Qixing Zhang
Make Anything Match Your Target: Universal Adversarial Perturbations against Closed-Source MLLMs via Multi-Crop Routed Meta Optimization
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Targeted adversarial attacks on closed-source multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have been increasingly explored under black-box transfer, yet prior methods are predominantly sample-specific and offer limited reusability across inputs. We instead study a more stringent setting, Universal Targeted Transferable Adversarial Attacks (UTTAA), where a single perturbation must consistently steer arbitrary inputs toward a specified target across unknown commercial MLLMs. Naively adapting existing sample-wise attacks to this universal setting faces three core difficulties: (i) target supervision becomes high-variance due to target-crop randomness, (ii) token-wise matching is unreliable because universality suppresses image-specific cues that would otherwise anchor alignment, and (iii) few-source per-target adaptation is highly initialization-sensitive, which can degrade the attainable performance. In this work, we propose MCRMO-Attack, which stabilizes supervision via Multi-Crop Aggregation with an Attention-Guided Crop, improves token-level reliability through alignability-gated Token Routing, and meta-learns a cross-target perturbation prior that yields stronger per-target solutions. Across commercial MLLMs, we boost unseen-image attack success rate by +23.7\% on GPT-4o and +19.9\% on Gemini-2.0 over the strongest universal baseline.
AODDiff: Probabilistic Reconstruction of Aerosol Optical Depth via Diffusion-based Bayesian Inference
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:High-quality reconstruction of Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) fields is critical for Atmosphere monitoring, yet current models remain constrained by the scarcity of complete training data and a lack of uncertainty quantification.To address these limitations, we propose AODDiff, a probabilistic reconstruction framework based on diffusion-based Bayesian inference. By leveraging the learned spatiotemporal probability distribution of the AOD field as a generative prior, this framework can be flexibly adapted to various reconstruction tasks without requiring task-specific retraining. We first introduce a corruption-aware training strategy to learns a spatiotemporal AOD prior solely from naturally incomplete data. Subsequently, we employ a decoupled annealing posterior sampling strategy that enables the more effective and integration of heterogeneous observations as constraints to guide the generation process. We validate the proposed framework through extensive experiments on Reanalysis data. Results across downscaling and inpainting tasks confirm the efficacy and robustness of AODDiff, specifically demonstrating its advantage in maintaining high spatial spectral fidelity. Furthermore, as a generative model, AODDiff inherently enables uncertainty quantification via multiple sampling, offering critical confidence metrics for downstream applications.
Wildfire Smoke Detection with Cross Contrast Patch Embedding
Nov 16, 2023



Abstract:The Transformer-based deep networks have increasingly shown significant advantages over CNNs. Some existing work has applied it in the field of wildfire recognition or detection. However, we observed that the vanilla Transformer is not friendly for extracting smoke features. Because low-level information such as color, transparency and texture is very important for smoke recognition, and transformer pays more attention to the semantic relevance between middle- or high-level features, and is not sensitive to the subtle changes of low-level features along the space. To solve this problem, we propose the Cross Contrast Patch Embedding(CCPE) module based on the Swin Transformer, which uses the multi-scales spatial frequency contrast information in both vertical and horizontal directions to improve the discrimination of the network on the underlying details. The fuzzy boundary of smoke makes the positive and negative label assignment for instances in a dilemma, which is another challenge for wildfires detection. To solve this problem, a Separable Negative Sampling Mechanism(SNSM) is proposed. By using two different negative instance sampling strategies on positive images and negative images respectively, the problem of supervision signal confusion caused by label diversity in the process of network training is alleviated. This paper also releases the RealFire Test, the largest real wildfire test set so far, to evaluate the proposed method and promote future research. It contains 50,535 images from 3,649 video clips. The proposed method has been extensively tested and evaluated on RealFire Test dataset, and has a significant performance improvement compared with the baseline detection models.
Video Smoke Detection Based on Deep Saliency Network
Sep 08, 2018
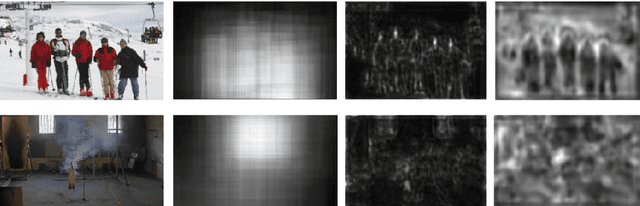
Abstract:Video smoke detection is a promising fire detection method especially in open or large spaces and outdoor environments. Traditional smoke detection consists of candidate region extraction and classification, but it lacks powerful characterization for smoke. In this paper, we propose a novel method for video smoke detection based on deep saliency network. Visual saliency detection aims to highlight the most important object regions in an image. The pixel-level and object-level salient CNNs are combined to extract the informative smoke saliency map. For the need of application for smoke event detection, an end-to-end framework for salient smoke detection and existence prediction of smoke is proposed. The deep feature map is combined with the saliency map to predict the existence of smoke in image. Initial dataset and augmented dataset are built to measure the performance of frameworks with different design strategies. Qualitative and quantitative analysis at frame-level and pixel-level demonstrates the excellent performance of the ultimate framework.
Domain Adaptation from Synthesis to Reality in Single-model Detector for Video Smoke Detection
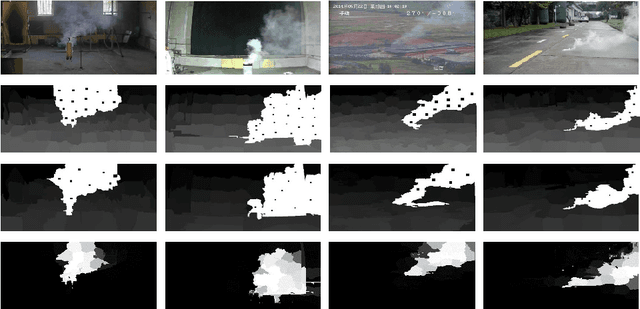
May 18, 2018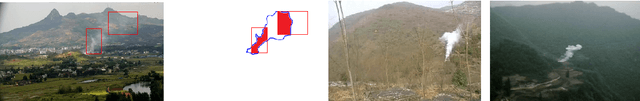
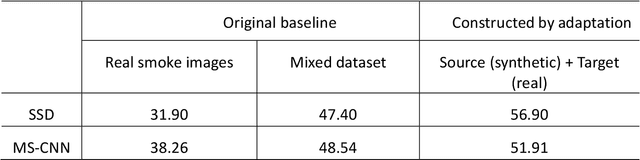
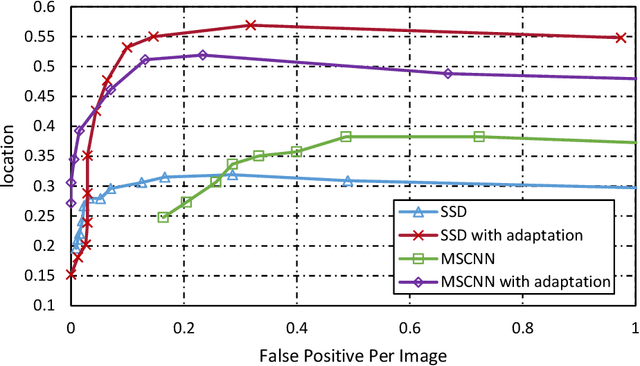
Abstract:This paper proposes a method for video smoke detection using synthetic smoke samples. The virtual data can automatically offer precise and rich annotated samples. However, the learning of smoke representations will be hurt by the appearance gap between real and synthetic smoke samples. The existed researches mainly work on the adaptation to samples extracted from original annotated samples. These methods take the object detection and domain adaptation as two independent parts. To train a strong detector with rich synthetic samples, we construct the adaptation to the detection layer of state-of-the-art single-model detectors (SSD and MS-CNN). The training procedure is an end-to-end stage. The classification, location and adaptation are combined in the learning. The performance of the proposed model surpasses the original baseline in our experiments. Meanwhile, our results show that the detectors based on the adversarial adaptation are superior to the detectors based on the discrepancy adaptation. Code will be made publicly available on http://smoke.ustc.edu.cn. Moreover, the domain adaptation for two-stage detector is described in Appendix A.
Deep Domain Adaptation Based Video Smoke Detection using Synthetic Smoke Images
Mar 31, 2017
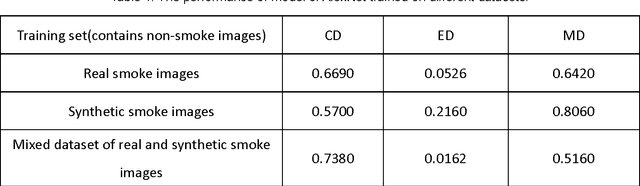
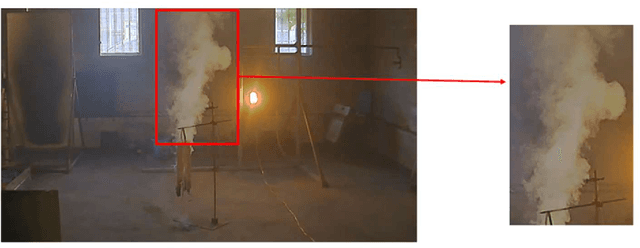
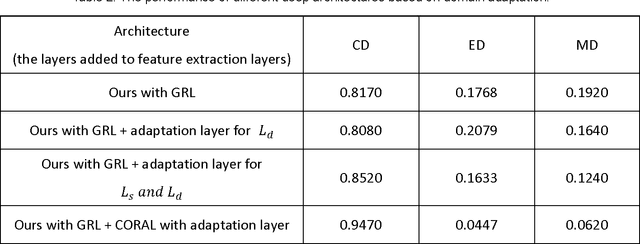
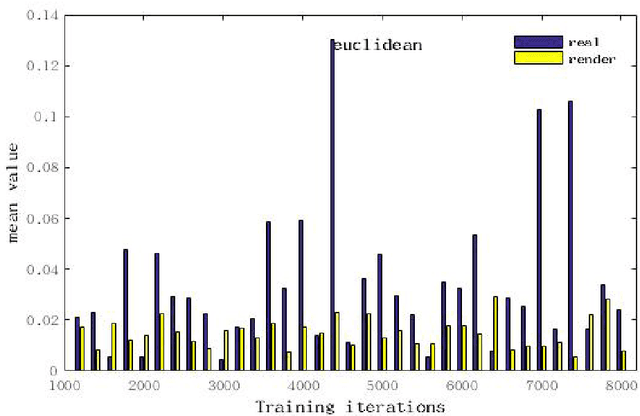
Abstract:In this paper, a deep domain adaptation based method for video smoke detection is proposed to extract a powerful feature representation of smoke. Due to the smoke image samples limited in scale and diversity for deep CNN training, we systematically produced adequate synthetic smoke images with a wide variation in the smoke shape, background and lighting conditions. Considering that the appearance gap (dataset bias) between synthetic and real smoke images degrades significantly the performance of the trained model on the test set composed fully of real images, we build deep architectures based on domain adaptation to confuse the distributions of features extracted from synthetic and real smoke images. This approach expands the domain-invariant feature space for smoke image samples. With their approximate feature distribution off non-smoke images, the recognition rate of the trained model is improved significantly compared to the model trained directly on mixed dataset of synthetic and real images. Experimentally, several deep architectures with different design choices are applied to the smoke detector. The ultimate framework can get a satisfactory result on the test set. We believe that our approach is a start in the direction of utilizing deep neural networks enhanced with synthetic smoke images for video smoke detection.
* The manuscript approved by all authors is our original work, and has submitted to Fire Safety Journal for peer review previously. There are 4516 words, 8 figures and 2 tables in this manuscript
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge