Petr Stibinger
RADRON: Cooperative Localization of Ionizing Radiation Sources by MAVs with Compton Cameras
Oct 29, 2025Abstract:We present a novel approach to localizing radioactive material by cooperating Micro Aerial Vehicles (MAVs). Our approach utilizes a state-of-the-art single-detector Compton camera as a highly sensitive, yet miniature detector of ionizing radiation. The detector's exceptionally low weight (40 g) opens up new possibilities of radiation detection by a team of cooperating agile MAVs. We propose a new fundamental concept of fusing the Compton camera measurements to estimate the position of the radiation source in real time even from extremely sparse measurements. The data readout and processing are performed directly onboard and the results are used in a dynamic feedback to drive the motion of the vehicles. The MAVs are stabilized in a tightly cooperating swarm to maximize the information gained by the Compton cameras, rapidly locate the radiation source, and even track a moving radiation source.
CAT-ORA: Collision-Aware Time-Optimal Formation Reshaping for Efficient Robot Coordination in 3D Environments
Nov 30, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we introduce an algorithm designed to address the problem of time-optimal formation reshaping in three-dimensional environments while preventing collisions between agents. The utility of the proposed approach is particularly evident in mobile robotics, where agents benefit from being organized and navigated in formation for a variety of real-world applications requiring frequent alterations in formation shape for efficient navigation or task completion. Given the constrained operational time inherent to battery-powered mobile robots, the time needed to complete the formation reshaping process is crucial for their efficient operation, especially in case of multi-rotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). The proposed Collision-Aware Time-Optimal formation Reshaping Algorithm (CAT-ORA) builds upon the Hungarian algorithm for the solution of the robot-to-goal assignment implementing the inter-agent collision avoidance through direct constraints on mutually exclusive robot-goal pairs combined with a trajectory generation approach minimizing the duration of the reshaping process. Theoretical validations confirm the optimality of CAT-ORA, with its efficacy further showcased through simulations, and a real-world outdoor experiment involving 19 UAVs. Thorough numerical analysis shows the potential of CAT-ORA to decrease the time required to perform complex formation reshaping tasks by up to 49%, and 12% on average compared to commonly used methods in randomly generated scenarios.
MRS Drone: A Modular Platform for Real-World Deployment of Aerial Multi-Robot Systems
Jun 12, 2023Abstract:This paper presents a modular autonomous Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) platform called the Multi-robot Systems (MRS) Drone that can be used in a large range of indoor and outdoor applications. The MRS Drone features unique modularity with respect to changes in actuators, frames, and sensory configuration. As the name suggests, the platform is specially tailored for deployment within a MRS group. The MRS Drone contributes to the state-of-the-art of UAV platforms by allowing smooth real-world deployment of multiple aerial robots, as well as by outperforming other platforms with its modularity. For real-world multi-robot deployment in various applications, the platform is easy to both assemble and modify. Moreover, it is accompanied by a realistic simulator to enable safe pre-flight testing and a smooth transition to complex real-world experiments. In this manuscript, we present mechanical and electrical designs, software architecture, and technical specifications to build a fully autonomous multi UAV system. Finally, we demonstrate the full capabilities and the unique modularity of the MRS Drone in various real-world applications that required a diverse range of platform configurations.
MRS Modular UAV Hardware Platforms for Supporting Research in Real-World Outdoor and Indoor Environments
Feb 09, 2023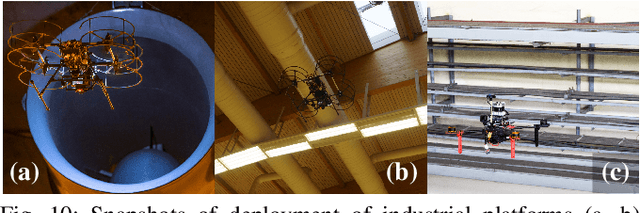



Abstract:This paper presents a family of autonomous Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) platforms designed for a diverse range of indoor and outdoor applications. The proposed UAV design is highly modular in terms of used actuators, sensor configurations, and even UAV frames. This allows to achieve, with minimal effort, a proper experimental setup for single, as well as, multi robot scenarios. Presented platforms are intended to facilitate the transition from simulations, and simplified laboratory experiments, into the deployment of aerial robots into uncertain and hard-to-model real-world conditions. We present mechanical designs, electric configurations, and dynamic models of the UAVs, followed by numerous recommendations and technical details required for building such a fully autonomous UAV system for experimental verification of scientific achievements. To show strength and high variability of the proposed system, we present results of tens of completely different real-robot experiments in various environments using distinct actuator and sensory configurations.
* 10 pages, 17 figures, conference
Mobile Manipulator for Autonomous Localization, Grasping and Precise Placement of Construction Material in a Semi-structured Environment
Nov 16, 2020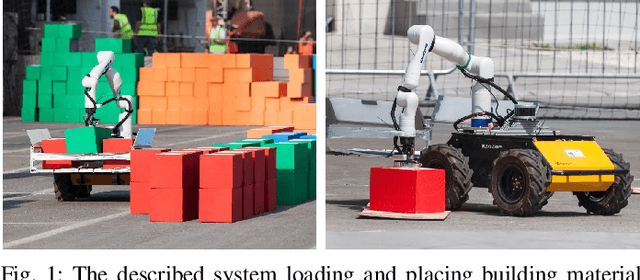
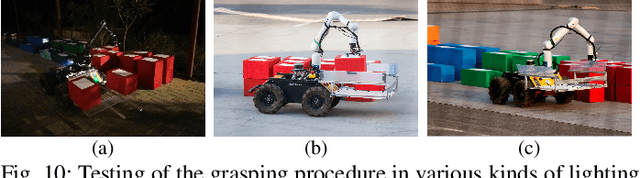
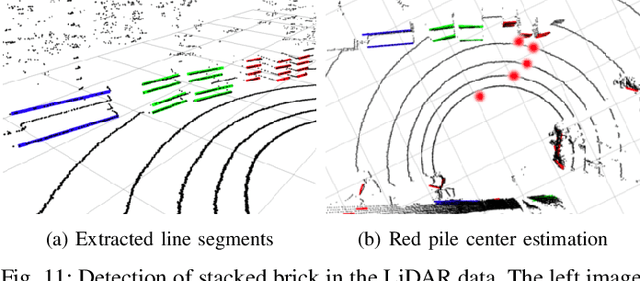
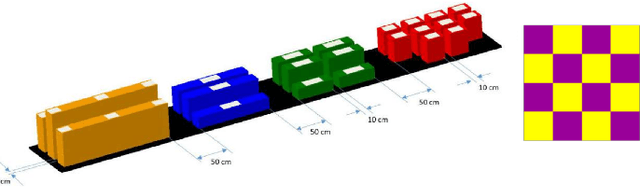
Abstract:Mobile manipulators have the potential to revolutionize modern agriculture, logistics and manufacturing. In this work, we present the design of a ground-based mobile manipulator for automated structure assembly. The proposed system is capable of autonomous localization, grasping, transportation and deployment of construction material in a semi-structured environment. Special effort was put into making the system invariant to lighting changes, and not reliant on external positioning systems. Therefore, the presented system is self-contained and capable of operating in outdoor and indoor conditions alike. Finally, we present means to extend the perceptive radius of the vehicle by using it in cooperation with an autonomous drone, which provides aerial reconnaissance. Performance of the proposed system has been evaluated in a series of experiments conducted in real-world conditions.
Gamma Radiation Source Localization for Micro Aerial Vehicles with a Miniature Single-Detector Compton Event Camera
Nov 06, 2020



Abstract:A novel miniature system for localization and estimation of compact sources of gamma radiation for Micro Aerial Vehicles is presented in this paper. The system utilizes a single-sensor Compton camera. The sensor is extremely small and weighs only 40 g, which opens the possibility for use on the widely accepted sub-250 g class of drones. The Compton camera uses the MiniPIX TPX3 CdTe event camera to measure Compton scattering products of incoming high-energy gamma photons. The 3D position and the sub-nanosecond time delay of the measured scattering products are used to reconstruct sets of possible directions to the source. An onboard filter fuses the measurements and estimates the position of the radiation source during the flight. The computations are executed in real-time onboard and allow integration of the sensor info into a fully-autonomous system. Moreover, the real-time nature of the estimator potentially allows estimating states of a moving radiation source. The proposed method was validated in a real-world experiment with a Cs137 radiation source. The approach is able to localize a gamma source without the need to estimate the gradient or contours of radiation intensity, which opens possibilities for localizing sources in a cluttered and urban environment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge