Santanu Pal
Beyond the Sentence: A Survey on Context-Aware Machine Translation with Large Language Models
Jun 09, 2025
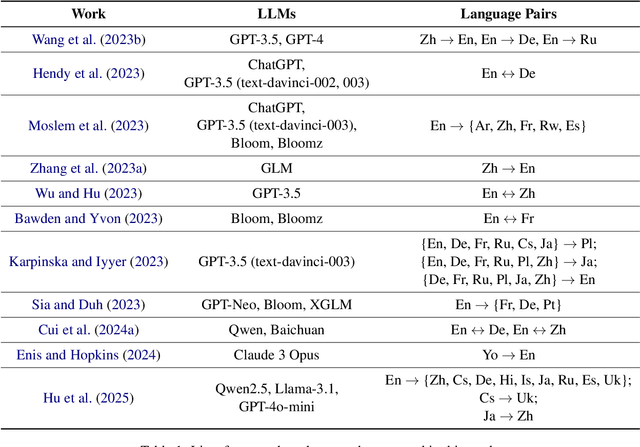
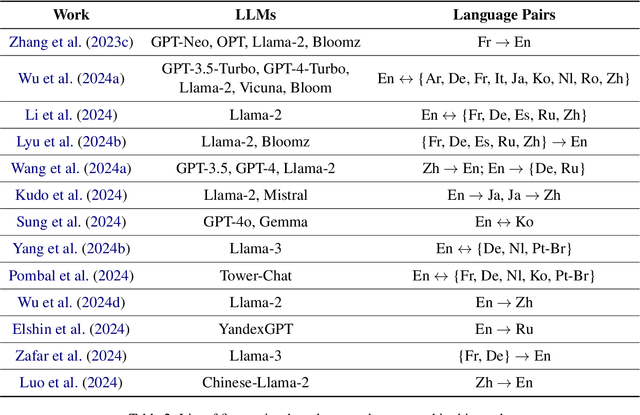
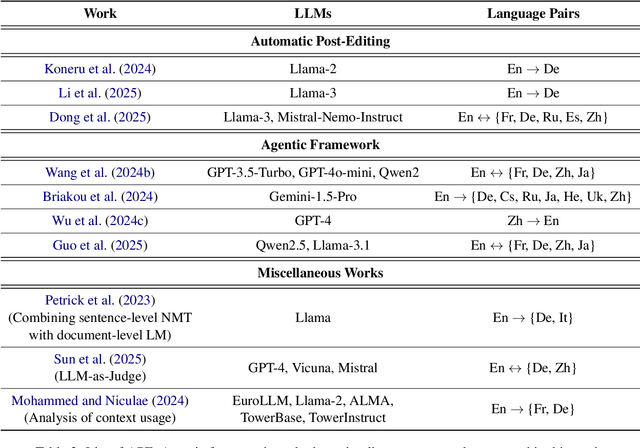
Abstract:Despite the popularity of the large language models (LLMs), their application to machine translation is relatively underexplored, especially in context-aware settings. This work presents a literature review of context-aware translation with LLMs. The existing works utilise prompting and fine-tuning approaches, with few focusing on automatic post-editing and creating translation agents for context-aware machine translation. We observed that the commercial LLMs (such as ChatGPT and Tower LLM) achieved better results than the open-source LLMs (such as Llama and Bloom LLMs), and prompt-based approaches serve as good baselines to assess the quality of translations. Finally, we present some interesting future directions to explore.
A Case Study on Context-Aware Neural Machine Translation with Multi-Task Learning
Jul 03, 2024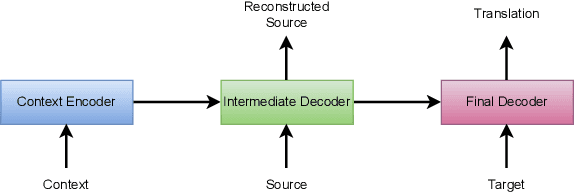
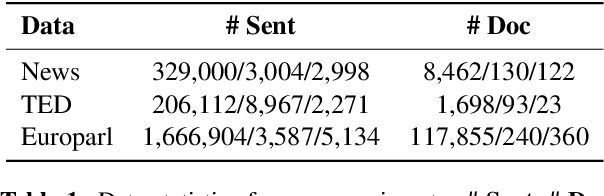
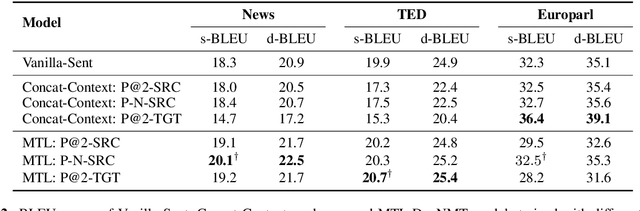
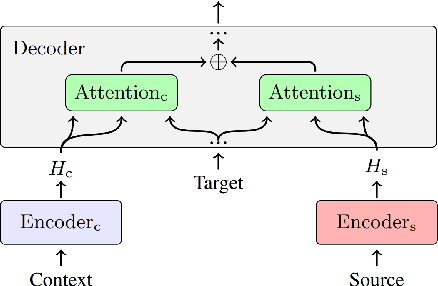
Abstract:In document-level neural machine translation (DocNMT), multi-encoder approaches are common in encoding context and source sentences. Recent studies \cite{li-etal-2020-multi-encoder} have shown that the context encoder generates noise and makes the model robust to the choice of context. This paper further investigates this observation by explicitly modelling context encoding through multi-task learning (MTL) to make the model sensitive to the choice of context. We conduct experiments on cascade MTL architecture, which consists of one encoder and two decoders. Generation of the source from the context is considered an auxiliary task, and generation of the target from the source is the main task. We experimented with German--English language pairs on News, TED, and Europarl corpora. Evaluation results show that the proposed MTL approach performs better than concatenation-based and multi-encoder DocNMT models in low-resource settings and is sensitive to the choice of context. However, we observe that the MTL models are failing to generate the source from the context. These observations align with the previous studies, and this might suggest that the available document-level parallel corpora are not context-aware, and a robust sentence-level model can outperform the context-aware models.
TRAVID: An End-to-End Video Translation Framework
Sep 20, 2023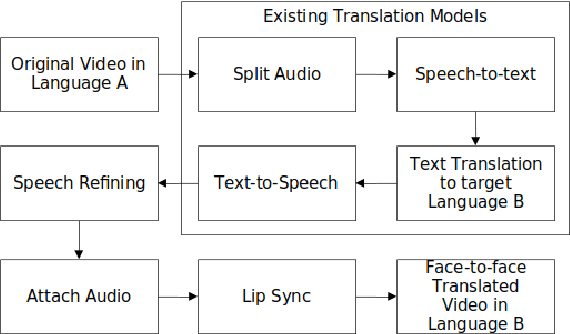
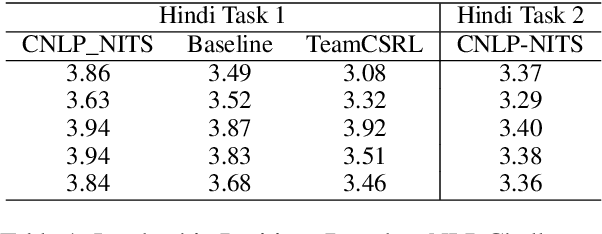
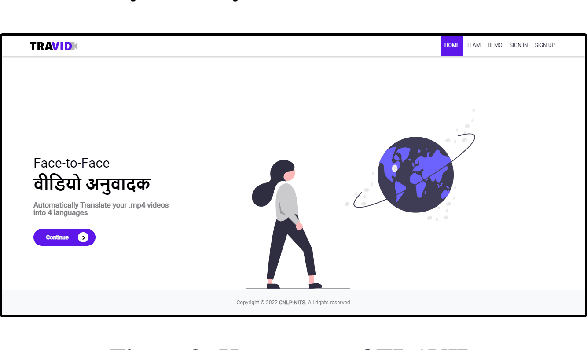
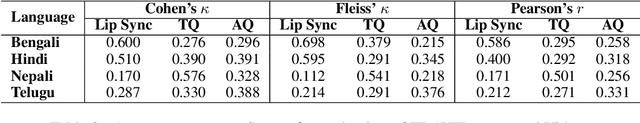
Abstract:In today's globalized world, effective communication with people from diverse linguistic backgrounds has become increasingly crucial. While traditional methods of language translation, such as written text or voice-only translations, can accomplish the task, they often fail to capture the complete context and nuanced information conveyed through nonverbal cues like facial expressions and lip movements. In this paper, we present an end-to-end video translation system that not only translates spoken language but also synchronizes the translated speech with the lip movements of the speaker. Our system focuses on translating educational lectures in various Indian languages, and it is designed to be effective even in low-resource system settings. By incorporating lip movements that align with the target language and matching them with the speaker's voice using voice cloning techniques, our application offers an enhanced experience for students and users. This additional feature creates a more immersive and realistic learning environment, ultimately making the learning process more effective and engaging.
A Case Study on Context Encoding in Multi-Encoder based Document-Level Neural Machine Translation
Aug 11, 2023



Abstract:Recent studies have shown that the multi-encoder models are agnostic to the choice of context, and the context encoder generates noise which helps improve the models in terms of BLEU score. In this paper, we further explore this idea by evaluating with context-aware pronoun translation test set by training multi-encoder models trained on three different context settings viz, previous two sentences, random two sentences, and a mix of both as context. Specifically, we evaluate the models on the ContraPro test set to study how different contexts affect pronoun translation accuracy. The results show that the model can perform well on the ContraPro test set even when the context is random. We also analyze the source representations to study whether the context encoder generates noise. Our analysis shows that the context encoder provides sufficient information to learn discourse-level information. Additionally, we observe that mixing the selected context (the previous two sentences in this case) and the random context is generally better than the other settings.
Is Attention always needed? A Case Study on Language Identification from Speech
Oct 05, 2021
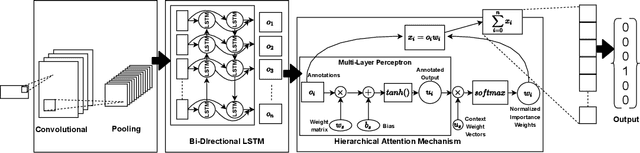
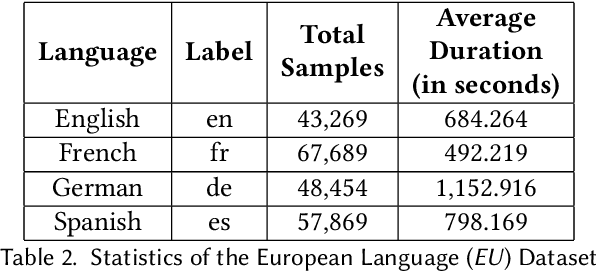
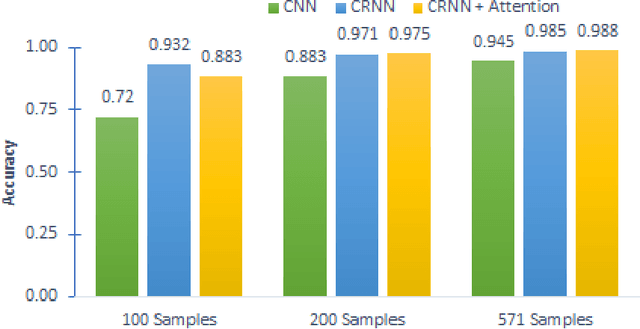
Abstract:Language Identification (LID), a recommended initial step to Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), is used to detect a spoken language from audio specimens. In state-of-the-art systems capable of multilingual speech processing, however, users have to explicitly set one or more languages before using them. LID, therefore, plays a very important role in situations where ASR based systems cannot parse the uttered language in multilingual contexts causing failure in speech recognition. We propose an attention based convolutional recurrent neural network (CRNN with Attention) that works on Mel-frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC) features of audio specimens. Additionally, we reproduce some state-of-the-art approaches, namely Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network (CRNN), and compare them to our proposed method. We performed extensive evaluation on thirteen different Indian languages and our model achieves classification accuracy over 98%. Our LID model is robust to noise and provides 91.2% accuracy in a noisy scenario. The proposed model is easily extensible to new languages.
The Transference Architecture for Automatic Post-Editing
Aug 26, 2019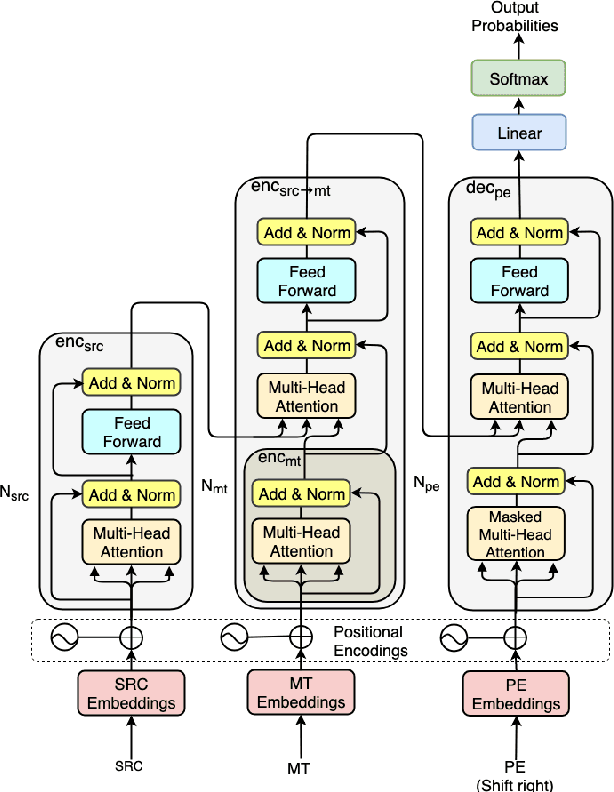
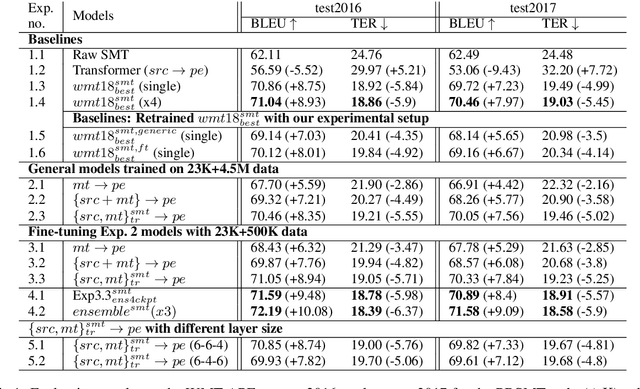
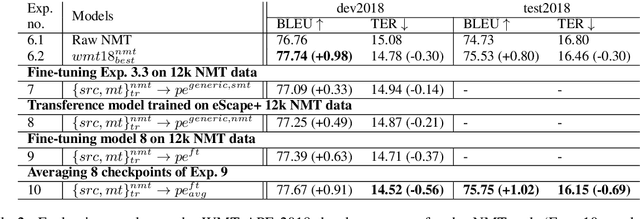
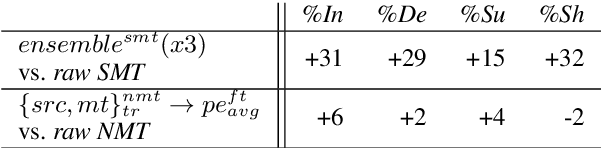
Abstract:In automatic post-editing (APE) it makes sense to condition post-editing (pe) decisions on both the source (src) and the machine translated text (mt) as input. This has led to multi-source encoder based APE approaches. A research challenge now is the search for architectures that best support the capture, preparation and provision of src and mt information and its integration with pe decisions. In this paper we present a new multi-source APE model, called transference. Unlike previous approaches, it (i) uses a transformer encoder block for src, (ii) followed by a decoder block, but without masking for self-attention on mt, which effectively acts as second encoder combining src -> mt, and (iii) feeds this representation into a final decoder block generating pe. Our model outperforms the state-of-the-art by 1 BLEU point on the WMT 2016, 2017, and 2018 English--German APE shared tasks (PBSMT and NMT). We further investigate the importance of our newly introduced second encoder and find that a too small amount of layers does hurt the performance, while reducing the number of layers of the decoder does not matter much.
Improving CAT Tools in the Translation Workflow: New Approaches and Evaluation
Aug 16, 2019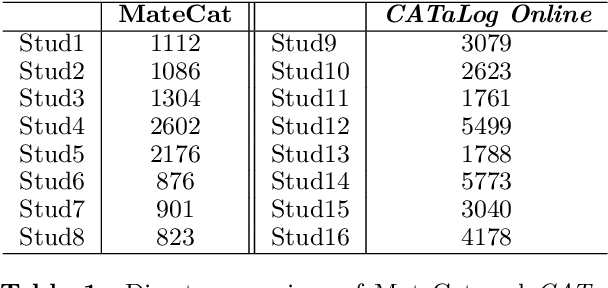
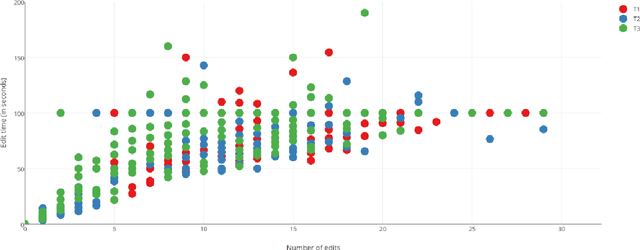
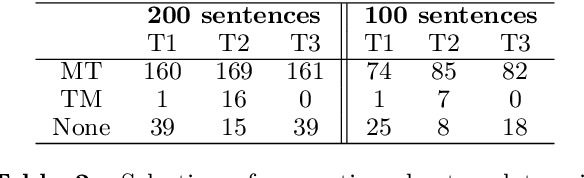
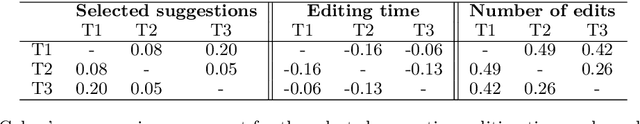
Abstract:This paper describes strategies to improve an existing web-based computer-aided translation (CAT) tool entitled CATaLog Online. CATaLog Online provides a post-editing environment with simple yet helpful project management tools. It offers translation suggestions from translation memories (TM), machine translation (MT), and automatic post-editing (APE) and records detailed logs of post-editing activities. To test the new approaches proposed in this paper, we carried out a user study on an English--German translation task using CATaLog Online. User feedback revealed that the users preferred using CATaLog Online over existing CAT tools in some respects, especially by selecting the output of the MT system and taking advantage of the color scheme for TM suggestions.
UDS--DFKI Submission to the WMT2019 Similar Language Translation Shared Task
Aug 16, 2019

Abstract:In this paper we present the UDS-DFKI system submitted to the Similar Language Translation shared task at WMT 2019. The first edition of this shared task featured data from three pairs of similar languages: Czech and Polish, Hindi and Nepali, and Portuguese and Spanish. Participants could choose to participate in any of these three tracks and submit system outputs in any translation direction. We report the results obtained by our system in translating from Czech to Polish and comment on the impact of out-of-domain test data in the performance of our system. UDS-DFKI achieved competitive performance ranking second among ten teams in Czech to Polish translation.
Integrating Artificial and Human Intelligence for Efficient Translation
Mar 07, 2019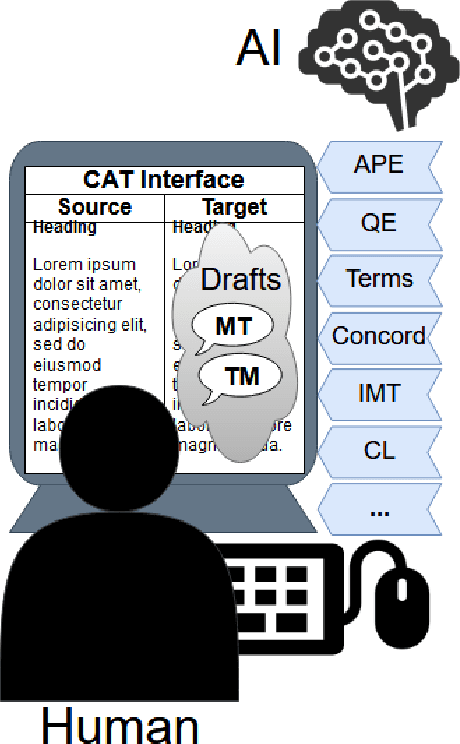
Abstract:Current advances in machine translation increase the need for translators to switch from traditional translation to post-editing of machine-translated text, a process that saves time and improves quality. Human and artificial intelligence need to be integrated in an efficient way to leverage the advantages of both for the translation task. This paper outlines approaches at this boundary of AI and HCI and discusses open research questions to further advance the field.
Discriminating between Indo-Aryan Languages Using SVM Ensembles
Jul 09, 2018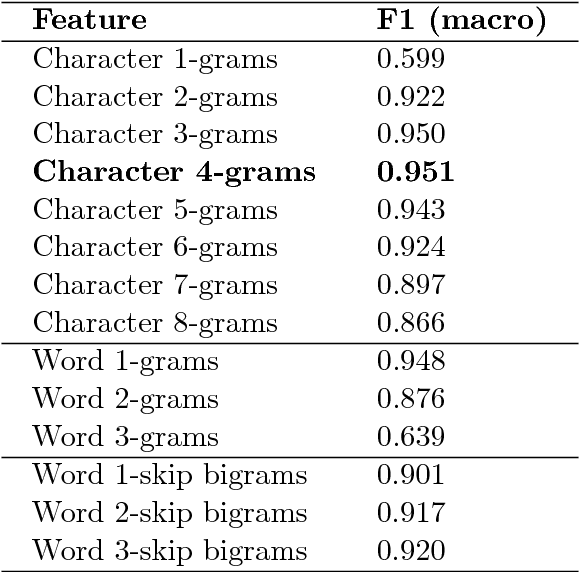
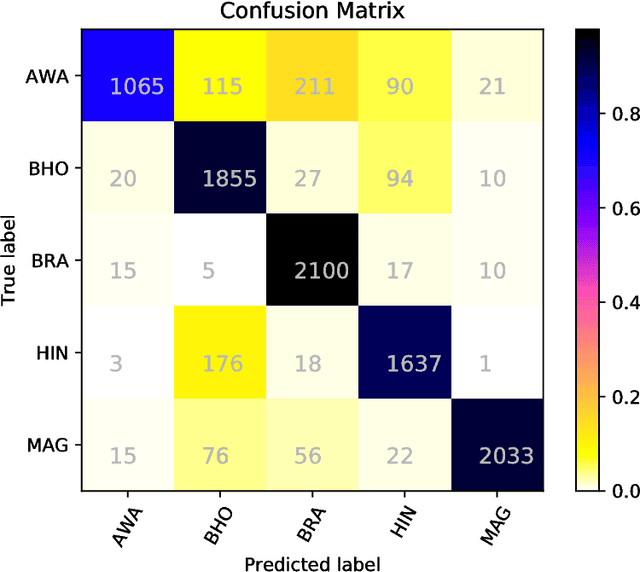

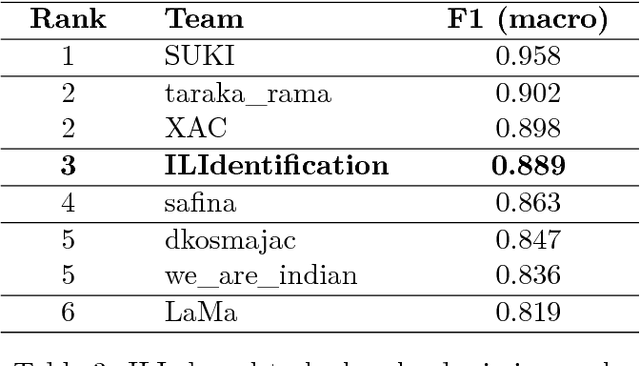
Abstract:In this paper we present a system based on SVM ensembles trained on characters and words to discriminate between five similar languages of the Indo-Aryan family: Hindi, Braj Bhasha, Awadhi, Bhojpuri, and Magahi. We investigate the performance of individual features and combine the output of single classifiers to maximize performance. The system competed in the Indo-Aryan Language Identification (ILI) shared task organized within the VarDial Evaluation Campaign 2018. Our best entry in the competition, named ILIdentification, scored 88:95% F1 score and it was ranked 3rd out of 8 teams.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge