Prasad Dutande
AI for Mycetoma Diagnosis in Histopathological Images: The MICCAI 2024 Challenge
Dec 25, 2025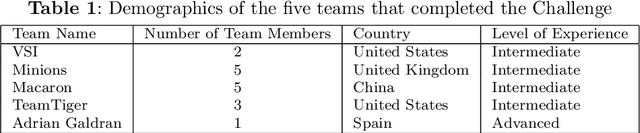
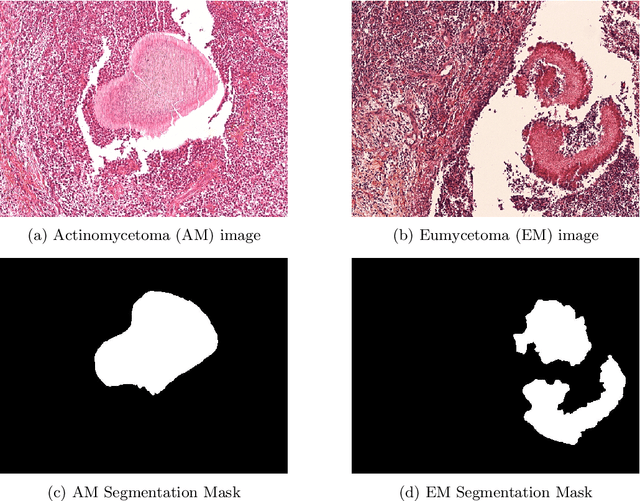
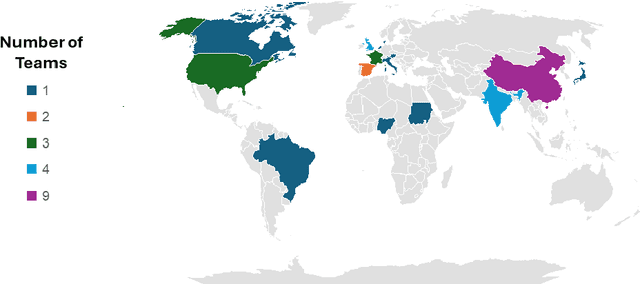

Abstract:Mycetoma is a neglected tropical disease caused by fungi or bacteria leading to severe tissue damage and disabilities. It affects poor and rural communities and presents medical challenges and socioeconomic burdens on patients and healthcare systems in endemic regions worldwide. Mycetoma diagnosis is a major challenge in mycetoma management, particularly in low-resource settings where expert pathologists are limited. To address this challenge, this paper presents an overview of the Mycetoma MicroImage: Detect and Classify Challenge (mAIcetoma) which was organized to advance mycetoma diagnosis through AI solutions. mAIcetoma focused on developing automated models for segmenting mycetoma grains and classifying mycetoma types from histopathological images. The challenge attracted the attention of several teams worldwide to participate and five finalist teams fulfilled the challenge objectives. The teams proposed various deep learning architectures for the ultimate goal of this challenge. Mycetoma database (MyData) was provided to participants as a standardized dataset to run the proposed models. Those models were evaluated using evaluation metrics. Results showed that all the models achieved high segmentation accuracy, emphasizing the necessitate of grain detection as a critical step in mycetoma diagnosis. In addition, the top-performing models show a significant performance in classifying mycetoma types.
Generative Adversarial Networks based Skin Lesion Segmentation
May 29, 2023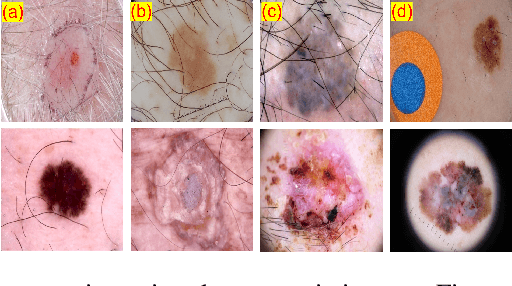
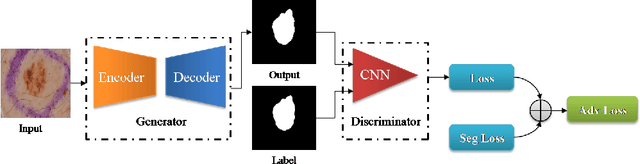
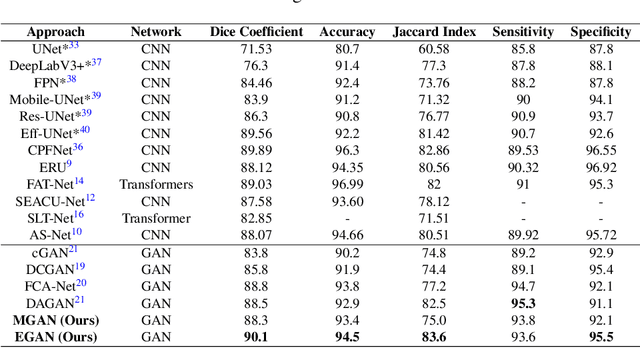
Abstract:Skin cancer is a serious condition that requires accurate identification and treatment. One way to assist clinicians in this task is by using computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) tools that can automatically segment skin lesions from dermoscopic images. To this end, a new adversarial learning-based framework called EGAN has been developed. This framework uses an unsupervised generative network to generate accurate lesion masks. It consists of a generator module with a top-down squeeze excitation-based compound scaled path and an asymmetric lateral connection-based bottom-up path, and a discriminator module that distinguishes between original and synthetic masks. Additionally, a morphology-based smoothing loss is implemented to encourage the network to create smooth semantic boundaries of lesions. The framework is evaluated on the International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC) Lesion Dataset 2018 and outperforms the current state-of-the-art skin lesion segmentation approaches with a Dice coefficient, Jaccard similarity, and Accuracy of 90.1%, 83.6%, and 94.5%, respectively. This represents a 2% increase in Dice Coefficient, 1% increase in Jaccard Index, and 1% increase in Accuracy.
Deep Learning based Novel Cascaded Approach for Skin Lesion Analysis
Jan 16, 2023



Abstract:Automatic lesion analysis is critical in skin cancer diagnosis and ensures effective treatment. The computer aided diagnosis of such skin cancer in dermoscopic images can significantly reduce the clinicians workload and help improve diagnostic accuracy. Although researchers are working extensively to address this problem, early detection and accurate identification of skin lesions remain challenging. This research focuses on a two step framework for skin lesion segmentation followed by classification for lesion analysis. We explored the effectiveness of deep convolutional neural network based architectures by designing an encoder-decoder architecture for skin lesion segmentation and CNN based classification network. The proposed approaches are evaluated quantitatively in terms of the Accuracy, mean Intersection over Union and Dice Similarity Coefficient. Our cascaded end to end deep learning based approach is the first of its kind, where the classification accuracy of the lesion is significantly improved because of prior segmentation.
The 1st Agriculture-Vision Challenge: Methods and Results
Apr 23, 2020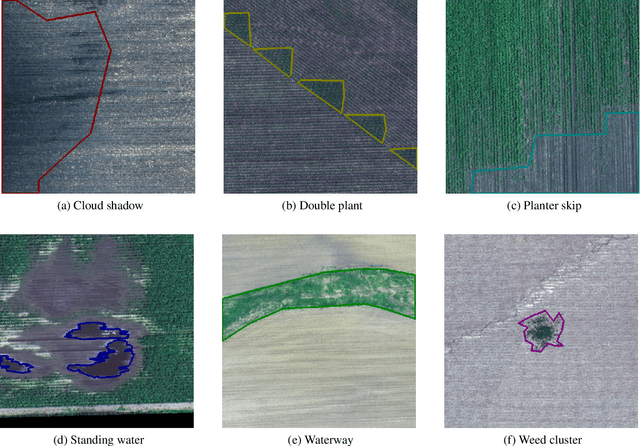
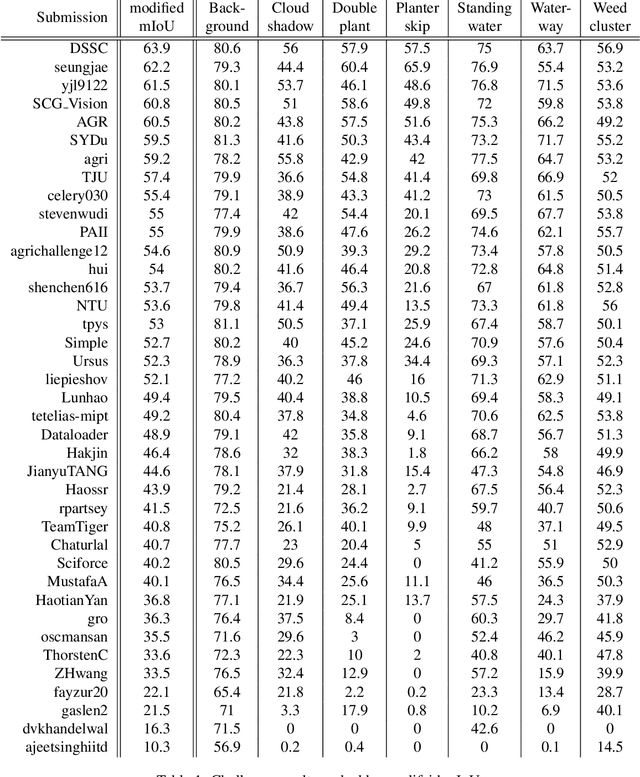
Abstract:The first Agriculture-Vision Challenge aims to encourage research in developing novel and effective algorithms for agricultural pattern recognition from aerial images, especially for the semantic segmentation task associated with our challenge dataset. Around 57 participating teams from various countries compete to achieve state-of-the-art in aerial agriculture semantic segmentation. The Agriculture-Vision Challenge Dataset was employed, which comprises of 21,061 aerial and multi-spectral farmland images. This paper provides a summary of notable methods and results in the challenge. Our submission server and leaderboard will continue to open for researchers that are interested in this challenge dataset and task; the link can be found here.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge