Ryan Riegel
A Neuro-Symbolic Approach to Multi-Agent RL for Interpretability and Probabilistic Decision Making
Feb 21, 2024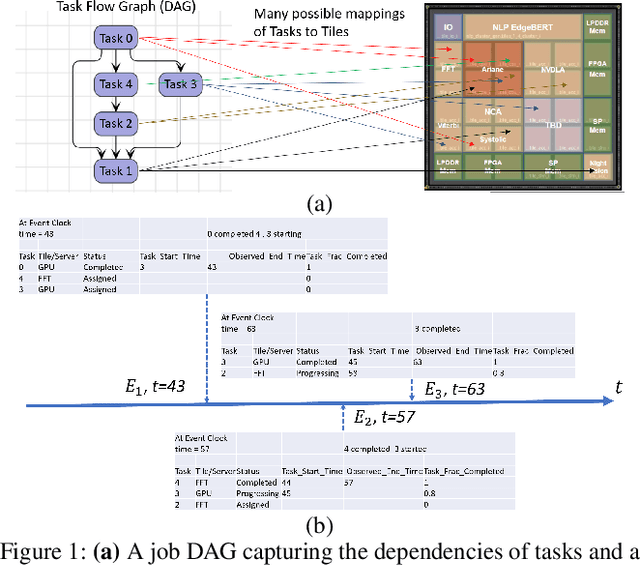
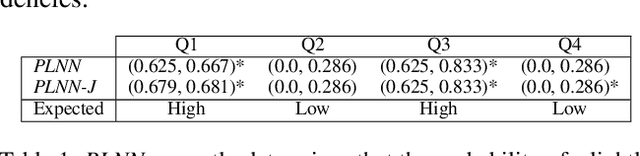
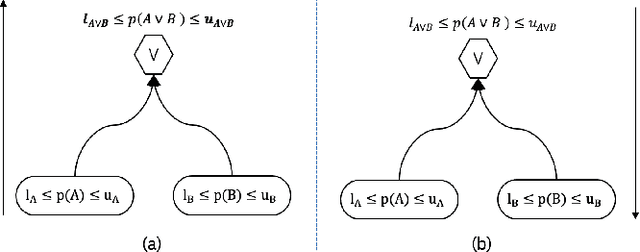
Abstract:Multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) is well-suited for runtime decision-making in optimizing the performance of systems where multiple agents coexist and compete for shared resources. However, applying common deep learning-based MARL solutions to real-world problems suffers from issues of interpretability, sample efficiency, partial observability, etc. To address these challenges, we present an event-driven formulation, where decision-making is handled by distributed co-operative MARL agents using neuro-symbolic methods. The recently introduced neuro-symbolic Logical Neural Networks (LNN) framework serves as a function approximator for the RL, to train a rules-based policy that is both logical and interpretable by construction. To enable decision-making under uncertainty and partial observability, we developed a novel probabilistic neuro-symbolic framework, Probabilistic Logical Neural Networks (PLNN), which combines the capabilities of logical reasoning with probabilistic graphical models. In PLNN, the upward/downward inference strategy, inherited from LNN, is coupled with belief bounds by setting the activation function for the logical operator associated with each neural network node to a probability-respecting generalization of the Fr\'echet inequalities. These PLNN nodes form the unifying element that combines probabilistic logic and Bayes Nets, permitting inference for variables with unobserved states. We demonstrate our contributions by addressing key MARL challenges for power sharing in a system-on-chip application.
A Benchmark for Generalizable and Interpretable Temporal Question Answering over Knowledge Bases
Jan 15, 2022
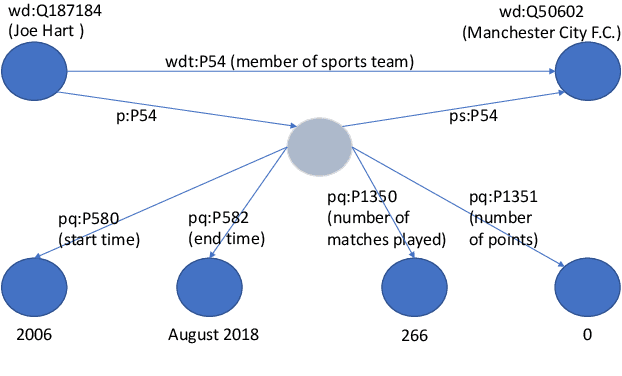


Abstract:Knowledge Base Question Answering (KBQA) tasks that involve complex reasoning are emerging as an important research direction. However, most existing KBQA datasets focus primarily on generic multi-hop reasoning over explicit facts, largely ignoring other reasoning types such as temporal, spatial, and taxonomic reasoning. In this paper, we present a benchmark dataset for temporal reasoning, TempQA-WD, to encourage research in extending the present approaches to target a more challenging set of complex reasoning tasks. Specifically, our benchmark is a temporal question answering dataset with the following advantages: (a) it is based on Wikidata, which is the most frequently curated, openly available knowledge base, (b) it includes intermediate sparql queries to facilitate the evaluation of semantic parsing based approaches for KBQA, and (c) it generalizes to multiple knowledge bases: Freebase and Wikidata. The TempQA-WD dataset is available at https://github.com/IBM/tempqa-wd.
Neuro-Symbolic Inductive Logic Programming with Logical Neural Networks
Dec 06, 2021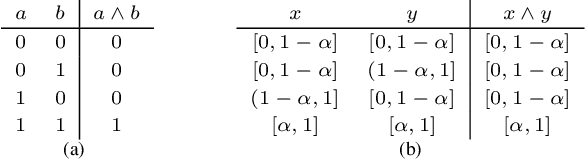
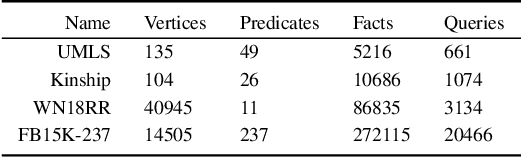
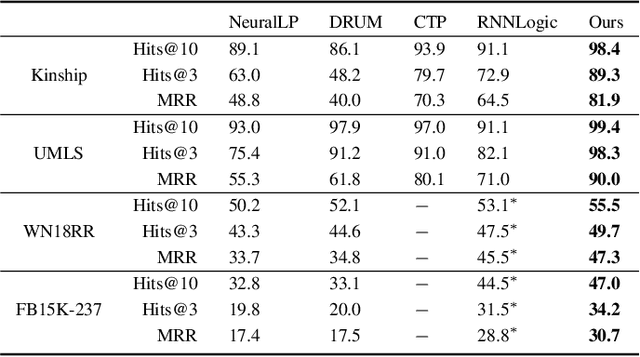
Abstract:Recent work on neuro-symbolic inductive logic programming has led to promising approaches that can learn explanatory rules from noisy, real-world data. While some proposals approximate logical operators with differentiable operators from fuzzy or real-valued logic that are parameter-free thus diminishing their capacity to fit the data, other approaches are only loosely based on logic making it difficult to interpret the learned "rules". In this paper, we propose learning rules with the recently proposed logical neural networks (LNN). Compared to others, LNNs offer strong connection to classical Boolean logic thus allowing for precise interpretation of learned rules while harboring parameters that can be trained with gradient-based optimization to effectively fit the data. We extend LNNs to induce rules in first-order logic. Our experiments on standard benchmarking tasks confirm that LNN rules are highly interpretable and can achieve comparable or higher accuracy due to their flexible parameterization.
Logical Credal Networks
Sep 25, 2021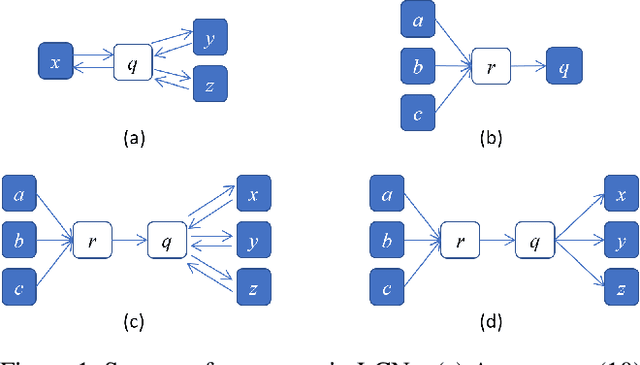
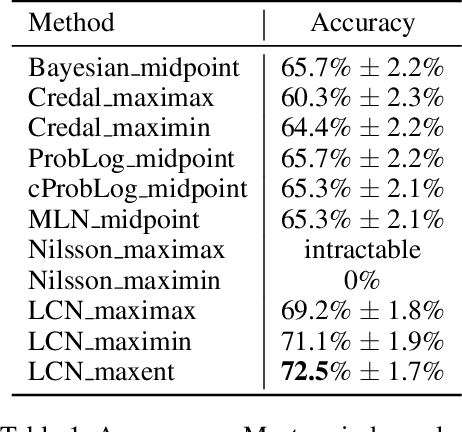
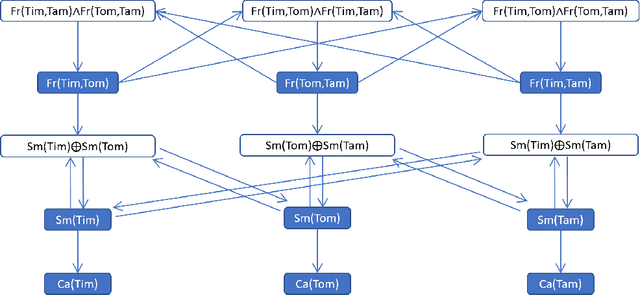
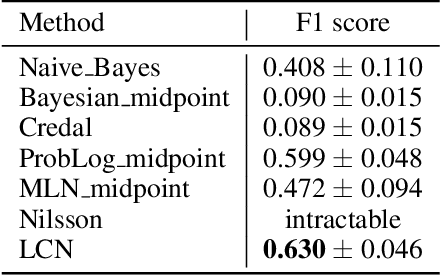
Abstract:This paper introduces Logical Credal Networks, an expressive probabilistic logic that generalizes many prior models that combine logic and probability. Given imprecise information represented by probability bounds and conditional probability bounds of logic formulas, this logic specifies a set of probability distributions over all interpretations. On the one hand, our approach allows propositional and first-order logic formulas with few restrictions, e.g., without requiring acyclicity. On the other hand, it has a Markov condition similar to Bayesian networks and Markov random fields that is critical in real-world applications. Having both these properties makes this logic unique, and we investigate its performance on maximum a posteriori inference tasks, including solving Mastermind games with uncertainty and detecting credit card fraud. The results show that the proposed method outperforms existing approaches, and its advantage lies in aggregating multiple sources of imprecise information.
Logic Embeddings for Complex Query Answering
Feb 28, 2021Abstract:Answering logical queries over incomplete knowledge bases is challenging because: 1) it calls for implicit link prediction, and 2) brute force answering of existential first-order logic queries is exponential in the number of existential variables. Recent work of query embeddings provides fast querying, but most approaches model set logic with closed regions, so lack negation. Query embeddings that do support negation use densities that suffer drawbacks: 1) only improvise logic, 2) use expensive distributions, and 3) poorly model answer uncertainty. In this paper, we propose Logic Embeddings, a new approach to embedding complex queries that uses Skolemisation to eliminate existential variables for efficient querying. It supports negation, but improves on density approaches: 1) integrates well-studied t-norm logic and directly evaluates satisfiability, 2) simplifies modeling with truth values, and 3) models uncertainty with truth bounds. Logic Embeddings are competitively fast and accurate in query answering over large, incomplete knowledge graphs, outperform on negation queries, and in particular, provide improved modeling of answer uncertainty as evidenced by a superior correlation between answer set size and embedding entropy.
Question Answering over Knowledge Bases by Leveraging Semantic Parsing and Neuro-Symbolic Reasoning
Dec 03, 2020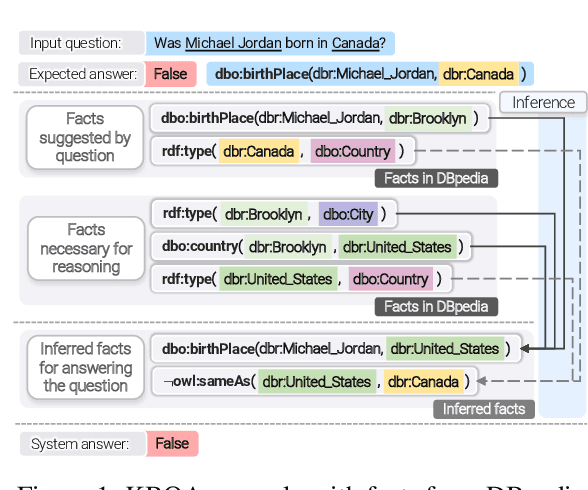
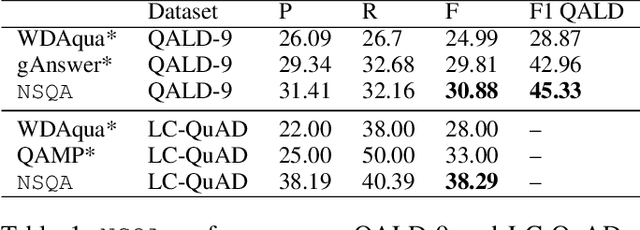
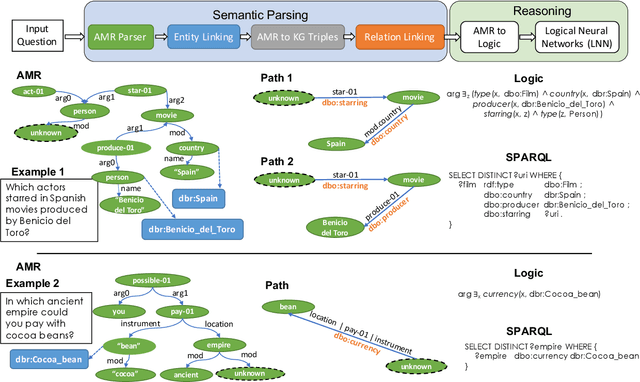

Abstract:Knowledge base question answering (KBQA) is an important task in Natural Language Processing. Existing approaches face significant challenges including complex question understanding, necessity for reasoning, and lack of large training datasets. In this work, we propose a semantic parsing and reasoning-based Neuro-Symbolic Question Answering(NSQA) system, that leverages (1) Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR) parses for task-independent question under-standing; (2) a novel path-based approach to transform AMR parses into candidate logical queries that are aligned to the KB; (3) a neuro-symbolic reasoner called Logical Neural Net-work (LNN) that executes logical queries and reasons over KB facts to provide an answer; (4) system of systems approach,which integrates multiple, reusable modules that are trained specifically for their individual tasks (e.g. semantic parsing,entity linking, and relationship linking) and do not require end-to-end training data. NSQA achieves state-of-the-art performance on QALD-9 and LC-QuAD 1.0. NSQA's novelty lies in its modular neuro-symbolic architecture and its task-general approach to interpreting natural language questions.
Foundations of Reasoning with Uncertainty via Real-valued Logics
Aug 06, 2020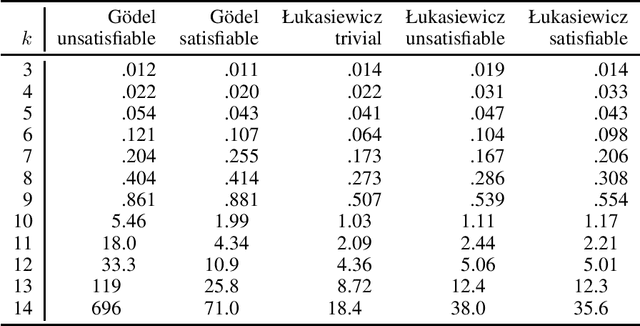
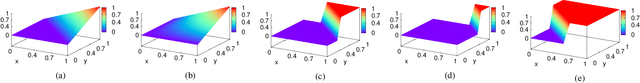
Abstract:Real-valued logics underlie an increasing number of neuro-symbolic approaches, though typically their logical inference capabilities are characterized only qualitatively. We provide foundations for establishing the correctness and power of such systems. For the first time, we give a sound and complete axiomatization for a broad class containing all the common real-valued logics. This axiomatization allows us to derive exactly what information can be inferred about the combinations of real values of a collection of formulas given information about the combinations of real values of several other collections of formulas. We then extend the axiomatization to deal with weighted subformulas. Finally, we give a decision procedure based on linear programming for deciding, under certain natural assumptions, whether a set of our sentences logically implies another of our sentences.
Logical Neural Networks
Jun 23, 2020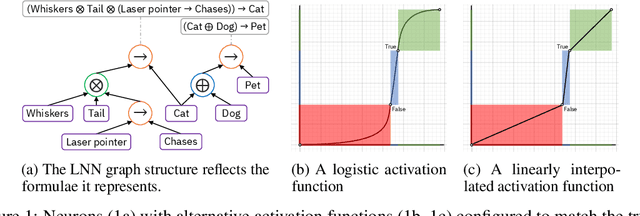
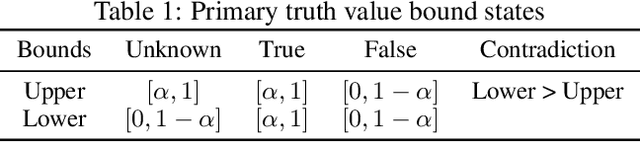
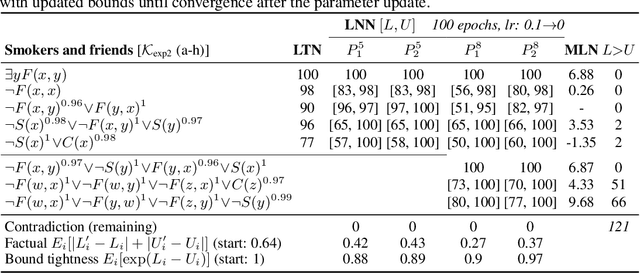
Abstract:We propose a novel framework seamlessly providing key properties of both neural nets (learning) and symbolic logic (knowledge and reasoning). Every neuron has a meaning as a component of a formula in a weighted real-valued logic, yielding a highly intepretable disentangled representation. Inference is omnidirectional rather than focused on predefined target variables, and corresponds to logical reasoning, including classical first-order logic theorem proving as a special case. The model is end-to-end differentiable, and learning minimizes a novel loss function capturing logical contradiction, yielding resilience to inconsistent knowledge. It also enables the open-world assumption by maintaining bounds on truth values which can have probabilistic semantics, yielding resilience to incomplete knowledge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge