Generative Adversarial Networks based Skin Lesion Segmentation
Paper and Code
May 29, 2023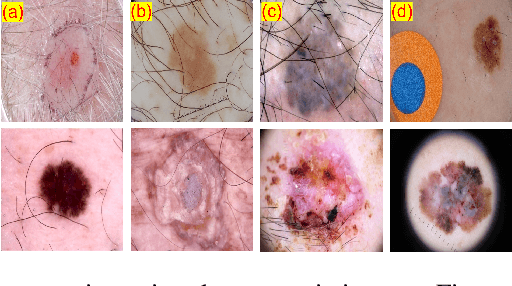
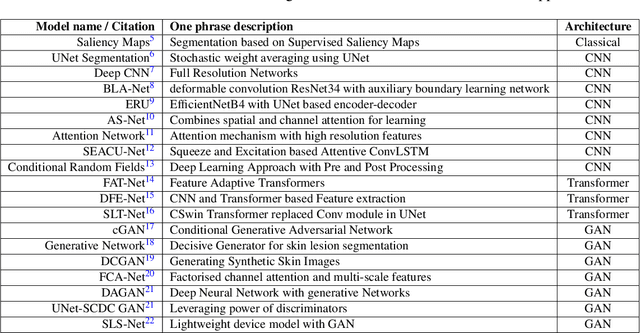
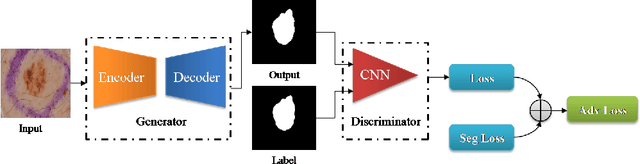
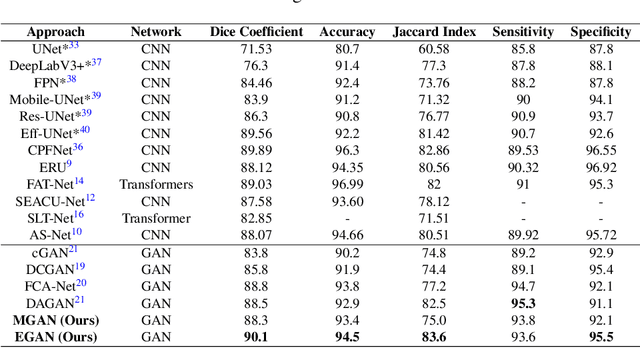
Skin cancer is a serious condition that requires accurate identification and treatment. One way to assist clinicians in this task is by using computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) tools that can automatically segment skin lesions from dermoscopic images. To this end, a new adversarial learning-based framework called EGAN has been developed. This framework uses an unsupervised generative network to generate accurate lesion masks. It consists of a generator module with a top-down squeeze excitation-based compound scaled path and an asymmetric lateral connection-based bottom-up path, and a discriminator module that distinguishes between original and synthetic masks. Additionally, a morphology-based smoothing loss is implemented to encourage the network to create smooth semantic boundaries of lesions. The framework is evaluated on the International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC) Lesion Dataset 2018 and outperforms the current state-of-the-art skin lesion segmentation approaches with a Dice coefficient, Jaccard similarity, and Accuracy of 90.1%, 83.6%, and 94.5%, respectively. This represents a 2% increase in Dice Coefficient, 1% increase in Jaccard Index, and 1% increase in Accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge