Pooneh Mousavi
Investigating Faithfulness in Large Audio Language Models
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Faithfulness measures whether chain-of-thought (CoT) representations accurately reflect a model's decision process and can be used as reliable explanations. Prior work has shown that CoTs from text-based LLMs are often unfaithful. This question has not been explored for large audio-language models (LALMs), where faithfulness is critical for safety-sensitive applications. Reasoning in LALMs is also more challenging, as models must first extract relevant clues from audio before reasoning over them. In this paper, we investigate the faithfulness of CoTs produced by several LALMs by applying targeted interventions, including paraphrasing, filler token injection, early answering, and introducing mistakes, on two challenging reasoning datasets: SAKURA and MMAR. After going through the aforementioned interventions across several datasets and tasks, our experiments suggest that, LALMs generally produce CoTs that appear to be faithful to their underlying decision processes.
Discrete Audio Tokens: More Than a Survey!
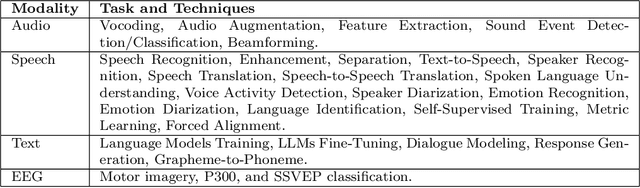
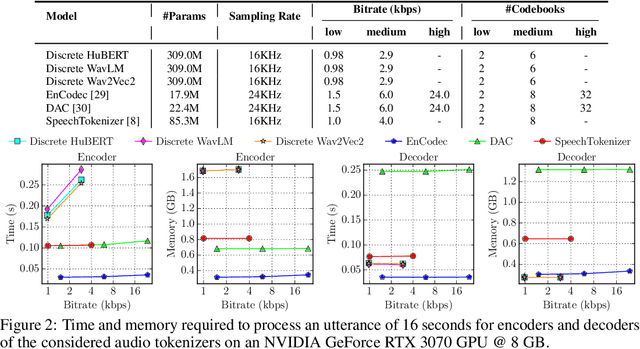
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Discrete audio tokens are compact representations that aim to preserve perceptual quality, phonetic content, and speaker characteristics while enabling efficient storage and inference, as well as competitive performance across diverse downstream tasks.They provide a practical alternative to continuous features, enabling the integration of speech and audio into modern large language models (LLMs). As interest in token-based audio processing grows, various tokenization methods have emerged, and several surveys have reviewed the latest progress in the field. However, existing studies often focus on specific domains or tasks and lack a unified comparison across various benchmarks. This paper presents a systematic review and benchmark of discrete audio tokenizers, covering three domains: speech, music, and general audio. We propose a taxonomy of tokenization approaches based on encoder-decoder, quantization techniques, training paradigm, streamability, and application domains. We evaluate tokenizers on multiple benchmarks for reconstruction, downstream performance, and acoustic language modeling, and analyze trade-offs through controlled ablation studies. Our findings highlight key limitations, practical considerations, and open challenges, providing insight and guidance for future research in this rapidly evolving area. For more information, including our main results and tokenizer database, please refer to our website: https://poonehmousavi.github.io/dates-website/.
ALAS: Measuring Latent Speech-Text Alignment For Spoken Language Understanding In Multimodal LLMs
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are widely used in Spoken Language Understanding (SLU). Recent SLU models process audio directly by adapting speech input into LLMs for better multimodal learning. A key consideration for these models is the cross-modal alignment between text and audio modalities, which is a telltale sign as to whether or not LLM is able to associate semantic meaning to audio segments. While various methods exist for fusing these modalities, there is no standard metric to evaluate alignment quality in LLMs. In this work, we propose a new metric, ALAS (Automatic Latent Alignment Score). Our study examines the correlation between audio and text representations across transformer layers, for two different tasks (Spoken Question Answering and Emotion Recognition). We showcase that our metric behaves as expected across different layers and different tasks.
LiSTEN: Learning Soft Token Embeddings for Neural Audio LLMs
May 24, 2025Abstract:Foundation models based on large language models (LLMs) have shown great success in handling various tasks and modalities. However, adapting these models for general-purpose audio-language tasks is challenging due to differences in acoustic environments and task variations. In this work, we introduce LiSTEN Learning Soft Token Embeddings for Neural Audio LLMs), a framework for adapting LLMs to speech and audio tasks. LiSTEN uses a dynamic prompt selection strategy with learnable key-value pairs, allowing the model to balance general and task-specific knowledge while avoiding overfitting in a multitask setting. Our approach reduces dependence on large-scale ASR or captioning datasets, achieves competitive performance with fewer trainable parameters, and simplifies training by using a single-stage process. Additionally, LiSTEN enhances interpretability by analyzing the diversity and overlap of selected prompts across different tasks.
What Are They Doing? Joint Audio-Speech Co-Reasoning
Sep 22, 2024


Abstract:In audio and speech processing, tasks usually focus on either the audio or speech modality, even when both sounds and human speech are present in the same audio clip. Recent Auditory Large Language Models (ALLMs) have made it possible to process audio and speech simultaneously within a single model, leading to further considerations of joint audio-speech tasks. In this paper, we investigate how well ALLMs can perform joint audio-speech processing. Specifically, we introduce Joint Audio-Speech Co-Reasoning (JASCO), a novel task that unifies audio and speech processing, strictly requiring co-reasoning across both modalities. We release a scene-reasoning dataset called "What Are They Doing" and establish a joint audio-speech benchmark to evaluate the joint reasoning capability of popular ALLMs. Additionally, we provide deeper insights into the models' behaviors by analyzing their dependence on each modality.
Open-Source Conversational AI with SpeechBrain 1.0
Jul 02, 2024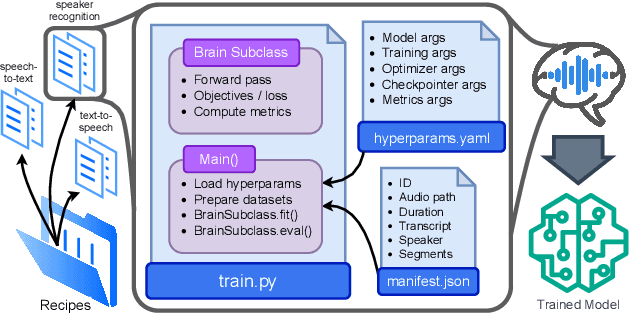
Abstract:SpeechBrain is an open-source Conversational AI toolkit based on PyTorch, focused particularly on speech processing tasks such as speech recognition, speech enhancement, speaker recognition, text-to-speech, and much more. It promotes transparency and replicability by releasing both the pre-trained models and the complete "recipes" of code and algorithms required for training them. This paper presents SpeechBrain 1.0, a significant milestone in the evolution of the toolkit, which now has over 200 recipes for speech, audio, and language processing tasks, and more than 100 models available on Hugging Face. SpeechBrain 1.0 introduces new technologies to support diverse learning modalities, Large Language Model (LLM) integration, and advanced decoding strategies, along with novel models, tasks, and modalities. It also includes a new benchmark repository, offering researchers a unified platform for evaluating models across diverse tasks
DASB -- Discrete Audio and Speech Benchmark
Jun 20, 2024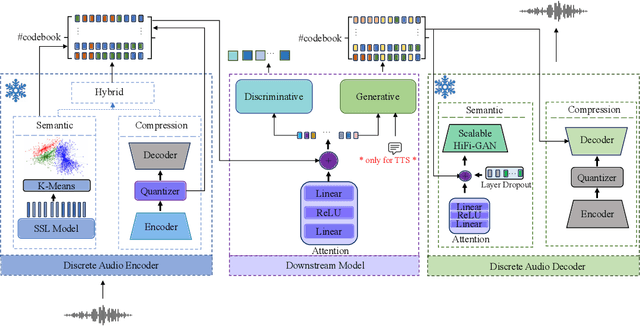
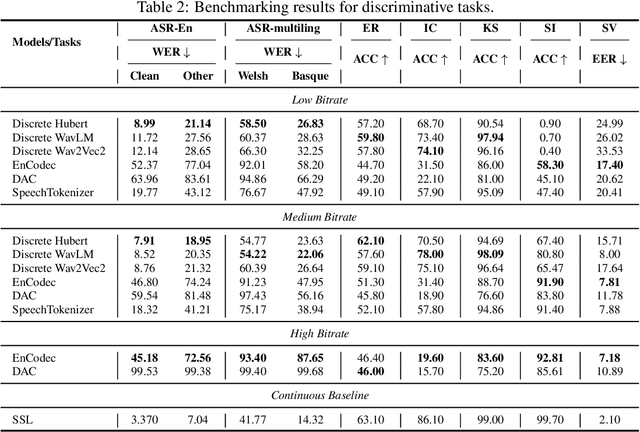
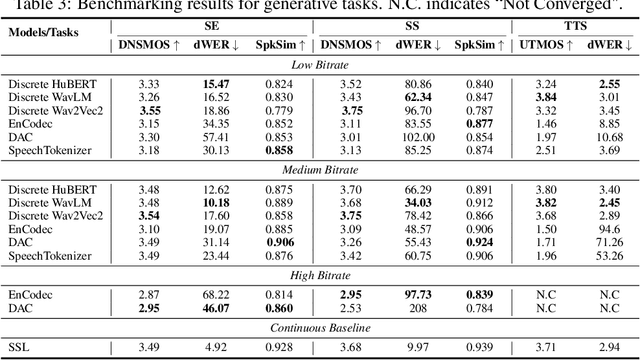
Abstract:Discrete audio tokens have recently gained considerable attention for their potential to connect audio and language processing, enabling the creation of modern multimodal large language models. Ideal audio tokens must effectively preserve phonetic and semantic content along with paralinguistic information, speaker identity, and other details. While several types of audio tokens have been recently proposed, identifying the optimal tokenizer for various tasks is challenging due to the inconsistent evaluation settings in existing studies. To address this gap, we release the Discrete Audio and Speech Benchmark (DASB), a comprehensive leaderboard for benchmarking discrete audio tokens across a wide range of discriminative tasks, including speech recognition, speaker identification and verification, emotion recognition, keyword spotting, and intent classification, as well as generative tasks such as speech enhancement, separation, and text-to-speech. Our results show that, on average, semantic tokens outperform compression tokens across most discriminative and generative tasks. However, the performance gap between semantic tokens and standard continuous representations remains substantial, highlighting the need for further research in this field.
How Should We Extract Discrete Audio Tokens from Self-Supervised Models?
Jun 15, 2024



Abstract:Discrete audio tokens have recently gained attention for their potential to bridge the gap between audio and language processing. Ideal audio tokens must preserve content, paralinguistic elements, speaker identity, and many other audio details. Current audio tokenization methods fall into two categories: Semantic tokens, acquired through quantization of Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) models, and Neural compression-based tokens (codecs). Although previous studies have benchmarked codec models to identify optimal configurations, the ideal setup for quantizing pretrained SSL models remains unclear. This paper explores the optimal configuration of semantic tokens across discriminative and generative tasks. We propose a scalable solution to train a universal vocoder across multiple SSL layers. Furthermore, an attention mechanism is employed to identify task-specific influential layers, enhancing the adaptability and performance of semantic tokens in diverse audio applications.
CL-MASR: A Continual Learning Benchmark for Multilingual ASR
Oct 25, 2023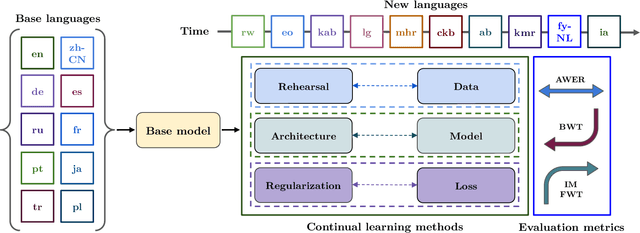
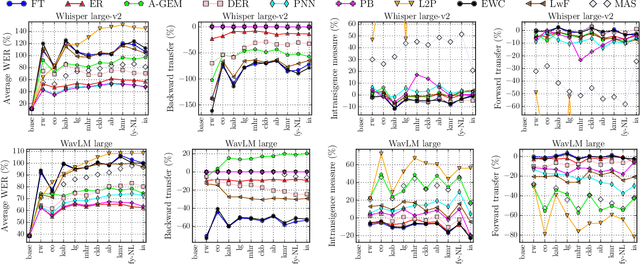
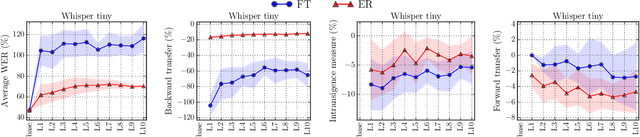
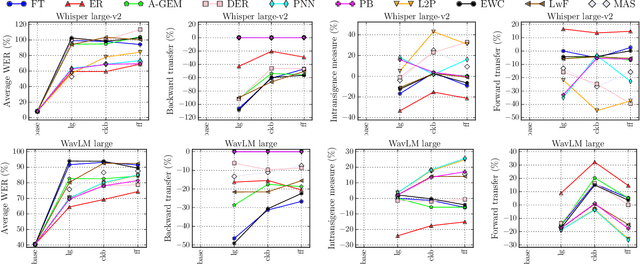
Abstract:Modern multilingual automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems like Whisper have made it possible to transcribe audio in multiple languages with a single model. However, current state-of-the-art ASR models are typically evaluated on individual languages or in a multi-task setting, overlooking the challenge of continually learning new languages. There is insufficient research on how to add new languages without losing valuable information from previous data. Furthermore, existing continual learning benchmarks focus mostly on vision and language tasks, leaving continual learning for multilingual ASR largely unexplored. To bridge this gap, we propose CL-MASR, a benchmark designed for studying multilingual ASR in a continual learning setting. CL-MASR provides a diverse set of continual learning methods implemented on top of large-scale pretrained ASR models, along with common metrics to assess the effectiveness of learning new languages while addressing the issue of catastrophic forgetting. To the best of our knowledge, CL-MASR is the first continual learning benchmark for the multilingual ASR task. The code is available at https://github.com/speechbrain/benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge