Issar Tzachor
VidVec: Unlocking Video MLLM Embeddings for Video-Text Retrieval
Feb 08, 2026Abstract:Recent studies have adapted generative Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) into embedding extractors for vision tasks, typically through fine-tuning to produce universal representations. However, their performance on video remains inferior to Video Foundation Models (VFMs). In this paper, we focus on leveraging MLLMs for video-text embedding and retrieval. We first conduct a systematic layer-wise analysis, showing that intermediate (pre-trained) MLLM layers already encode substantial task-relevant information. Leveraging this insight, we demonstrate that combining intermediate-layer embeddings with a calibrated MLLM head yields strong zero-shot retrieval performance without any training. Building on these findings, we introduce a lightweight text-based alignment strategy which maps dense video captions to short summaries and enables task-related video-text embedding learning without visual supervision. Remarkably, without any fine-tuning beyond text, our method outperforms current methods, often by a substantial margin, achieving state-of-the-art results across common video retrieval benchmarks.
Fast Autoregressive Video Diffusion and World Models with Temporal Cache Compression and Sparse Attention
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Autoregressive video diffusion models enable streaming generation, opening the door to long-form synthesis, video world models, and interactive neural game engines. However, their core attention layers become a major bottleneck at inference time: as generation progresses, the KV cache grows, causing both increasing latency and escalating GPU memory, which in turn restricts usable temporal context and harms long-range consistency. In this work, we study redundancy in autoregressive video diffusion and identify three persistent sources: near-duplicate cached keys across frames, slowly evolving (largely semantic) queries/keys that make many attention computations redundant, and cross-attention over long prompts where only a small subset of tokens matters per frame. Building on these observations, we propose a unified, training-free attention framework for autoregressive diffusion: TempCache compresses the KV cache via temporal correspondence to bound cache growth; AnnCA accelerates cross-attention by selecting frame-relevant prompt tokens using fast approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) matching; and AnnSA sparsifies self-attention by restricting each query to semantically matched keys, also using a lightweight ANN. Together, these modules reduce attention, compute, and memory and are compatible with existing autoregressive diffusion backbones and world models. Experiments demonstrate up to x5--x10 end-to-end speedups while preserving near-identical visual quality and, crucially, maintaining stable throughput and nearly constant peak GPU memory usage over long rollouts, where prior methods progressively slow down and suffer from increasing memory usage.
Find your Needle: Small Object Image Retrieval via Multi-Object Attention Optimization
Mar 10, 2025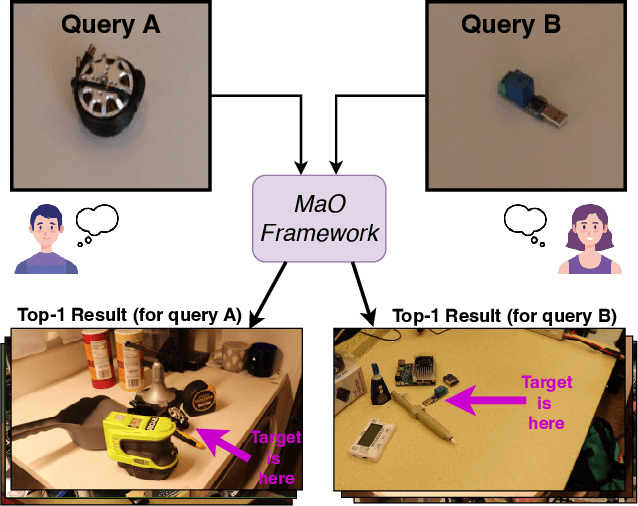
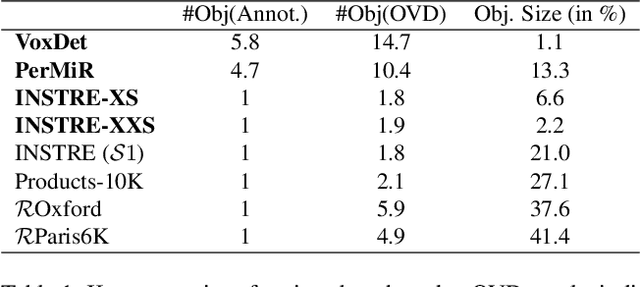
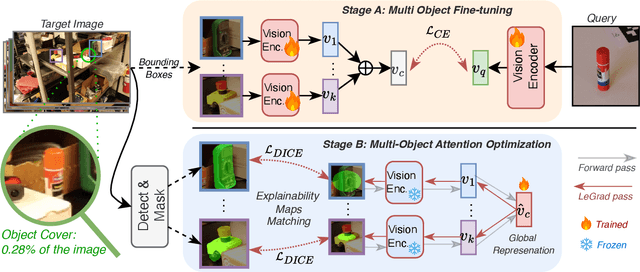
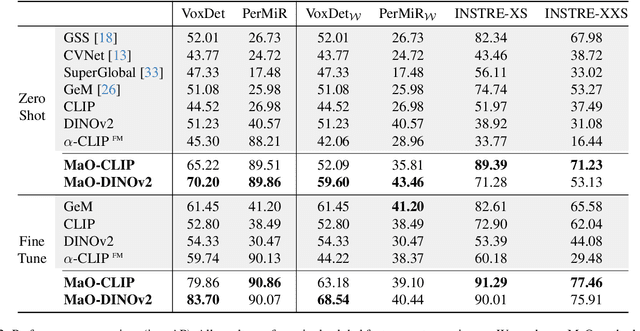
Abstract:We address the challenge of Small Object Image Retrieval (SoIR), where the goal is to retrieve images containing a specific small object, in a cluttered scene. The key challenge in this setting is constructing a single image descriptor, for scalable and efficient search, that effectively represents all objects in the image. In this paper, we first analyze the limitations of existing methods on this challenging task and then introduce new benchmarks to support SoIR evaluation. Next, we introduce Multi-object Attention Optimization (MaO), a novel retrieval framework which incorporates a dedicated multi-object pre-training phase. This is followed by a refinement process that leverages attention-based feature extraction with object masks, integrating them into a single unified image descriptor. Our MaO approach significantly outperforms existing retrieval methods and strong baselines, achieving notable improvements in both zero-shot and lightweight multi-object fine-tuning. We hope this work will lay the groundwork and inspire further research to enhance retrieval performance for this highly practical task.
EffoVPR: Effective Foundation Model Utilization for Visual Place Recognition
May 28, 2024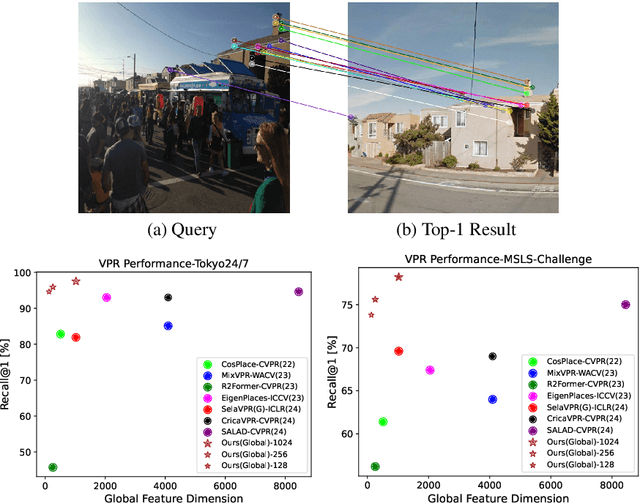
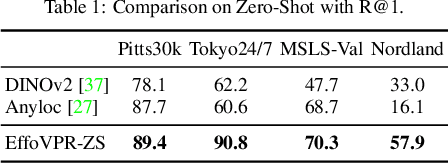
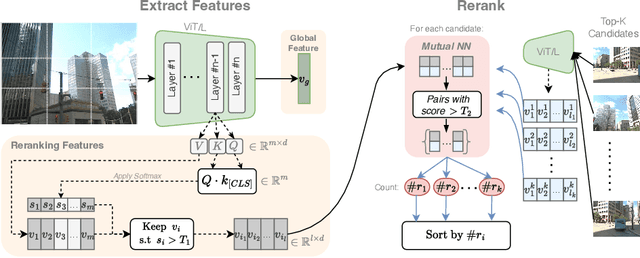
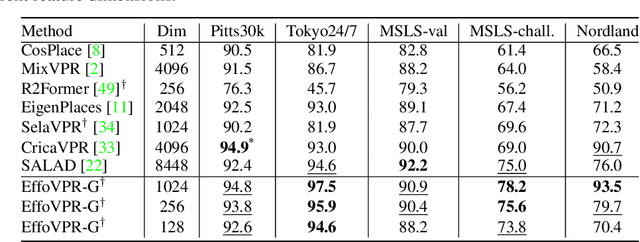
Abstract:The task of Visual Place Recognition (VPR) is to predict the location of a query image from a database of geo-tagged images. Recent studies in VPR have highlighted the significant advantage of employing pre-trained foundation models like DINOv2 for the VPR task. However, these models are often deemed inadequate for VPR without further fine-tuning on task-specific data. In this paper, we propose a simple yet powerful approach to better exploit the potential of a foundation model for VPR. We first demonstrate that features extracted from self-attention layers can serve as a powerful re-ranker for VPR. Utilizing these features in a zero-shot manner, our method surpasses previous zero-shot methods and achieves competitive results compared to supervised methods across multiple datasets. Subsequently, we demonstrate that a single-stage method leveraging internal ViT layers for pooling can generate global features that achieve state-of-the-art results, even when reduced to a dimensionality as low as 128D. Nevertheless, incorporating our local foundation features for re-ranking, expands this gap. Our approach further demonstrates remarkable robustness and generalization, achieving state-of-the-art results, with a significant gap, in challenging scenarios, involving occlusion, day-night variations, and seasonal changes.
Set Features for Anomaly Detection
Nov 24, 2023Abstract:This paper proposes set features for detecting anomalies in samples that consist of unusual combinations of normal elements. Many leading methods discover anomalies by detecting an unusual part of a sample. For example, state-of-the-art segmentation-based approaches, first classify each element of the sample (e.g., image patch) as normal or anomalous and then classify the entire sample as anomalous if it contains anomalous elements. However, such approaches do not extend well to scenarios where the anomalies are expressed by an unusual combination of normal elements. In this paper, we overcome this limitation by proposing set features that model each sample by the distribution of its elements. We compute the anomaly score of each sample using a simple density estimation method, using fixed features. Our approach outperforms the previous state-of-the-art in image-level logical anomaly detection and sequence-level time series anomaly detection.
Set Features for Fine-grained Anomaly Detection
Mar 02, 2023



Abstract:Fine-grained anomaly detection has recently been dominated by segmentation based approaches. These approaches first classify each element of the sample (e.g., image patch) as normal or anomalous and then classify the entire sample as anomalous if it contains anomalous elements. However, such approaches do not extend to scenarios where the anomalies are expressed by an unusual combination of normal elements. In this paper, we overcome this limitation by proposing set features that model each sample by the distribution its elements. We compute the anomaly score of each sample using a simple density estimation method. Our simple-to-implement approach outperforms the state-of-the-art in image-level logical anomaly detection (+3.4%) and sequence-level time-series anomaly detection (+2.4%).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge