Qingye Meng
ColorfulClouds Technology Co., Ltd
FlowCast-ODE: Continuous Hourly Weather Forecasting with Dynamic Flow Matching and ODE Integration
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Accurate hourly weather forecasting is critical for numerous applications. Recent deep learning models have demonstrated strong capability on 6-hour intervals, yet achieving accurate and stable hourly predictions remains a critical challenge. This is primarily due to the rapid accumulation of errors in autoregressive rollouts and temporal discontinuities within the ERA5 data's 12-hour assimilation cycle. To address these issues, we propose FlowCast-ODE, a framework that models atmospheric state evolution as a continuous flow. FlowCast-ODE learns the conditional flow path directly from the previous state, an approach that aligns more naturally with physical dynamic systems and enables efficient computation. A coarse-to-fine strategy is introduced to train the model on 6-hour data using dynamic flow matching and then refined on hourly data that incorporates an Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE) solver to achieve temporally coherent forecasts. In addition, a lightweight low-rank AdaLN-Zero modulation mechanism is proposed and reduces model size by 15% without compromising accuracy. Experiments demonstrate that FlowCast-ODE outperforms strong baselines, yielding lower root mean square error (RMSE) and better energy conservation, which reduces blurring and preserves more fine-scale spatial details. It also shows comparable performance to the state-of-the-art model in forecasting extreme events like typhoons. Furthermore, the model alleviates temporal discontinuities associated with assimilation cycle transitions.
PCDCNet: A Surrogate Model for Air Quality Forecasting with Physical-Chemical Dynamics and Constraints
May 26, 2025Abstract:Air quality forecasting (AQF) is critical for public health and environmental management, yet remains challenging due to the complex interplay of emissions, meteorology, and chemical transformations. Traditional numerical models, such as CMAQ and WRF-Chem, provide physically grounded simulations but are computationally expensive and rely on uncertain emission inventories. Deep learning models, while computationally efficient, often struggle with generalization due to their lack of physical constraints. To bridge this gap, we propose PCDCNet, a surrogate model that integrates numerical modeling principles with deep learning. PCDCNet explicitly incorporates emissions, meteorological influences, and domain-informed constraints to model pollutant formation, transport, and dissipation. By combining graph-based spatial transport modeling, recurrent structures for temporal accumulation, and representation enhancement for local interactions, PCDCNet achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in 72-hour station-level PM2.5 and O3 forecasting while significantly reducing computational costs. Furthermore, our model is deployed in an online platform, providing free, real-time air quality forecasts, demonstrating its scalability and societal impact. By aligning deep learning with physical consistency, PCDCNet offers a practical and interpretable solution for AQF, enabling informed decision-making for both personal and regulatory applications.
CNCast: Leveraging 3D Swin Transformer and DiT for Enhanced Regional Weather Forecasting
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:This study introduces a cutting-edge regional weather forecasting model based on the SwinTransformer 3D architecture. This model is specifically designed to deliver precise hourly weather predictions ranging from 1 hour to 5 days, significantly improving the reliability and practicality of short-term weather forecasts. Our model has demonstrated generally superior performance when compared to Pangu, a well-established global model. The evaluation indicates that our model excels in predicting most weather variables, highlighting its potential as a more effective alternative in the field of limited area modeling. A noteworthy feature of this model is the integration of enhanced boundary conditions, inspired by traditional numerical weather prediction (NWP) techniques. This integration has substantially improved the model's predictive accuracy. Additionally, the model includes an innovative approach for diagnosing hourly total precipitation at a high spatial resolution of approximately 5 kilometers. This is achieved through a latent diffusion model, offering an alternative method for generating high-resolution precipitation data.
Benchmarking and Understanding Compositional Relational Reasoning of LLMs
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:Compositional relational reasoning (CRR) is a hallmark of human intelligence, but we lack a clear understanding of whether and how existing transformer large language models (LLMs) can solve CRR tasks. To enable systematic exploration of the CRR capability of LLMs, we first propose a new synthetic benchmark called Generalized Associative Recall (GAR) by integrating and generalizing the essence of several tasks in mechanistic interpretability (MI) study in a unified framework. Evaluation shows that GAR is challenging enough for existing LLMs, revealing their fundamental deficiency in CRR. Meanwhile, it is easy enough for systematic MI study. Then, to understand how LLMs solve GAR tasks, we use attribution patching to discover the core circuits reused by Vicuna-33B across different tasks and a set of vital attention heads. Intervention experiments show that the correct functioning of these heads significantly impacts task performance. Especially, we identify two classes of heads whose activations represent the abstract notion of true and false in GAR tasks respectively. They play a fundamental role in CRR across various models and tasks. The dataset and code are available at https://github.com/Caiyun-AI/GAR.
Improving Transformers with Dynamically Composable Multi-Head Attention
May 14, 2024



Abstract:Multi-Head Attention (MHA) is a key component of Transformer. In MHA, attention heads work independently, causing problems such as low-rank bottleneck of attention score matrices and head redundancy. We propose Dynamically Composable Multi-Head Attention (DCMHA), a parameter and computation efficient attention architecture that tackles the shortcomings of MHA and increases the expressive power of the model by dynamically composing attention heads. At the core of DCMHA is a $\it{Compose}$ function that transforms the attention score and weight matrices in an input-dependent way. DCMHA can be used as a drop-in replacement of MHA in any transformer architecture to obtain the corresponding DCFormer. DCFormer significantly outperforms Transformer on different architectures and model scales in language modeling, matching the performance of models with ~1.7x-2.0x compute. For example, DCPythia-6.9B outperforms open source Pythia-12B on both pretraining perplexity and downstream task evaluation. The code and models are available at https://github.com/Caiyun-AI/DCFormer.
InterHT: Knowledge Graph Embeddings by Interaction between Head and Tail Entities
Feb 10, 2022
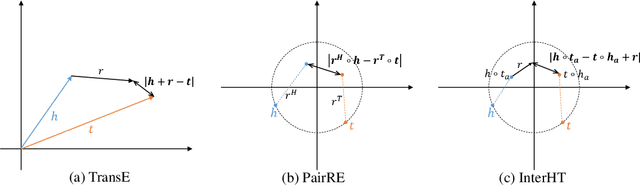
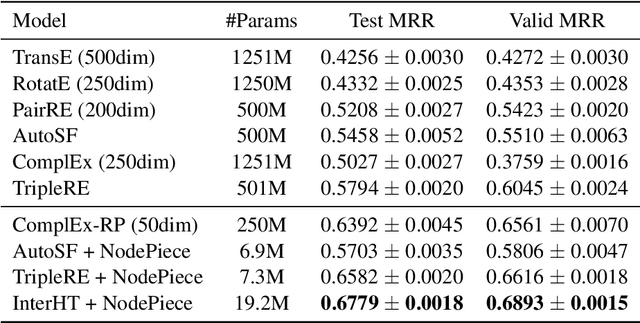
Abstract:Knowledge graph embedding (KGE) models learn the representation of entities and relations in knowledge graphs. Distance-based methods show promising performance on link prediction task, which predicts the result by the distance between two entity representations. However, most of these methods represent the head entity and tail entity separately, which limits the model capacity. We propose a novel distance-based method named InterHT that allows the head and tail entities to interact better and get better entity representation. Experimental results show that our proposed method achieves the best results on ogbl-wikikg2 dataset.
PM2.5-GNN: A Domain Knowledge Enhanced Graph Neural Network For PM2.5 Forecasting
Feb 10, 2020
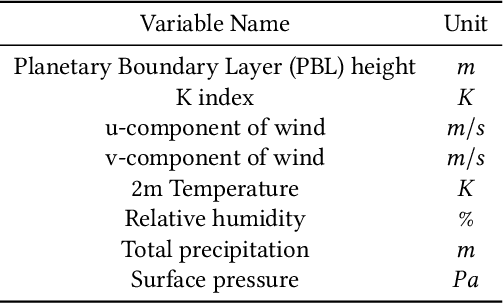

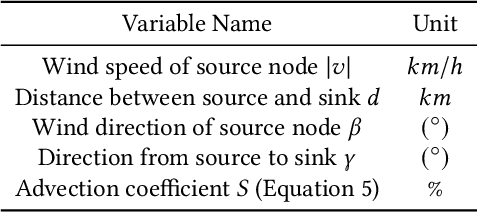
Abstract:When predicting PM2.5 concentrations, it is necessary to consider complex information sources since the concentrations are influenced by various factors within a long period. In this paper, we identify a set of critical domain knowledge for PM2.5 forecasting and develop a novel graph based model, PM2.5-GNN, being capable of capturing long-term dependencies. On a real-world dataset, we validate the effectiveness of the proposed model and examine its abilities of capturing both fine-grained and long-term influences in PM2.5 process. The proposed PM2.5-GNN has also been deployed online to provide free forecasting service.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge