Sanjay Singh
Jack
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
A Multimodal Dataset for Enhancing Industrial Task Monitoring and Engagement Prediction
Jan 10, 2025



Abstract:Detecting and interpreting operator actions, engagement, and object interactions in dynamic industrial workflows remains a significant challenge in human-robot collaboration research, especially within complex, real-world environments. Traditional unimodal methods often fall short of capturing the intricacies of these unstructured industrial settings. To address this gap, we present a novel Multimodal Industrial Activity Monitoring (MIAM) dataset that captures realistic assembly and disassembly tasks, facilitating the evaluation of key meta-tasks such as action localization, object interaction, and engagement prediction. The dataset comprises multi-view RGB, depth, and Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) data collected from 22 sessions, amounting to 290 minutes of untrimmed video, annotated in detail for task performance and operator behavior. Its distinctiveness lies in the integration of multiple data modalities and its emphasis on real-world, untrimmed industrial workflows-key for advancing research in human-robot collaboration and operator monitoring. Additionally, we propose a multimodal network that fuses RGB frames, IMU data, and skeleton sequences to predict engagement levels during industrial tasks. Our approach improves the accuracy of recognizing engagement states, providing a robust solution for monitoring operator performance in dynamic industrial environments. The dataset and code can be accessed from https://github.com/navalkishoremehta95/MIAM/.
Optimizing Multitask Industrial Processes with Predictive Action Guidance
Jan 09, 2025



Abstract:Monitoring complex assembly processes is critical for maintaining productivity and ensuring compliance with assembly standards. However, variability in human actions and subjective task preferences complicate accurate task anticipation and guidance. To address these challenges, we introduce the Multi-Modal Transformer Fusion and Recurrent Units (MMTFRU) Network for egocentric activity anticipation, utilizing multimodal fusion to improve prediction accuracy. Integrated with the Operator Action Monitoring Unit (OAMU), the system provides proactive operator guidance, preventing deviations in the assembly process. OAMU employs two strategies: (1) Top-5 MMTF-RU predictions, combined with a reference graph and an action dictionary, for next-step recommendations; and (2) Top-1 MMTF-RU predictions, integrated with a reference graph, for detecting sequence deviations and predicting anomaly scores via an entropy-informed confidence mechanism. We also introduce Time-Weighted Sequence Accuracy (TWSA) to evaluate operator efficiency and ensure timely task completion. Our approach is validated on the industrial Meccano dataset and the largescale EPIC-Kitchens-55 dataset, demonstrating its effectiveness in dynamic environments.
Towards Lensless Image Deblurring with Prior-Embedded Implicit Neural Representations in the Low-Data Regime
Nov 27, 2024



Abstract:The field of computational imaging has witnessed a promising paradigm shift with the emergence of untrained neural networks, offering novel solutions to inverse computational imaging problems. While existing techniques have demonstrated impressive results, they often operate either in the high-data regime, leveraging Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) as image priors, or through untrained iterative reconstruction in a data-agnostic manner. This paper delves into lensless image reconstruction, a subset of computational imaging that replaces traditional lenses with computation, enabling the development of ultra-thin and lightweight imaging systems. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to leverage implicit neural representations for lensless image deblurring, achieving reconstructions without the requirement of prior training. We perform prior-embedded untrained iterative optimization to enhance reconstruction performance and speed up convergence, effectively bridging the gap between the no-data and high-data regimes. Through a thorough comparative analysis encompassing various untrained and low-shot methods, including under-parameterized non-convolutional methods and domain-restricted low-shot methods, we showcase the superior performance of our approach by a significant margin.
Supporting Assessment of Novelty of Design Problems Using Concept of Problem SAPPhIRE
Oct 24, 2024



Abstract:This paper proposes a framework for assessing the novelty of design problems using the SAPPhIRE model of causality. The novelty of a problem is measured as its minimum distance from the problems in a reference problem database. The distance is calculated by comparing the current problem and each reference past problem at the various levels of abstraction in the SAPPhIRE ontology. The basis for comparison is textual similarity. To demonstrate the applicability of the proposed framework, The current set of problems associated with an artifact, as collected from its stakeholders, were compared with the past set of problems, as collected from patents and other web sources, to assess the novelty of the current set. This approach is aimed at providing a better understanding of the degree of novelty of any given set of current problems by comparing them to similar problems available from historical records. Since manual assessment, the current mode of such assessments as reported in the literature, is a tedious process, to reduce time complexity and to afford better applicability for larger sets of problem statements, an automated assessment is proposed and used in this paper.
The Llama 3 Herd of Models
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:Modern artificial intelligence (AI) systems are powered by foundation models. This paper presents a new set of foundation models, called Llama 3. It is a herd of language models that natively support multilinguality, coding, reasoning, and tool usage. Our largest model is a dense Transformer with 405B parameters and a context window of up to 128K tokens. This paper presents an extensive empirical evaluation of Llama 3. We find that Llama 3 delivers comparable quality to leading language models such as GPT-4 on a plethora of tasks. We publicly release Llama 3, including pre-trained and post-trained versions of the 405B parameter language model and our Llama Guard 3 model for input and output safety. The paper also presents the results of experiments in which we integrate image, video, and speech capabilities into Llama 3 via a compositional approach. We observe this approach performs competitively with the state-of-the-art on image, video, and speech recognition tasks. The resulting models are not yet being broadly released as they are still under development.
Towards Physics-informed Cyclic Adversarial Multi-PSF Lensless Imaging
Jul 09, 2024



Abstract:Lensless imaging has emerged as a promising field within inverse imaging, offering compact, cost-effective solutions with the potential to revolutionize the computational camera market. By circumventing traditional optical components like lenses and mirrors, novel approaches like mask-based lensless imaging eliminate the need for conventional hardware. However, advancements in lensless image reconstruction, particularly those leveraging Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), are hindered by the reliance on data-driven training processes, resulting in network specificity to the Point Spread Function (PSF) of the imaging system. This necessitates a complete retraining for minor PSF changes, limiting adaptability and generalizability across diverse imaging scenarios. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach to multi-PSF lensless imaging, employing a dual discriminator cyclic adversarial framework. We propose a unique generator architecture with a sparse convolutional PSF-aware auxiliary branch, coupled with a forward model integrated into the training loop to facilitate physics-informed learning to handle the substantial domain gap between lensless and lensed images. Comprehensive performance evaluation and ablation studies underscore the effectiveness of our model, offering robust and adaptable lensless image reconstruction capabilities. Our method achieves comparable performance to existing PSF-agnostic generative methods for single PSF cases and demonstrates resilience to PSF changes without the need for retraining.
Autonomous Control of a Novel Closed Chain Five Bar Active Suspension via Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jun 27, 2024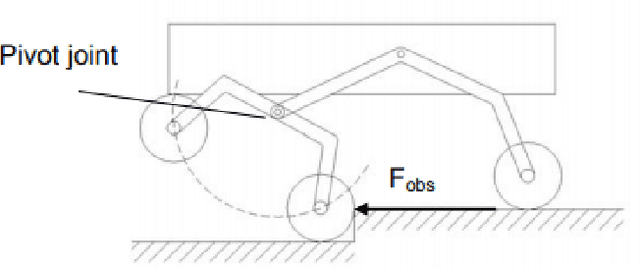
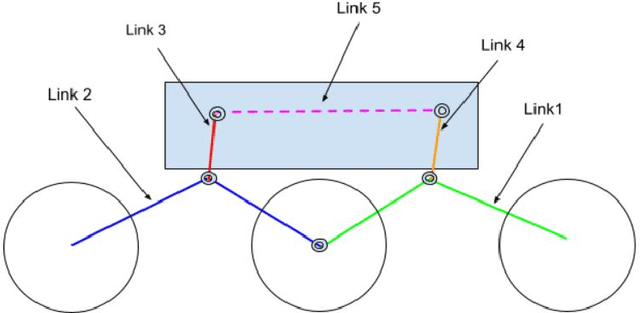
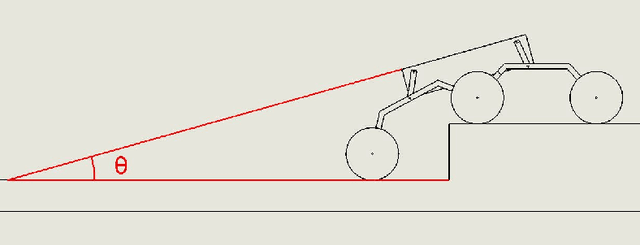

Abstract:Planetary exploration requires traversal in environments with rugged terrains. In addition, Mars rovers and other planetary exploration robots often carry sensitive scientific experiments and components onboard, which must be protected from mechanical harm. This paper deals with an active suspension system focused on chassis stabilisation and an efficient traversal method while encountering unavoidable obstacles. Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) was applied along with Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) control to stabilise the chassis and traverse large obstacles at low speeds. The model uses the rover's distance from surrounding obstacles, the height of the obstacle, and the chassis' orientation to actuate the control links of the suspension accurately. Simulations carried out in the Gazebo environment are used to validate the proposed active system.
Gaze-Vector Estimation in the Dark with Temporally Encoded Event-driven Neural Networks
Mar 05, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we address the intricate challenge of gaze vector prediction, a pivotal task with applications ranging from human-computer interaction to driver monitoring systems. Our innovative approach is designed for the demanding setting of extremely low-light conditions, leveraging a novel temporal event encoding scheme, and a dedicated neural network architecture. The temporal encoding method seamlessly integrates Dynamic Vision Sensor (DVS) events with grayscale guide frames, generating consecutively encoded images for input into our neural network. This unique solution not only captures diverse gaze responses from participants within the active age group but also introduces a curated dataset tailored for low-light conditions. The encoded temporal frames paired with our network showcase impressive spatial localization and reliable gaze direction in their predictions. Achieving a remarkable 100-pixel accuracy of 100%, our research underscores the potency of our neural network to work with temporally consecutive encoded images for precise gaze vector predictions in challenging low-light videos, contributing to the advancement of gaze prediction technologies.
ParaColorizer: Realistic Image Colorization using Parallel Generative Networks
Aug 17, 2022
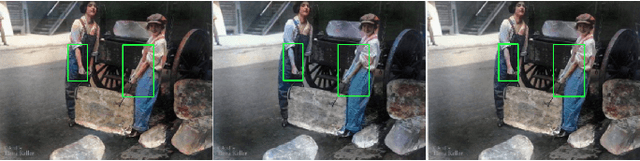


Abstract:Grayscale image colorization is a fascinating application of AI for information restoration. The inherently ill-posed nature of the problem makes it even more challenging since the outputs could be multi-modal. The learning-based methods currently in use produce acceptable results for straightforward cases but usually fail to restore the contextual information in the absence of clear figure-ground separation. Also, the images suffer from color bleeding and desaturated backgrounds since a single model trained on full image features is insufficient for learning the diverse data modes. To address these issues, we present a parallel GAN-based colorization framework. In our approach, each separately tailored GAN pipeline colorizes the foreground (using object-level features) or the background (using full-image features). The foreground pipeline employs a Residual-UNet with self-attention as its generator trained using the full-image features and the corresponding object-level features from the COCO dataset. The background pipeline relies on full-image features and additional training examples from the Places dataset. We design a DenseFuse-based fusion network to obtain the final colorized image by feature-based fusion of the parallelly generated outputs. We show the shortcomings of the non-perceptual evaluation metrics commonly used to assess multi-modal problems like image colorization and perform extensive performance evaluation of our framework using multiple perceptual metrics. Our approach outperforms most of the existing learning-based methods and produces results comparable to the state-of-the-art. Further, we performed a runtime analysis and obtained an average inference time of 24ms per image.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge