Gallil Maimon
Discrete Audio Tokens: More Than a Survey!
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Discrete audio tokens are compact representations that aim to preserve perceptual quality, phonetic content, and speaker characteristics while enabling efficient storage and inference, as well as competitive performance across diverse downstream tasks.They provide a practical alternative to continuous features, enabling the integration of speech and audio into modern large language models (LLMs). As interest in token-based audio processing grows, various tokenization methods have emerged, and several surveys have reviewed the latest progress in the field. However, existing studies often focus on specific domains or tasks and lack a unified comparison across various benchmarks. This paper presents a systematic review and benchmark of discrete audio tokenizers, covering three domains: speech, music, and general audio. We propose a taxonomy of tokenization approaches based on encoder-decoder, quantization techniques, training paradigm, streamability, and application domains. We evaluate tokenizers on multiple benchmarks for reconstruction, downstream performance, and acoustic language modeling, and analyze trade-offs through controlled ablation studies. Our findings highlight key limitations, practical considerations, and open challenges, providing insight and guidance for future research in this rapidly evolving area. For more information, including our main results and tokenizer database, please refer to our website: https://poonehmousavi.github.io/dates-website/.
StressTest: Can YOUR Speech LM Handle the Stress?
May 28, 2025Abstract:Sentence stress refers to emphasis, placed on specific words within a spoken utterance to highlight or contrast an idea, or to introduce new information. It is often used to imply an underlying intention that is not explicitly stated. Recent advances in speech-aware language models (SLMs) have enabled direct processing of audio, allowing models to bypass transcription and access the full richness of the speech signal and perform audio reasoning tasks such as spoken question answering. Despite the crucial role of sentence stress in shaping meaning and speaker intent, it remains largely overlooked in evaluation and development of such models. In this work, we address this gap by introducing StressTest, a benchmark specifically designed to evaluate a model's ability to distinguish between interpretations of spoken sentences based on the stress pattern. We assess the performance of several leading SLMs and find that, despite their overall capabilities, they perform poorly on such tasks. To overcome this limitation, we propose a novel synthetic data generation pipeline, and create Stress17k, a training set that simulates change of meaning implied by stress variation. Then, we empirically show that optimizing models with this synthetic dataset aligns well with real-world recordings and enables effective finetuning of SLMs. Results suggest, that our finetuned model, StresSLM, significantly outperforms existing models on both sentence stress reasoning and detection tasks. Code, models, data, and audio samples - pages.cs.huji.ac.il/adiyoss-lab/stresstest.
Scaling Analysis of Interleaved Speech-Text Language Models
Apr 03, 2025



Abstract:Existing Speech Language Model (SLM) scaling analysis paints a bleak picture. They predict that SLMs require much more compute and data compared to text, leading some to question the feasibility of training high-quality SLMs. However, modern SLMs are often initialised from pre-trained TextLMs using speech-text interleaving to allow knowledge transfer. This raises the question - Do interleaved SLMs scale more efficiently than textless-SLMs? In this paper we answer a resounding, yes! We conduct scaling analysis of interleaved SLMs by training several dozen and analysing the scaling trends. We see that under this setup SLMs scale more efficiently with compute. Additionally, our results indicate that the scaling-dynamics are significantly different than textless-SLMs, suggesting one should allocate notably more of the compute budget for increasing model size over training tokens. We also study the role of synthetic data and TextLM model families in unlocking this potential. Results suggest, that our scaled up model achieves comparable performance with leading models on speech semantic metrics while using less compute and data than other approaches. We open source models, samples, and data - https://pages.cs.huji.ac.il/adiyoss-lab/sims.
Slamming: Training a Speech Language Model on One GPU in a Day
Feb 19, 2025


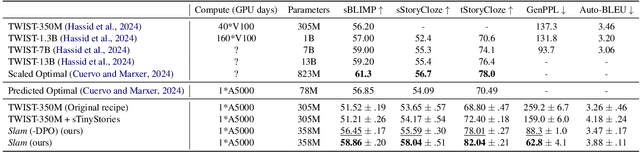
Abstract:We introduce Slam, a recipe for training high-quality Speech Language Models (SLMs) on a single academic GPU in 24 hours. We do so through empirical analysis of model initialisation and architecture, synthetic training data, preference optimisation with synthetic data and tweaking all other components. We empirically demonstrate that this training recipe also scales well with more compute getting results on par with leading SLMs in a fraction of the compute cost. We hope these insights will make SLM training and research more accessible. In the context of SLM scaling laws, our results far outperform predicted compute optimal performance, giving an optimistic view to SLM feasibility. See code, data, models, samples at - https://pages.cs.huji.ac.il/adiyoss-lab/slamming .
A Suite for Acoustic Language Model Evaluation
Sep 11, 2024Abstract:Speech language models have recently demonstrated great potential as universal speech processing systems. Such models have the ability to model the rich acoustic information existing in audio signals, beyond spoken content, such as emotion, background noise, etc. Despite this, evaluation benchmarks which evaluate awareness to a wide range of acoustic aspects, are lacking. To help bridge this gap, we introduce SALMon, a novel evaluation suite encompassing background noise, emotion, speaker identity and room impulse response. The proposed benchmarks both evaluate the consistency of the inspected element and how much it matches the spoken text. We follow a modelling based approach, measuring whether a model gives correct samples higher scores than incorrect ones. This approach makes the benchmark fast to compute even for large models. We evaluated several speech language models on SALMon, thus highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of each evaluated method. Code and data are publicly available at https://pages.cs.huji.ac.il/adiyoss-lab/salmon/ .
Silent Killer: Optimizing Backdoor Trigger Yields a Stealthy and Powerful Data Poisoning Attack
Jan 05, 2023



Abstract:We propose a stealthy and powerful backdoor attack on neural networks based on data poisoning (DP). In contrast to previous attacks, both the poison and the trigger in our method are stealthy. We are able to change the model's classification of samples from a source class to a target class chosen by the attacker. We do so by using a small number of poisoned training samples with nearly imperceptible perturbations, without changing their labels. At inference time, we use a stealthy perturbation added to the attacked samples as a trigger. This perturbation is crafted as a universal adversarial perturbation (UAP), and the poison is crafted using gradient alignment coupled to this trigger. Our method is highly efficient in crafting time compared to previous methods and requires only a trained surrogate model without additional retraining. Our attack achieves state-of-the-art results in terms of attack success rate while maintaining high accuracy on clean samples.
Speaking Style Conversion With Discrete Self-Supervised Units
Dec 19, 2022



Abstract:Voice Conversion (VC) is the task of making a spoken utterance by one speaker sound as if uttered by a different speaker, while keeping other aspects like content unchanged. Current VC methods, focus primarily on spectral features like timbre, while ignoring the unique speaking style of people which often impacts prosody. In this study, we introduce a method for converting not only the timbre, but also prosodic information (i.e., rhythm and pitch changes) to those of the target speaker. The proposed approach is based on a pretrained, self-supervised, model for encoding speech to discrete units, which make it simple, effective, and easy to optimise. We consider the many-to-many setting with no paired data. We introduce a suite of quantitative and qualitative evaluation metrics for this setup, and empirically demonstrate the proposed approach is significantly superior to the evaluated baselines. Code and samples can be found under https://pages.cs.huji.ac.il/adiyoss-lab/dissc/ .
A Universal Adversarial Policy for Text Classifiers
Jun 19, 2022



Abstract:Discovering the existence of universal adversarial perturbations had large theoretical and practical impacts on the field of adversarial learning. In the text domain, most universal studies focused on adversarial prefixes which are added to all texts. However, unlike the vision domain, adding the same perturbation to different inputs results in noticeably unnatural inputs. Therefore, we introduce a new universal adversarial setup - a universal adversarial policy, which has many advantages of other universal attacks but also results in valid texts - thus making it relevant in practice. We achieve this by learning a single search policy over a predefined set of semantics preserving text alterations, on many texts. This formulation is universal in that the policy is successful in finding adversarial examples on new texts efficiently. Our approach uses text perturbations which were extensively shown to produce natural attacks in the non-universal setup (specific synonym replacements). We suggest a strong baseline approach for this formulation which uses reinforcement learning. It's ability to generalise (from as few as 500 training texts) shows that universal adversarial patterns exist in the text domain as well.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge