess performance transferability to real-world data on the absolute position task. We conduct exhaustive evaluations on both synthetic and real-world benchmarks. Our experiments reveal two key findings: 1) fine-tuning on balanced synthetic data yields uniform performance across the visual scene and mitigates common biases; and 2) fine-tuning on synthetic stimuli significantly improves performance on real-world data (COCO), outperforming models fine-tuned in the matched setting.
CIVET: Systematic Evaluation of Understanding in VLMs
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:While Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have achieved competitive performance in various tasks, their comprehension of the underlying structure and semantics of a scene remains understudied. To investigate the understanding of VLMs, we study their capability regarding object properties and relations in a controlled and interpretable manner. To this scope, we introduce CIVET, a novel and extensible framework for systematiC evaluatIon Via controllEd sTimuli. CIVET addresses the lack of standardized systematic evaluation for assessing VLMs' understanding, enabling researchers to test hypotheses with statistical rigor. With CIVET, we evaluate five state-of-the-art VLMs on exhaustive sets of stimuli, free from annotation noise, dataset-specific biases, and uncontrolled scene complexity. Our findings reveal that 1) current VLMs can accurately recognize only a limited set of basic object properties; 2) their performance heavily depends on the position of the object in the scene; 3) they struggle to understand basic relations among objects. Furthermore, a comparative evaluation with human annotators reveals that VLMs still fall short of achieving human-level accuracy.
Open-Source Conversational AI with SpeechBrain 1.0
Jul 02, 2024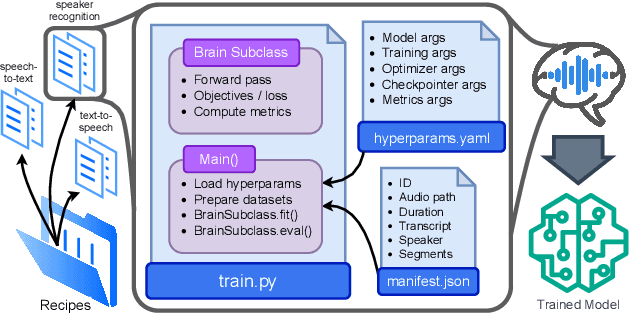
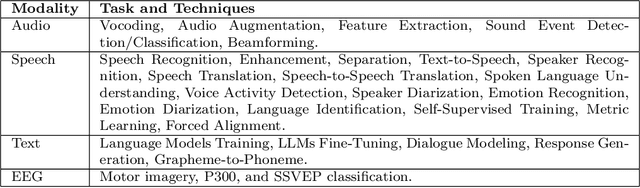
Abstract:SpeechBrain is an open-source Conversational AI toolkit based on PyTorch, focused particularly on speech processing tasks such as speech recognition, speech enhancement, speaker recognition, text-to-speech, and much more. It promotes transparency and replicability by releasing both the pre-trained models and the complete "recipes" of code and algorithms required for training them. This paper presents SpeechBrain 1.0, a significant milestone in the evolution of the toolkit, which now has over 200 recipes for speech, audio, and language processing tasks, and more than 100 models available on Hugging Face. SpeechBrain 1.0 introduces new technologies to support diverse learning modalities, Large Language Model (LLM) integration, and advanced decoding strategies, along with novel models, tasks, and modalities. It also includes a new benchmark repository, offering researchers a unified platform for evaluating models across diverse tasks
Should We Fine-Tune or RAG? Evaluating Different Techniques to Adapt LLMs for Dialogue
Jun 10, 2024



Abstract:We study the limitations of Large Language Models (LLMs) for the task of response generation in human-machine dialogue. Several techniques have been proposed in the literature for different dialogue types (e.g., Open-Domain). However, the evaluations of these techniques have been limited in terms of base LLMs, dialogue types and evaluation metrics. In this work, we extensively analyze different LLM adaptation techniques when applied to different dialogue types. We have selected two base LLMs, Llama-2 and Mistral, and four dialogue types Open-Domain, Knowledge-Grounded, Task-Oriented, and Question Answering. We evaluate the performance of in-context learning and fine-tuning techniques across datasets selected for each dialogue type. We assess the impact of incorporating external knowledge to ground the generation in both scenarios of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and gold knowledge. We adopt consistent evaluation and explainability criteria for automatic metrics and human evaluation protocols. Our analysis shows that there is no universal best-technique for adapting large language models as the efficacy of each technique depends on both the base LLM and the specific type of dialogue. Last but not least, the assessment of the best adaptation technique should include human evaluation to avoid false expectations and outcomes derived from automatic metrics.
Is Your LLM Outdated? Benchmarking LLMs & Alignment Algorithms for Time-Sensitive Knowledge
Apr 10, 2024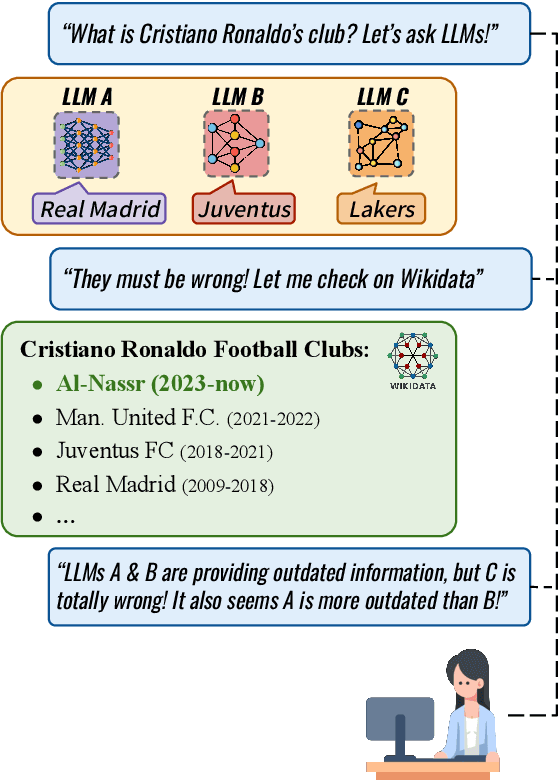
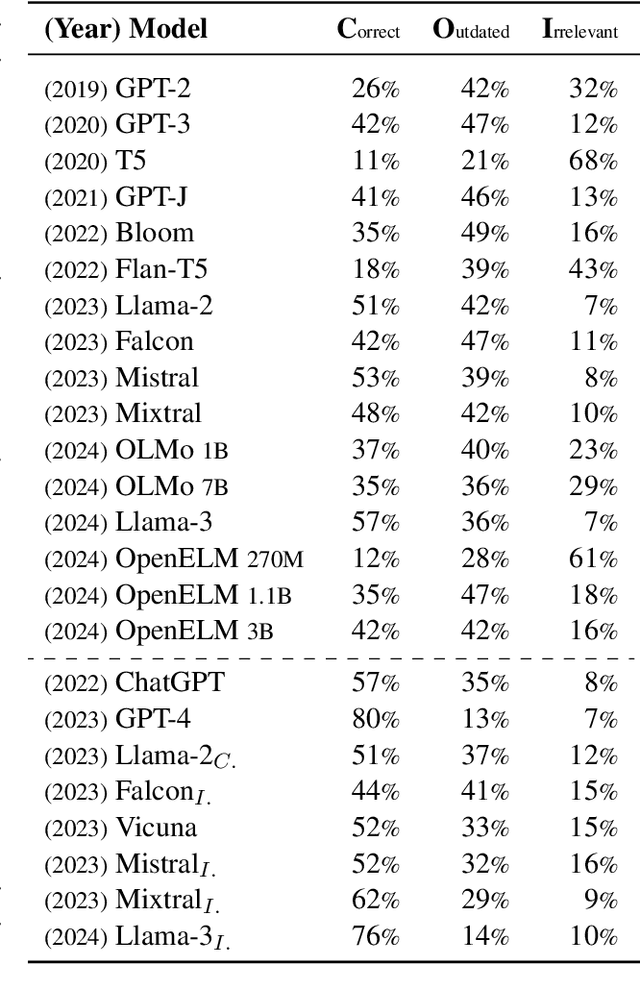

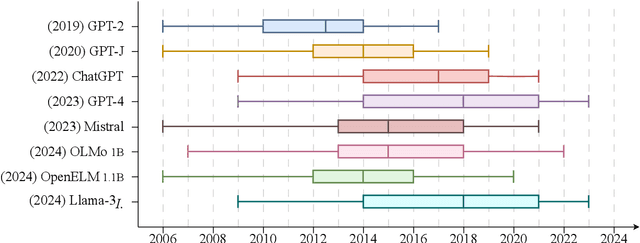
Abstract:We study the appropriateness of Large Language Models (LLMs) as knowledge repositories. We focus on the challenge of maintaining LLMs' factual knowledge up-to-date over time. Motivated by the lack of studies on identifying outdated knowledge within LLMs, we design and develop a dynamic benchmark with up-to-date ground truth answers for each target factual question. We evaluate eighteen open-source and closed-source state-of-the-art LLMs on time-sensitive knowledge retrieved in real-time from Wikidata. We select time-sensitive domain facts in politics, sports, and organizations, and estimate the recency of the information learned by the model during pre-training\fine-tuning. In the second contribution, we evaluate the effectiveness of knowledge editing methods for aligning LLMs with up-to-date factual knowledge and compare their performance with Retrieval Augmented Generation. The dynamic benchmark is designed to be used as-is to assess LLMs's up-to-dateness, as well as to be extended to other domains by sharing the code, the dataset, as well as evaluation and visualization scripts.
Are LLMs Robust for Spoken Dialogues?
Jan 04, 2024
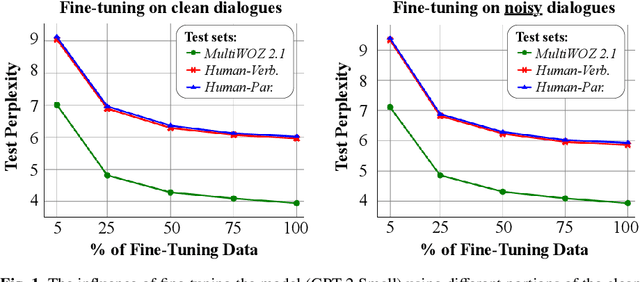

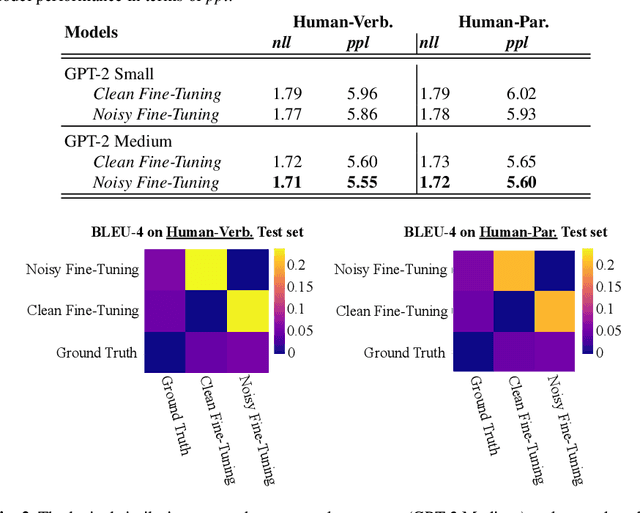
Abstract:Large Pre-Trained Language Models have demonstrated state-of-the-art performance in different downstream tasks, including dialogue state tracking and end-to-end response generation. Nevertheless, most of the publicly available datasets and benchmarks on task-oriented dialogues focus on written conversations. Consequently, the robustness of the developed models to spoken interactions is unknown. In this work, we have evaluated the performance of LLMs for spoken task-oriented dialogues on the DSTC11 test sets. Due to the lack of proper spoken dialogue datasets, we have automatically transcribed a development set of spoken dialogues with a state-of-the-art ASR engine. We have characterized the ASR-error types and their distributions and simulated these errors in a large dataset of dialogues. We report the intrinsic (perplexity) and extrinsic (human evaluation) performance of fine-tuned GPT-2 and T5 models in two subtasks of response generation and dialogue state tracking, respectively. The results show that LLMs are not robust to spoken noise by default, however, fine-tuning/training such models on a proper dataset of spoken TODs can result in a more robust performance.
Understanding Emotion Valence is a Joint Deep Learning Task
May 27, 2023



Abstract:The valence analysis of speakers' utterances or written posts helps to understand the activation and variations of the emotional state throughout the conversation. More recently, the concept of Emotion Carriers (EC) has been introduced to explain the emotion felt by the speaker and its manifestations. In this work, we investigate the natural inter-dependency of valence and ECs via a multi-task learning approach. We experiment with Pre-trained Language Models (PLM) for single-task, two-step, and joint settings for the valence and EC prediction tasks. We compare and evaluate the performance of generative (GPT-2) and discriminative (BERT) architectures in each setting. We observed that providing the ground truth label of one task improves the prediction performance of the models in the other task. We further observed that the discriminative model achieves the best trade-off of valence and EC prediction tasks in the joint prediction setting. As a result, we attain a single model that performs both tasks, thus, saving computation resources at training and inference times.
Response Generation in Longitudinal Dialogues: Which Knowledge Representation Helps?
May 25, 2023Abstract:Longitudinal Dialogues (LD) are the most challenging type of conversation for human-machine dialogue systems. LDs include the recollections of events, personal thoughts, and emotions specific to each individual in a sparse sequence of dialogue sessions. Dialogue systems designed for LDs should uniquely interact with the users over multiple sessions and long periods of time (e.g. weeks), and engage them in personal dialogues to elaborate on their feelings, thoughts, and real-life events. In this paper, we study the task of response generation in LDs. We evaluate whether general-purpose Pre-trained Language Models (PLM) are appropriate for this purpose. We fine-tune two PLMs, GePpeTto (GPT-2) and iT5, using a dataset of LDs. We experiment with different representations of the personal knowledge extracted from LDs for grounded response generation, including the graph representation of the mentioned events and participants. We evaluate the performance of the models via automatic metrics and the contribution of the knowledge via the Integrated Gradients technique. We categorize the natural language generation errors via human evaluations of contextualization, appropriateness and engagement of the user.
Whats New? Identifying the Unfolding of New Events in Narratives
Feb 20, 2023
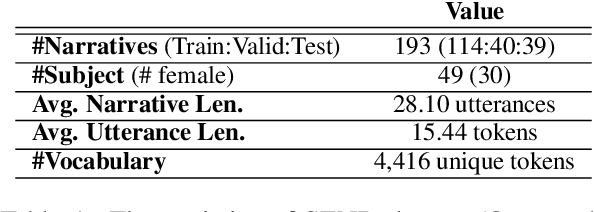
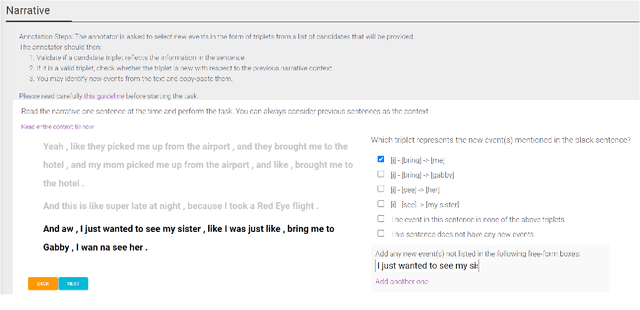
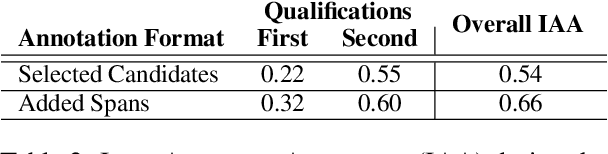
Abstract:Narratives include a rich source of events unfolding over time and context. Automatic understanding of these events may provide a summarised comprehension of the narrative for further computation (such as reasoning). In this paper, we study the Information Status (IS) of the events and propose a novel challenging task: the automatic identification of new events in a narrative. We define an event as a triplet of subject, predicate, and object. The event is categorized as new with respect to the discourse context and whether it can be inferred through commonsense reasoning. We annotated a publicly available corpus of narratives with the new events at sentence level using human annotators. We present the annotation protocol and a study aiming at validating the quality of the annotation and the difficulty of the task. We publish the annotated dataset, annotation materials, and machine learning baseline models for the task of new event extraction for narrative understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge