Qi Shen
BARE: Towards Bias-Aware and Reasoning-Enhanced One-Tower Visual Grounding
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Visual Grounding (VG), which aims to locate a specific region referred to by expressions, is a fundamental yet challenging task in the multimodal understanding fields. While recent grounding transfer works have advanced the field through one-tower architectures, they still suffer from two primary limitations: (1) over-entangled multimodal representations that exacerbate deceptive modality biases, and (2) insufficient semantic reasoning that hinders the comprehension of referential cues. In this paper, we propose BARE, a bias-aware and reasoning-enhanced framework for one-tower visual grounding. BARE introduces a mechanism that preserves modality-specific features and constructs referential semantics through three novel modules: (i) language salience modulator, (ii) visual bias correction and (iii) referential relationship enhancement, which jointly mitigate multimodal distractions and enhance referential comprehension. Extensive experimental results on five benchmarks demonstrate that BARE not only achieves state-of-the-art performance but also delivers superior computational efficiency compared to existing approaches. The code is publicly accessible at https://github.com/Marloweeee/BARE.
BEDA: Belief Estimation as Probabilistic Constraints for Performing Strategic Dialogue Acts
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Strategic dialogue requires agents to execute distinct dialogue acts, for which belief estimation is essential. While prior work often estimates beliefs accurately, it lacks a principled mechanism to use those beliefs during generation. We bridge this gap by first formalizing two core acts Adversarial and Alignment, and by operationalizing them via probabilistic constraints on what an agent may generate. We instantiate this idea in BEDA, a framework that consists of the world set, the belief estimator for belief estimation, and the conditional generator that selects acts and realizes utterances consistent with the inferred beliefs. Across three settings, Conditional Keeper Burglar (CKBG, adversarial), Mutual Friends (MF, cooperative), and CaSiNo (negotiation), BEDA consistently outperforms strong baselines: on CKBG it improves success rate by at least 5.0 points across backbones and by 20.6 points with GPT-4.1-nano; on Mutual Friends it achieves an average improvement of 9.3 points; and on CaSiNo it achieves the optimal deal relative to all baselines. These results indicate that casting belief estimation as constraints provides a simple, general mechanism for reliable strategic dialogue.
Towards Evaluating the Robustness of Automatic Speech Recognition Systems via Audio Style Transfer
May 15, 2024



Abstract:In light of the widespread application of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems, their security concerns have received much more attention than ever before, primarily due to the susceptibility of Deep Neural Networks. Previous studies have illustrated that surreptitiously crafting adversarial perturbations enables the manipulation of speech recognition systems, resulting in the production of malicious commands. These attack methods mostly require adding noise perturbations under $\ell_p$ norm constraints, inevitably leaving behind artifacts of manual modifications. Recent research has alleviated this limitation by manipulating style vectors to synthesize adversarial examples based on Text-to-Speech (TTS) synthesis audio. However, style modifications based on optimization objectives significantly reduce the controllability and editability of audio styles. In this paper, we propose an attack on ASR systems based on user-customized style transfer. We first test the effect of Style Transfer Attack (STA) which combines style transfer and adversarial attack in sequential order. And then, as an improvement, we propose an iterative Style Code Attack (SCA) to maintain audio quality. Experimental results show that our method can meet the need for user-customized styles and achieve a success rate of 82% in attacks, while keeping sound naturalness due to our user study.
Text2Bundle: Towards Personalized Query-based Bundle Generation
Oct 27, 2023



Abstract:Bundle generation aims to provide a bundle of items for the user, and has been widely studied and applied on online service platforms. Existing bundle generation methods mainly utilized user's preference from historical interactions in common recommendation paradigm, and ignored the potential textual query which is user's current explicit intention. There can be a scenario in which a user proactively queries a bundle with some natural language description, the system should be able to generate a bundle that exactly matches the user's intention through the user's query and preferences. In this work, we define this user-friendly scenario as Query-based Bundle Generation task and propose a novel framework Text2Bundle that leverages both the user's short-term interests from the query and the user's long-term preferences from the historical interactions. Our framework consists of three modules: (1) a query interest extractor that mines the user's fine-grained interests from the query; (2) a unified state encoder that learns the current bundle context state and the user's preferences based on historical interaction and current query; and (3) a bundle generator that generates personalized and complementary bundles using a reinforcement learning with specifically designed rewards. We conduct extensive experiments on three real-world datasets and demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework compared with several state-of-the-art methods.
Towards Multi-Subsession Conversational Recommendation
Oct 20, 2023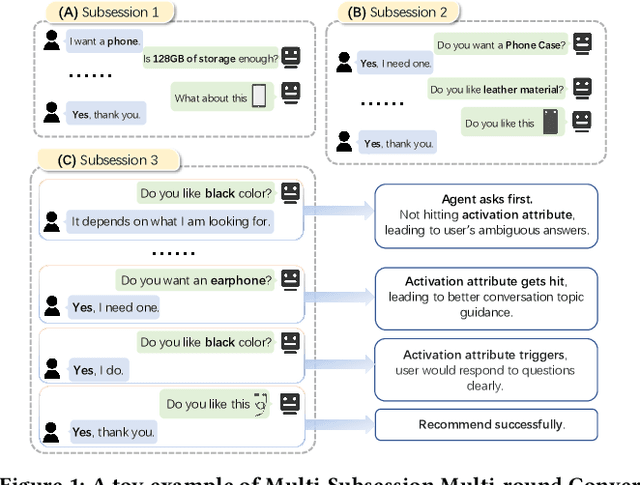
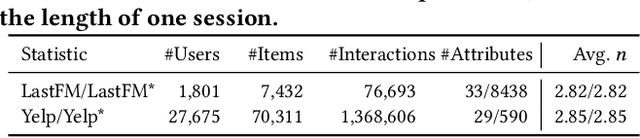
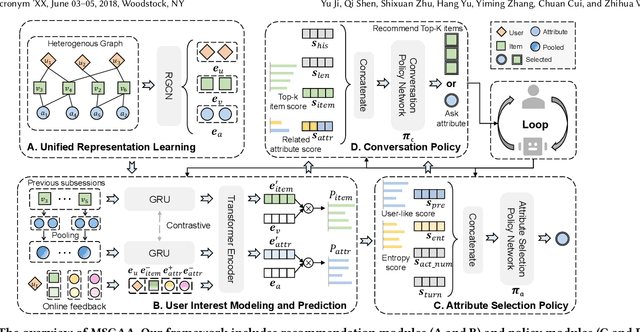
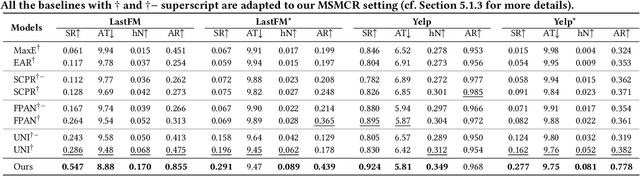
Abstract:Conversational recommendation systems (CRS) could acquire dynamic user preferences towards desired items through multi-round interactive dialogue. Previous CRS mainly focuses on the single conversation (subsession) that user quits after a successful recommendation, neglecting the common scenario where user has multiple conversations (multi-subsession) over a short period. Therefore, we propose a novel conversational recommendation scenario named Multi-Subsession Multi-round Conversational Recommendation (MSMCR), where user would still resort to CRS after several subsessions and might preserve vague interests, and system would proactively ask attributes to activate user interests in the current subsession. To fill the gap in this new CRS scenario, we devise a novel framework called Multi-Subsession Conversational Recommender with Activation Attributes (MSCAA). Specifically, we first develop a context-aware recommendation module, comprehensively modeling user interests from historical interactions, previous subsessions, and feedback in the current subsession. Furthermore, an attribute selection policy module is proposed to learn a flexible strategy for asking appropriate attributes to elicit user interests. Finally, we design a conversation policy module to manage the above two modules to decide actions between asking and recommending. Extensive experiments on four datasets verify the effectiveness of our MSCAA framework for the MSMCR setting.
Video and Audio are Images: A Cross-Modal Mixer for Original Data on Video-Audio Retrieval
Aug 26, 2023



Abstract:Cross-modal retrieval has become popular in recent years, particularly with the rise of multimedia. Generally, the information from each modality exhibits distinct representations and semantic information, which makes feature tends to be in separate latent spaces encoded with dual-tower architecture and makes it difficult to establish semantic relationships between modalities, resulting in poor retrieval performance. To address this issue, we propose a novel framework for cross-modal retrieval which consists of a cross-modal mixer, a masked autoencoder for pre-training, and a cross-modal retriever for downstream tasks.In specific, we first adopt cross-modal mixer and mask modeling to fuse the original modality and eliminate redundancy. Then, an encoder-decoder architecture is applied to achieve a fuse-then-separate task in the pre-training phase.We feed masked fused representations into the encoder and reconstruct them with the decoder, ultimately separating the original data of two modalities. In downstream tasks, we use the pre-trained encoder to build the cross-modal retrieval method. Extensive experiments on 2 real-world datasets show that our approach outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods in video-audio matching tasks, improving retrieval accuracy by up to 2 times. Furthermore, we prove our model performance by transferring it to other downstream tasks as a universal model.
Data-Augmented Counterfactual Learning for Bundle Recommendation
Oct 19, 2022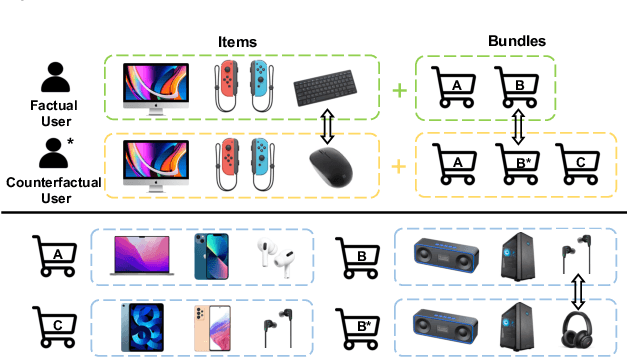
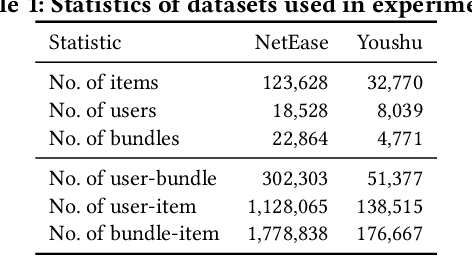
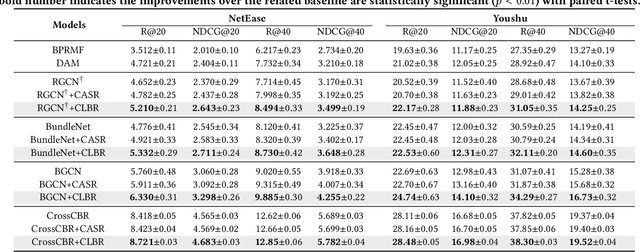
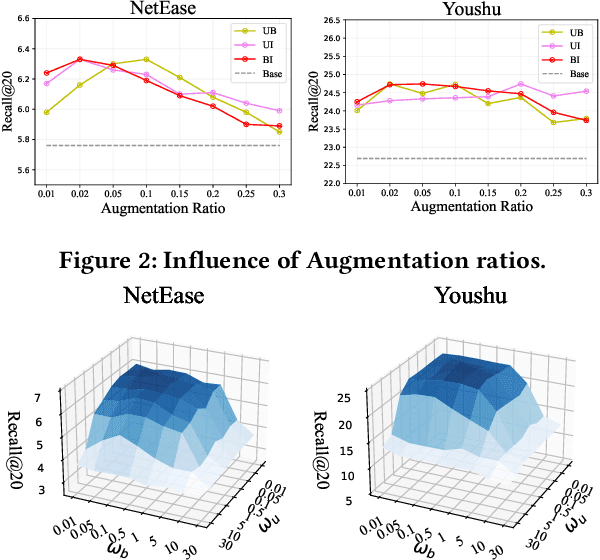
Abstract:Bundle Recommendation (BR) aims at recommending bundled items on online content or e-commerce platform, such as song lists on a music platform or book lists on a reading website. Several graph based models have achieved state-of-the-art performance on BR task. But their performance is still sub-optimal, since the data sparsity problem tends to be more severe in real bundle recommendation scenarios, which limits graph-based models from more sufficient learning. In this paper, we propose a novel graph learning paradigm called Counterfactual Learning for Bundle Recommendation (CLBR) to mitigate the impact of data sparsity problem and improve bundle recommendation. Our paradigm consists of two main parts: counterfactual data augmentation and counterfactual constraint. The main idea of our paradigm lies in answering the counterfactual questions: "What would a user interact with if his/her interaction history changes?" "What would a user interact with if the bundle-item affiliation relations change?" In counterfactual data augmentation, we design a heuristic sampler to generate counterfactual graph views for graph-based models, which has better noise controlling than the stochastic sampler. We further propose counterfactual loss to constrain model learning for mitigating the effects of residual noise in augmented data and achieving more sufficient model optimization. Further theoretical analysis demonstrates the rationality of our design. Extensive experiments of BR models applied with our paradigm on two real-world datasets are conducted to verify the effectiveness of the paradigm
Intention Adaptive Graph Neural Network for Category-aware Session-based Recommendation
Dec 31, 2021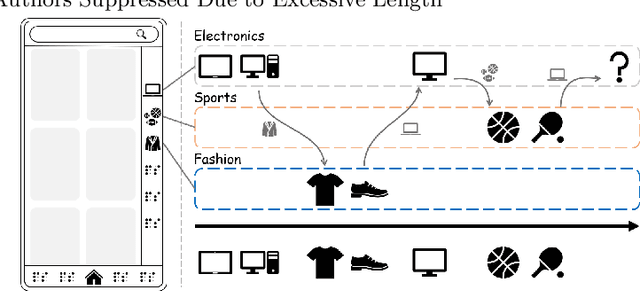
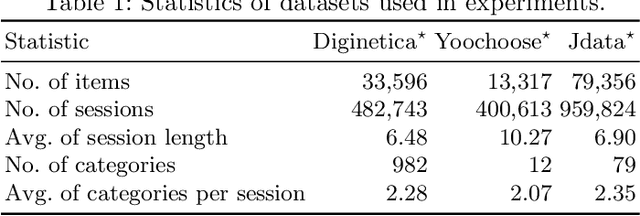
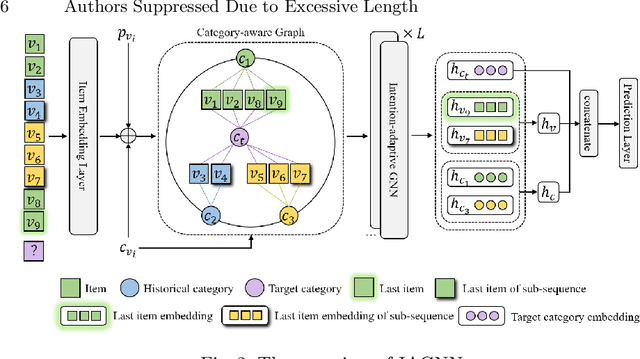
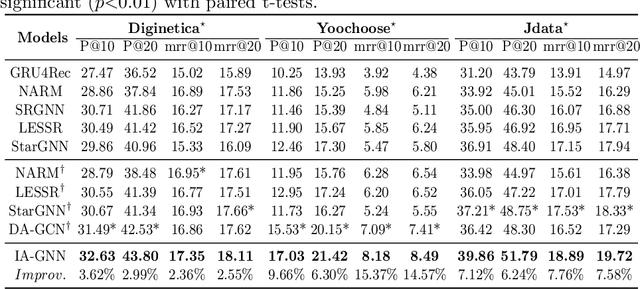
Abstract:Session-based recommendation (SBR) is proposed to recommend items within short sessions given that user profiles are invisible in various scenarios nowadays, such as e-commerce and short video recommendation. There is a common scenario that user specifies a target category of items as a global filter, however previous SBR settings mainly consider the item sequence and overlook the rich target category information in this scenario. Therefore, we define a new task called Category-aware Session-Based Recommendation (CSBR), focusing on the above scenario, in which the user-specified category can be efficiently utilized by the recommendation system. To address the challenges of the proposed task, we develop a novel method called Intention Adaptive Graph Neural Network (IAGNN), which takes advantage of relationship between items and their categories to achieve an accurate recommendation result. Specifically, we construct a category-aware graph with both item and category nodes to represent the complex transition information in the session. An intention-adaptive graph neural network on the category-aware graph is utilized to capture user intention by transferring the historical interaction information to the user-specified category domain. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets are conducted to show our IAGNN outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines in the new task.
Temporal aware Multi-Interest Graph Neural Network For Session-based Recommendation
Dec 31, 2021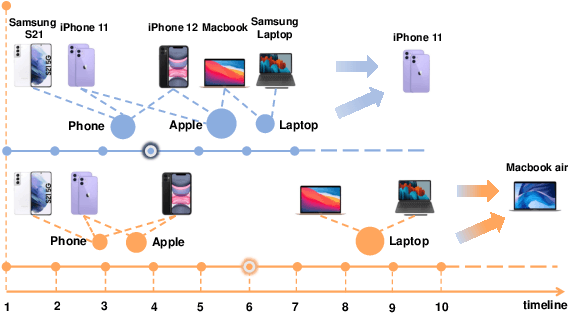
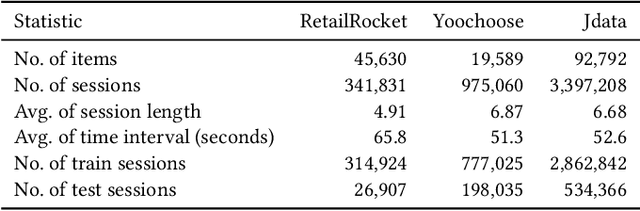
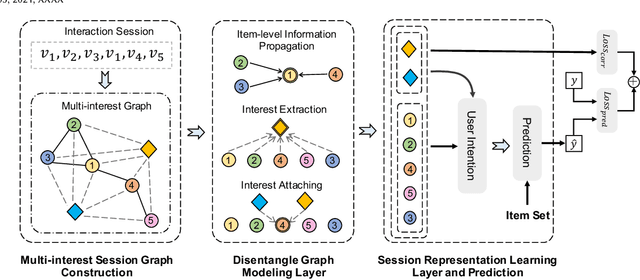
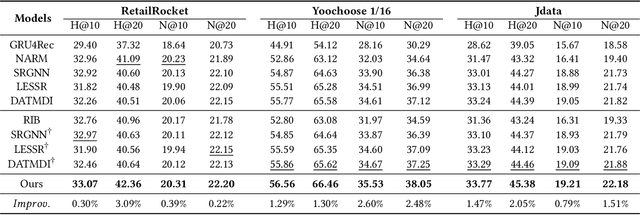
Abstract:Session-based recommendation (SBR) is a challenging task, which aims at recommending next items based on anonymous interaction sequences. Despite the superior performance of existing methods for SBR, there are still several limitations: (i) Almost all existing works concentrate on single interest extraction and fail to disentangle multiple interests of user, which easily results in suboptimal representations for SBR. (ii) Furthermore, previous methods also ignore the multi-form temporal information, which is significant signal to obtain current intention for SBR. To address the limitations mentioned above, we propose a novel method, called \emph{Temporal aware Multi-Interest Graph Neural Network} (TMI-GNN) to disentangle multi-interest and yield refined intention representations with the injection of two level temporal information. Specifically, by appending multiple interest nodes, we construct a multi-interest graph for current session, and adopt the GNNs to model the item-item relation to capture adjacent item transitions, item-interest relation to disentangle the multi-interests, and interest-item relation to refine the item representation. Meanwhile, we incorporate item-level time interval signals to guide the item information propagation, and interest-level time distribution information to assist the scattering of interest information. Experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that TMI-GNN outperforms other state-of-the-art methods consistently.
Multi-Choice Questions based Multi-Interest Policy Learning for Conversational Recommendation
Dec 22, 2021



Abstract:Conversational recommendation system (CRS) is able to obtain fine-grained and dynamic user preferences based on interactive dialogue. Previous CRS assumes that the user has a clear target item. However, for many users who resort to CRS, they might not have a clear idea about what they really like. Specifically, the user may have a clear single preference for some attribute types (e.g. color) of items, while for other attribute types, the user may have multiple preferences or even no clear preferences, which leads to multiple acceptable attribute instances (e.g. black and red) of one attribute type. Therefore, the users could show their preferences over items under multiple combinations of attribute instances rather than a single item with unique combination of all attribute instances. As a result, we first propose a more realistic CRS learning setting, namely Multi-Interest Multi-round Conversational Recommendation, where users may have multiple interests in attribute instance combinations and accept multiple items with partially overlapped combinations of attribute instances. To effectively cope with the new CRS learning setting, in this paper, we propose a novel learning framework namely, Multi-Choice questions based Multi-Interest Policy Learning . In order to obtain user preferences more efficiently, the agent generates multi-choice questions rather than binary yes/no ones on specific attribute instance. Besides, we propose a union set strategy to select candidate items instead of existing intersection set strategy in order to overcome over-filtering items during the conversation. Finally, we design a Multi-Interest Policy Learning module, which utilizes captured multiple interests of the user to decide next action, either asking attribute instances or recommending items. Extensive experimental results on four datasets verify the superiority of our method for the proposed setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge