Rami Ben-Ari
Fast Autoregressive Video Diffusion and World Models with Temporal Cache Compression and Sparse Attention
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Autoregressive video diffusion models enable streaming generation, opening the door to long-form synthesis, video world models, and interactive neural game engines. However, their core attention layers become a major bottleneck at inference time: as generation progresses, the KV cache grows, causing both increasing latency and escalating GPU memory, which in turn restricts usable temporal context and harms long-range consistency. In this work, we study redundancy in autoregressive video diffusion and identify three persistent sources: near-duplicate cached keys across frames, slowly evolving (largely semantic) queries/keys that make many attention computations redundant, and cross-attention over long prompts where only a small subset of tokens matters per frame. Building on these observations, we propose a unified, training-free attention framework for autoregressive diffusion: TempCache compresses the KV cache via temporal correspondence to bound cache growth; AnnCA accelerates cross-attention by selecting frame-relevant prompt tokens using fast approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) matching; and AnnSA sparsifies self-attention by restricting each query to semantically matched keys, also using a lightweight ANN. Together, these modules reduce attention, compute, and memory and are compatible with existing autoregressive diffusion backbones and world models. Experiments demonstrate up to x5--x10 end-to-end speedups while preserving near-identical visual quality and, crucially, maintaining stable throughput and nearly constant peak GPU memory usage over long rollouts, where prior methods progressively slow down and suffer from increasing memory usage.
SSNAPS: Audio-Visual Separation of Speech and Background Noise with Diffusion Inverse Sampling
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of audio-visual single-microphone speech separation and enhancement in the presence of real-world environmental noise. Our approach is based on generative inverse sampling, where we model clean speech and ambient noise with dedicated diffusion priors and jointly leverage them to recover all underlying sources. To achieve this, we reformulate a recent inverse sampler to match our setting. We evaluate on mixtures of 1, 2, and 3 speakers with noise and show that, despite being entirely unsupervised, our method consistently outperforms leading supervised baselines in \ac{WER} across all conditions. We further extend our framework to handle off-screen speaker separation. Moreover, the high fidelity of the separated noise component makes it suitable for downstream acoustic scene detection. Demo page: https://ssnapsicml.github.io/ssnapsicml2026/
Find your Needle: Small Object Image Retrieval via Multi-Object Attention Optimization
Mar 10, 2025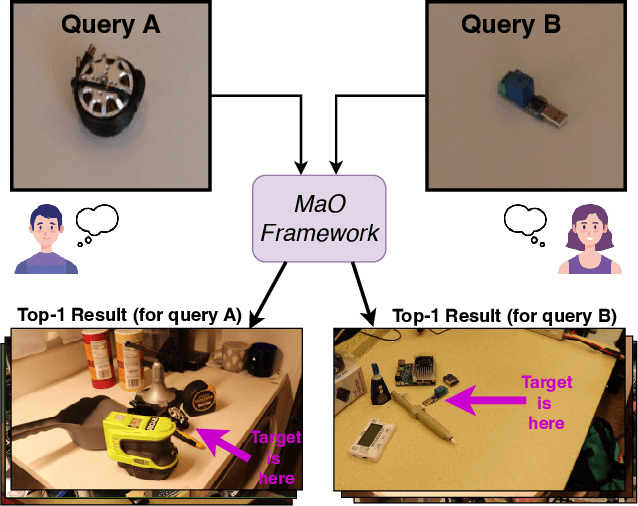
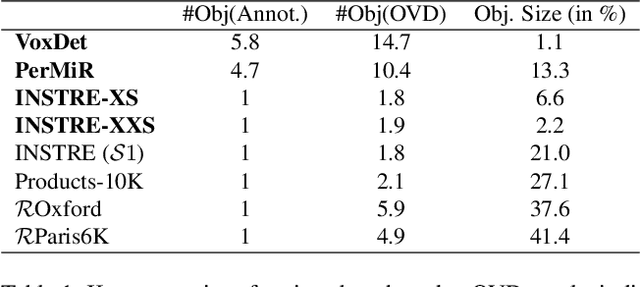
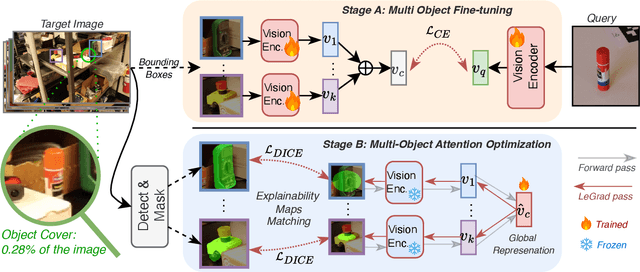
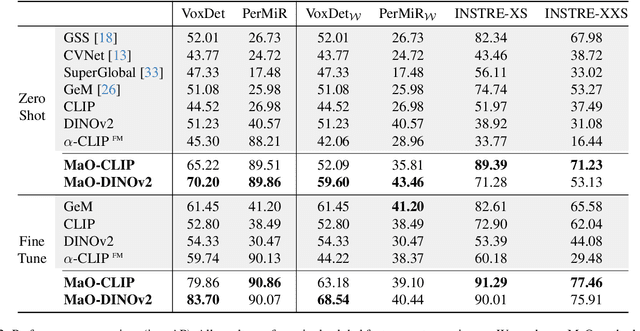
Abstract:We address the challenge of Small Object Image Retrieval (SoIR), where the goal is to retrieve images containing a specific small object, in a cluttered scene. The key challenge in this setting is constructing a single image descriptor, for scalable and efficient search, that effectively represents all objects in the image. In this paper, we first analyze the limitations of existing methods on this challenging task and then introduce new benchmarks to support SoIR evaluation. Next, we introduce Multi-object Attention Optimization (MaO), a novel retrieval framework which incorporates a dedicated multi-object pre-training phase. This is followed by a refinement process that leverages attention-based feature extraction with object masks, integrating them into a single unified image descriptor. Our MaO approach significantly outperforms existing retrieval methods and strong baselines, achieving notable improvements in both zero-shot and lightweight multi-object fine-tuning. We hope this work will lay the groundwork and inspire further research to enhance retrieval performance for this highly practical task.
CarGait: Cross-Attention based Re-ranking for Gait recognition
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Gait recognition is a computer vision task that identifies individuals based on their walking patterns. Gait recognition performance is commonly evaluated by ranking a gallery of candidates and measuring the accuracy at the top Rank-$K$. Existing models are typically single-staged, i.e. searching for the probe's nearest neighbors in a gallery using a single global feature representation. Although these models typically excel at retrieving the correct identity within the top-$K$ predictions, they struggle when hard negatives appear in the top short-list, leading to relatively low performance at the highest ranks (e.g., Rank-1). In this paper, we introduce CarGait, a Cross-Attention Re-ranking method for gait recognition, that involves re-ordering the top-$K$ list leveraging the fine-grained correlations between pairs of gait sequences through cross-attention between gait strips. This re-ranking scheme can be adapted to existing single-stage models to enhance their final results. We demonstrate the capabilities of CarGait by extensive experiments on three common gait datasets, Gait3D, GREW, and OU-MVLP, and seven different gait models, showing consistent improvements in Rank-1,5 accuracy, superior results over existing re-ranking methods, and strong baselines.
Task-Specific Adaptation with Restricted Model Access
Feb 02, 2025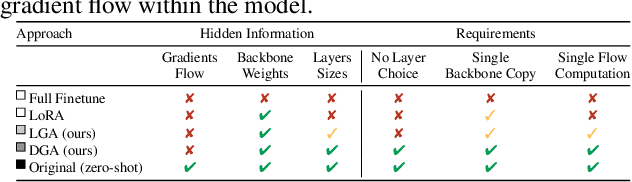
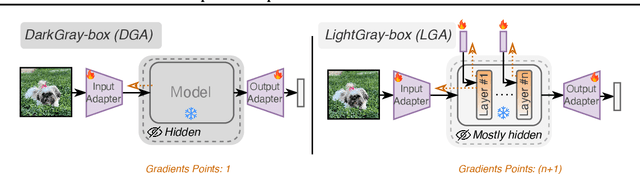
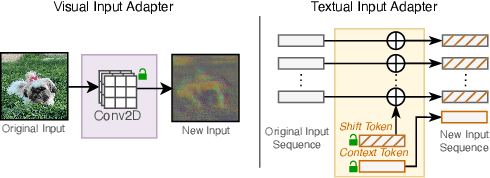
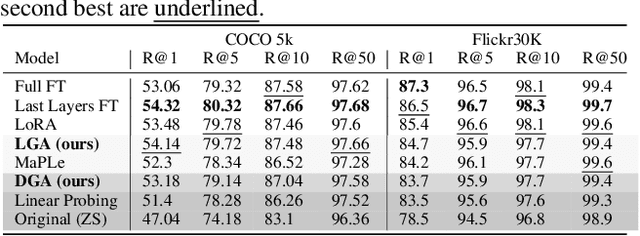
Abstract:The emergence of foundational models has greatly improved performance across various downstream tasks, with fine-tuning often yielding even better results. However, existing fine-tuning approaches typically require access to model weights and layers, leading to challenges such as managing multiple model copies or inference pipelines, inefficiencies in edge device optimization, and concerns over proprietary rights, privacy, and exposure to unsafe model variants. In this paper, we address these challenges by exploring "Gray-box" fine-tuning approaches, where the model's architecture and weights remain hidden, allowing only gradient propagation. We introduce a novel yet simple and effective framework that adapts to new tasks using two lightweight learnable modules at the model's input and output. Additionally, we present a less restrictive variant that offers more entry points into the model, balancing performance with model exposure. We evaluate our approaches across several backbones on benchmarks such as text-image alignment, text-video alignment, and sketch-image alignment. Results show that our Gray-box approaches are competitive with full-access fine-tuning methods, despite having limited access to the model.
Active Learning via Classifier Impact and Greedy Selection for Interactive Image Retrieval
Dec 03, 2024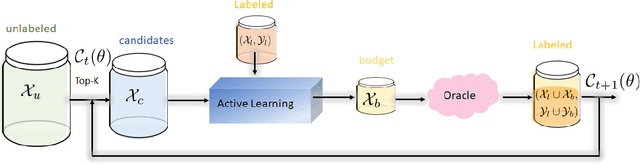
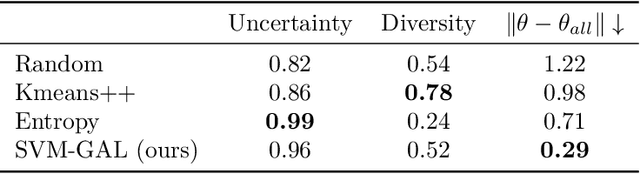
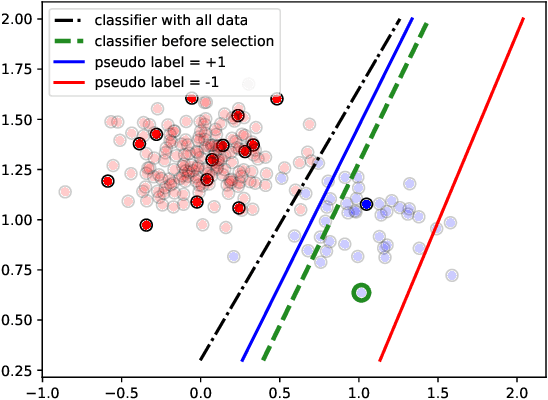
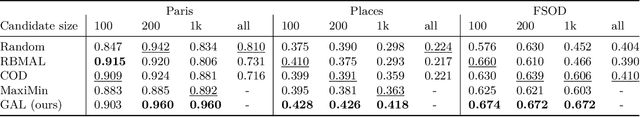
Abstract:Active Learning (AL) is a user-interactive approach aimed at reducing annotation costs by selecting the most crucial examples to label. Although AL has been extensively studied for image classification tasks, the specific scenario of interactive image retrieval has received relatively little attention. This scenario presents unique characteristics, including an open-set and class-imbalanced binary classification, starting with very few labeled samples. We introduce a novel batch-mode Active Learning framework named GAL (Greedy Active Learning) that better copes with this application. It incorporates a new acquisition function for sample selection that measures the impact of each unlabeled sample on the classifier. We further embed this strategy in a greedy selection approach, better exploiting the samples within each batch. We evaluate our framework with both linear (SVM) and non-linear MLP/Gaussian Process classifiers. For the Gaussian Process case, we show a theoretical guarantee on the greedy approximation. Finally, we assess our performance for the interactive content-based image retrieval task on several benchmarks and demonstrate its superiority over existing approaches and common baselines. Code is available at https://github.com/barleah/GreedyAL.
EffoVPR: Effective Foundation Model Utilization for Visual Place Recognition
May 28, 2024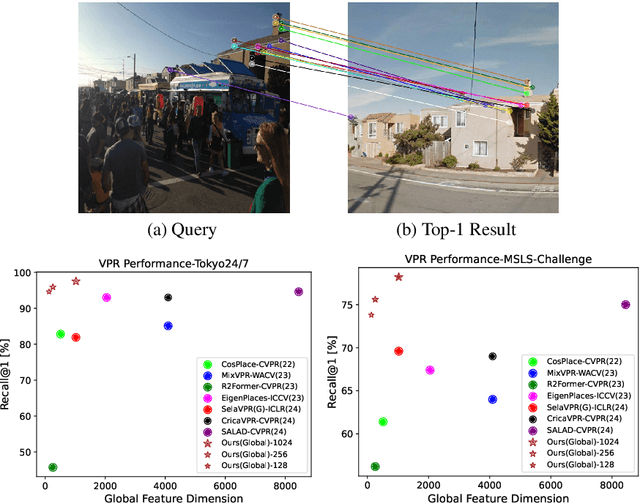
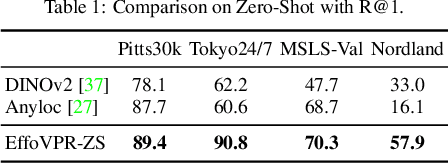
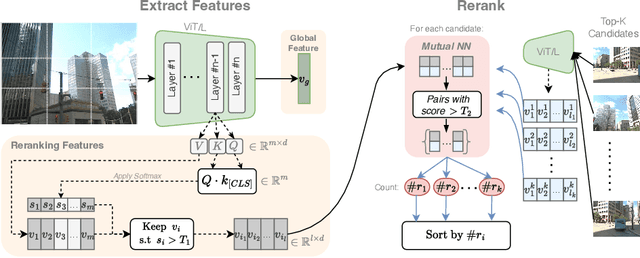
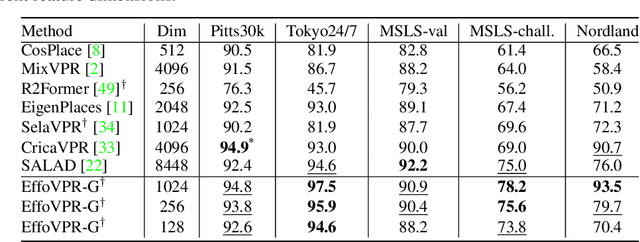
Abstract:The task of Visual Place Recognition (VPR) is to predict the location of a query image from a database of geo-tagged images. Recent studies in VPR have highlighted the significant advantage of employing pre-trained foundation models like DINOv2 for the VPR task. However, these models are often deemed inadequate for VPR without further fine-tuning on task-specific data. In this paper, we propose a simple yet powerful approach to better exploit the potential of a foundation model for VPR. We first demonstrate that features extracted from self-attention layers can serve as a powerful re-ranker for VPR. Utilizing these features in a zero-shot manner, our method surpasses previous zero-shot methods and achieves competitive results compared to supervised methods across multiple datasets. Subsequently, we demonstrate that a single-stage method leveraging internal ViT layers for pooling can generate global features that achieve state-of-the-art results, even when reduced to a dimensionality as low as 128D. Nevertheless, incorporating our local foundation features for re-ranking, expands this gap. Our approach further demonstrates remarkable robustness and generalization, achieving state-of-the-art results, with a significant gap, in challenging scenarios, involving occlusion, day-night variations, and seasonal changes.
Unveiling the Power of Diffusion Features For Personalized Segmentation and Retrieval
May 28, 2024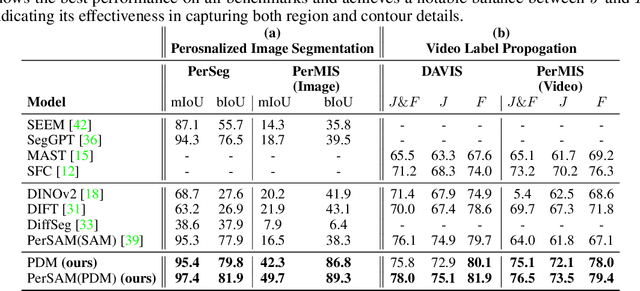

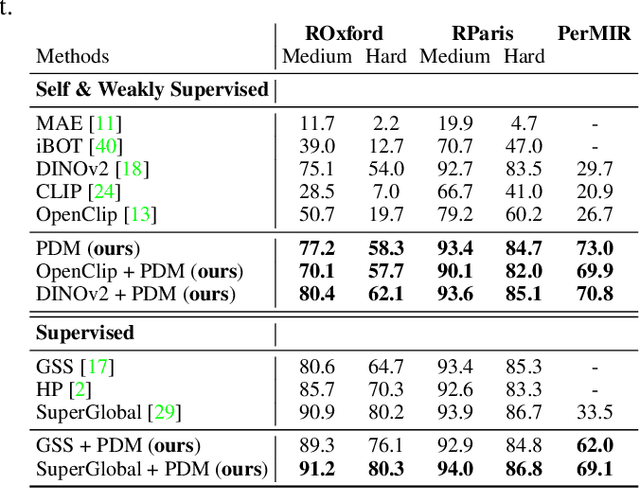
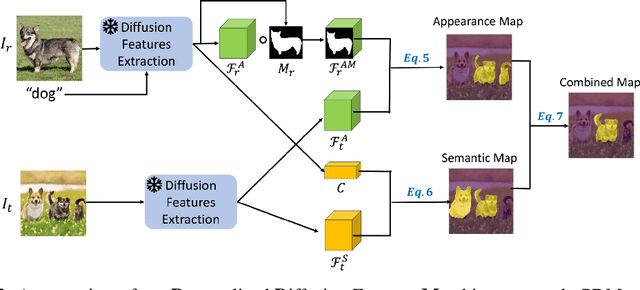
Abstract:Personalized retrieval and segmentation aim to locate specific instances within a dataset based on an input image and a short description of the reference instance. While supervised methods are effective, they require extensive labeled data for training. Recently, self-supervised foundation models have been introduced to these tasks showing comparable results to supervised methods. However, a significant flaw in these models is evident: they struggle to locate a desired instance when other instances within the same class are presented. In this paper, we explore text-to-image diffusion models for these tasks. Specifically, we propose a novel approach called PDM for Personalized Features Diffusion Matching, that leverages intermediate features of pre-trained text-to-image models for personalization tasks without any additional training. PDM demonstrates superior performance on popular retrieval and segmentation benchmarks, outperforming even supervised methods. We also highlight notable shortcomings in current instance and segmentation datasets and propose new benchmarks for these tasks.
Fixed-point Inversion for Text-to-image diffusion models
Dec 19, 2023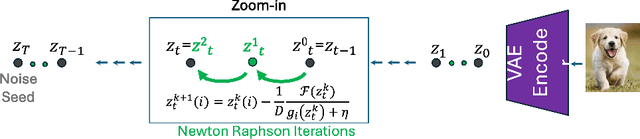
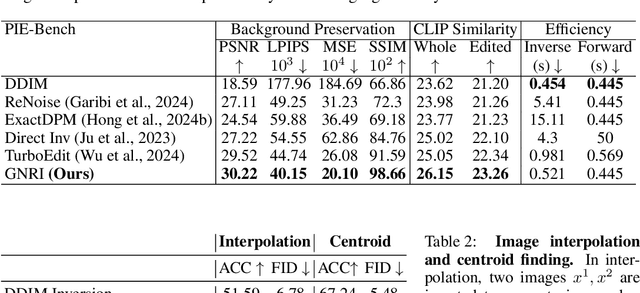
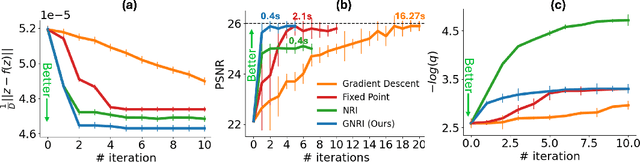
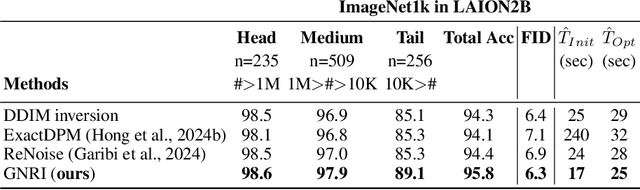
Abstract:Text-guided diffusion models offer powerful new ways to generate and manipulate images. Several applications of these models, including image editing interpolation, and semantic augmentation, require diffusion inversion. This is the process of finding a noise seed that can be used to generate a given image. Current techniques for inverting a given image can be slow or inaccurate. The technical challenge for inverting the diffusion process arises from an implicit equation over the latent that cannot be solved in closed form. Previous approaches proposed to solve this issue by approximation or various learning schemes. Here, we formulate the problem as a fixed-point equation problem and solve it using fixed-point iterations, a well-studied approach in numerical analysis. We further identify a source of inconsistency that significantly hurts the inversion of real images encoded to the latent space. We show how to correct it by applying a prompt-aware adjustment of the encoding. Our solution, Fixed-point inversion, is much faster than previous techniques like EDICT and Null-text, with similar inversion quality. It can be combined with any pretrained diffusion model and requires no model training, prompt tuning, or additional parameters. In a series of experiments, we find that Fixed-point inversion shows improved results in several downstream tasks: image editing, image interpolation, and generation of rare objects.
Advancing Image Retrieval with Few-Shot Learning and Relevance Feedback
Dec 18, 2023Abstract:With such a massive growth in the number of images stored, efficient search in a database has become a crucial endeavor managed by image retrieval systems. Image Retrieval with Relevance Feedback (IRRF) involves iterative human interaction during the retrieval process, yielding more meaningful outcomes. This process can be generally cast as a binary classification problem with only {\it few} labeled samples derived from user feedback. The IRRF task frames a unique few-shot learning characteristics including binary classification of imbalanced and asymmetric classes, all in an open-set regime. In this paper, we study this task through the lens of few-shot learning methods. We propose a new scheme based on a hyper-network, that is tailored to the task and facilitates swift adjustment to user feedback. Our approach's efficacy is validated through comprehensive evaluations on multiple benchmarks and two supplementary tasks, supported by theoretical analysis. We demonstrate the advantage of our model over strong baselines on 4 different datasets in IRRF, addressing also retrieval of images with multiple objects. Furthermore, we show that our method can attain SoTA results in few-shot one-class classification and reach comparable results in binary classification task of few-shot open-set recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge