Alina Maria Ciobanu
Classifier Ensembles for Dialect and Language Variety Identification
Aug 14, 2018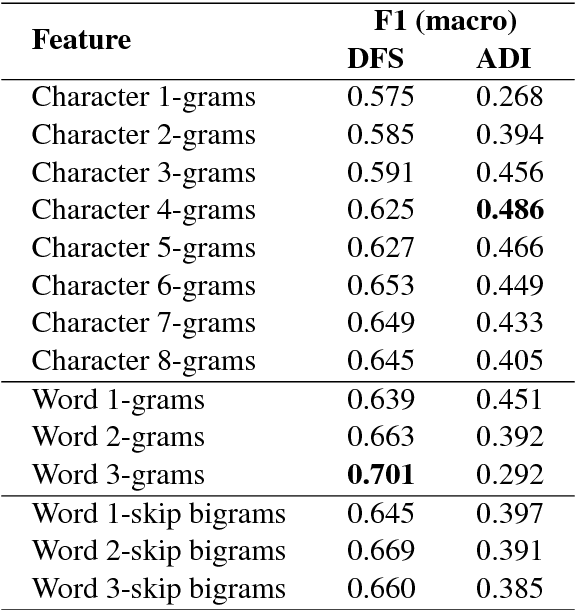
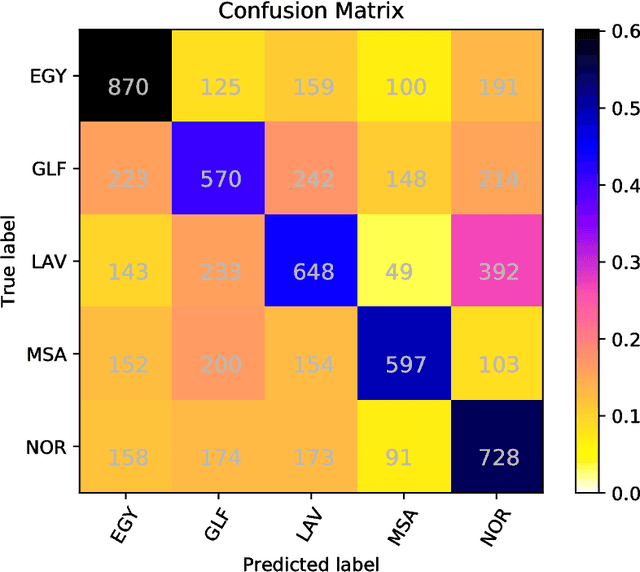
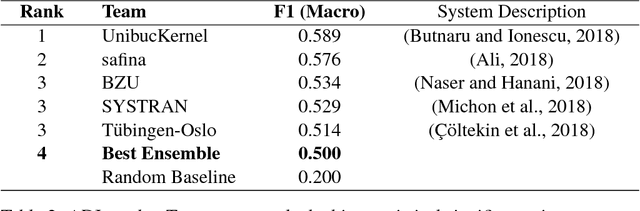
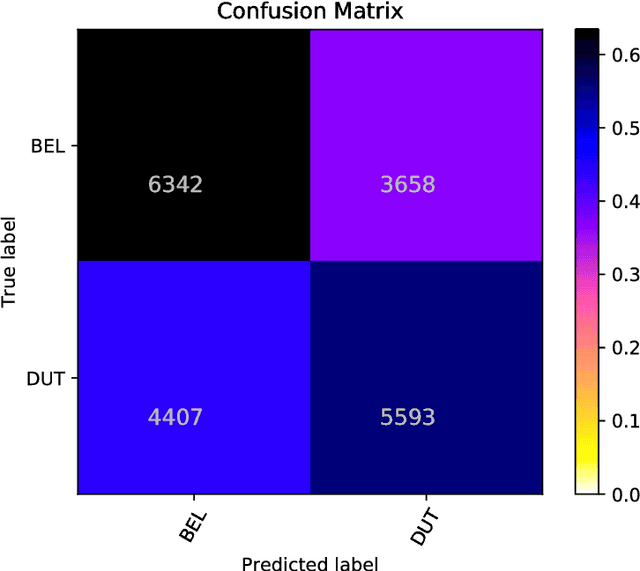
Abstract:In this paper we present ensemble-based systems for dialect and language variety identification using the datasets made available by the organizers of the VarDial Evaluation Campaign 2018. We present a system developed to discriminate between Flemish and Dutch in subtitles and a system trained to discriminate between four Arabic dialects: Egyptian, Levantine, Gulf, North African, and Modern Standard Arabic in speech broadcasts. Finally, we compare the performance of these two systems with the other systems submitted to the Discriminating between Dutch and Flemish in Subtitles (DFS) and the Arabic Dialect Identification (ADI) shared tasks at VarDial 2018.
German Dialect Identification Using Classifier Ensembles
Jul 22, 2018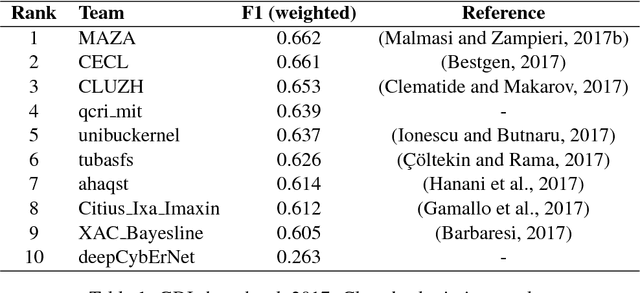
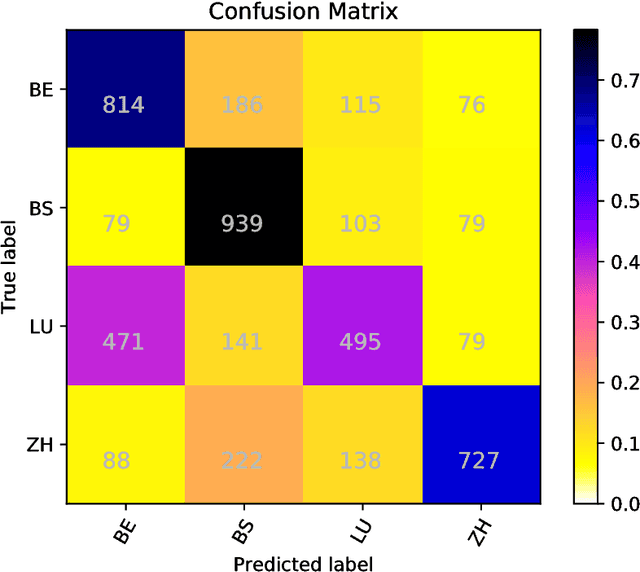
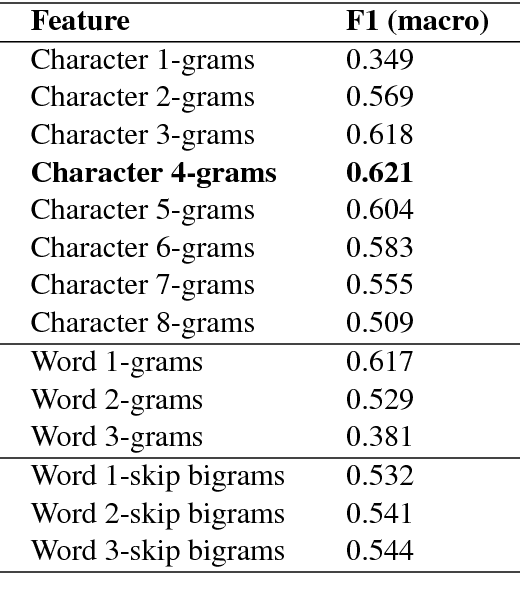
Abstract:In this paper we present the GDI_classification entry to the second German Dialect Identification (GDI) shared task organized within the scope of the VarDial Evaluation Campaign 2018. We present a system based on SVM classifier ensembles trained on characters and words. The system was trained on a collection of speech transcripts of five Swiss-German dialects provided by the organizers. The transcripts included in the dataset contained speakers from Basel, Bern, Lucerne, and Zurich. Our entry in the challenge reached 62.03% F1-score and was ranked third out of eight teams.
Discriminating between Indo-Aryan Languages Using SVM Ensembles
Jul 09, 2018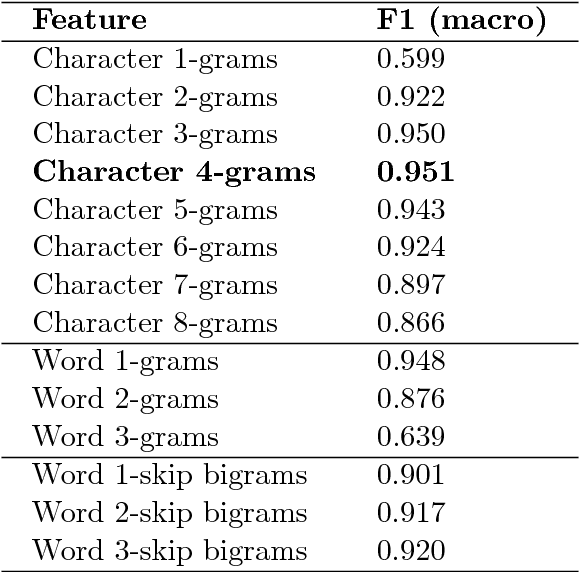
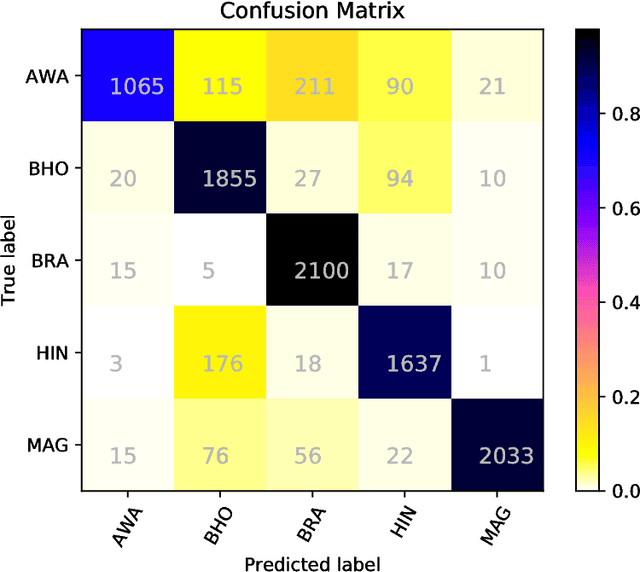

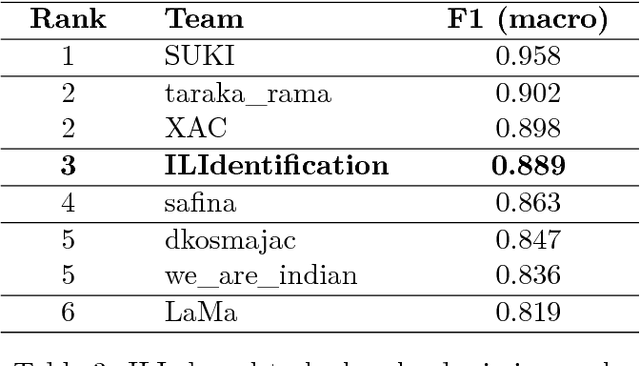
Abstract:In this paper we present a system based on SVM ensembles trained on characters and words to discriminate between five similar languages of the Indo-Aryan family: Hindi, Braj Bhasha, Awadhi, Bhojpuri, and Magahi. We investigate the performance of individual features and combine the output of single classifiers to maximize performance. The system competed in the Indo-Aryan Language Identification (ILI) shared task organized within the VarDial Evaluation Campaign 2018. Our best entry in the competition, named ILIdentification, scored 88:95% F1 score and it was ranked 3rd out of 8 teams.
Native Language Identification on Text and Speech
Jul 22, 2017
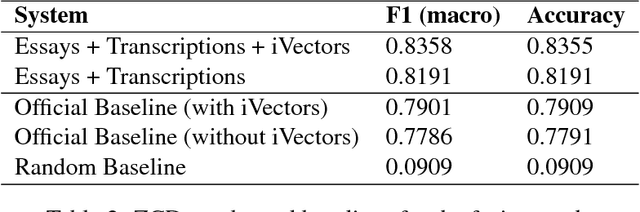
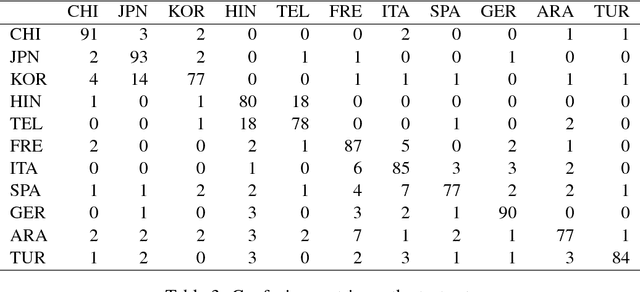

Abstract:This paper presents an ensemble system combining the output of multiple SVM classifiers to native language identification (NLI). The system was submitted to the NLI Shared Task 2017 fusion track which featured students essays and spoken responses in form of audio transcriptions and iVectors by non-native English speakers of eleven native languages. Our system competed in the challenge under the team name ZCD and was based on an ensemble of SVM classifiers trained on character n-grams achieving 83.58% accuracy and ranking 3rd in the shared task.
Including Dialects and Language Varieties in Author Profiling
Jul 03, 2017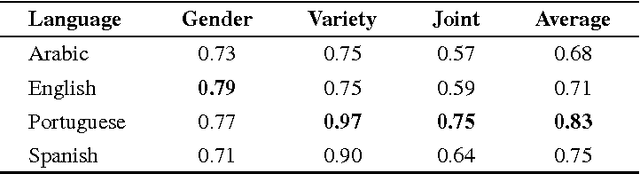
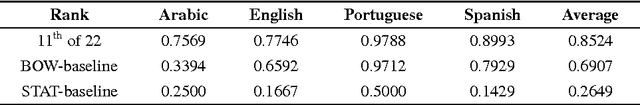
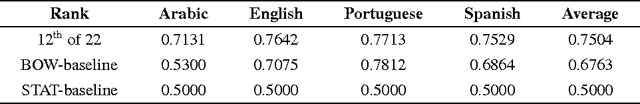
Abstract:This paper presents a computational approach to author profiling taking gender and language variety into account. We apply an ensemble system with the output of multiple linear SVM classifiers trained on character and word $n$-grams. We evaluate the system using the dataset provided by the organizers of the 2017 PAN lab on author profiling. Our approach achieved 75% average accuracy on gender identification on tweets written in four languages and 97% accuracy on language variety identification for Portuguese.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge